Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3979 - Acute Portal Vein Thrombosis in COVID-19 Patient: A Rare Thromboembolic Complication
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- MG
Muhammad Gilani, MD
Marshfield Clinic
Marshfield, Wisconsin
Presenting Author(s)
Muhammad Gilani, MD, Tugce Akcan, MD, Hiral Patel, MD, Ahmed Zahid, MD
Marshfield Clinic, Marshfield, WI
Introduction: COVID-19 pneumonia has a number of extra-pulmonary complications, including rare ones like acute portal vein thrombosis.
Case Description/Methods: 28-year-old male with past medical history significant for obesity who presented with right upper quadrant severe abdominal pain for the past 3 days. The patient was tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 two weeks before presentation. He denies any chest pain, shortness of breath, prolonged immobilization, traveling, recent surgeries, personal or family history of bleeding or blood clots. His vitals were stable and on exam, he had right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Lab work up was significant for elevated total bilirubin at 1.2 mg/dL, elevated ALT at 84 U/L, with normal direct and indirect bilirubin, AST and total alkaline phosphatase. CT abdomen/pelvis was significant for thrombosis of right portal vein. Left portal vein, main portal vein, hepatic veins were noted to be patent. Hypercoaguable work-up was inconclusive. Patient was discharged on oral anticoagulation. Follow up in outpatient showed improvement in symptoms and LFT.
Discussion: COVID-related thromboembolism is a well-known phenomenon. SARS-CoV-2 leading to a cytokine storm, fibrinolytic suppression, activation of coagulation cascade along with complement system, and direct endothelial damage is proposed to be the probable reason While acute life-threatening events such as DVT, P.E, MI, and stroke have been frequently reported, Portal Vein Thrombosis (PVT) has not been described much. The most common predisposing conditions are cirrhosis, hepatobiliary malignancy, major infectious or inflammatory abdominal disease, myeloproliferative disorders. This diagnosis is often overlooked because it mimics COVID’s gastrointestinal symptoms. Intestinal infarction, perforation, shock, and multi-organ failure leading to death are some of the horrific complications of untreated portal vein thrombosis. Therefore timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment are of prime importance to reduce morbidity and mortality. MRI is the most sensitive and specific test followed by ultrasonography with Doppler imaging. The duration of treatment in COVID patients is not well studied. In PVT patients, regardless of COVID infection, symptoms and systemic inflammation improve after initiation of anticoagulation. Our patient did not have any risk factors besides being unvaccinated against COVID and having COVID. In consultation with Hematology Department, patient was recommended three months of anticoagulation therapy.

Disclosures:
Muhammad Gilani, MD, Tugce Akcan, MD, Hiral Patel, MD, Ahmed Zahid, MD. P3979 - Acute Portal Vein Thrombosis in COVID-19 Patient: A Rare Thromboembolic Complication, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Marshfield Clinic, Marshfield, WI
Introduction: COVID-19 pneumonia has a number of extra-pulmonary complications, including rare ones like acute portal vein thrombosis.
Case Description/Methods: 28-year-old male with past medical history significant for obesity who presented with right upper quadrant severe abdominal pain for the past 3 days. The patient was tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 two weeks before presentation. He denies any chest pain, shortness of breath, prolonged immobilization, traveling, recent surgeries, personal or family history of bleeding or blood clots. His vitals were stable and on exam, he had right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Lab work up was significant for elevated total bilirubin at 1.2 mg/dL, elevated ALT at 84 U/L, with normal direct and indirect bilirubin, AST and total alkaline phosphatase. CT abdomen/pelvis was significant for thrombosis of right portal vein. Left portal vein, main portal vein, hepatic veins were noted to be patent. Hypercoaguable work-up was inconclusive. Patient was discharged on oral anticoagulation. Follow up in outpatient showed improvement in symptoms and LFT.
Discussion: COVID-related thromboembolism is a well-known phenomenon. SARS-CoV-2 leading to a cytokine storm, fibrinolytic suppression, activation of coagulation cascade along with complement system, and direct endothelial damage is proposed to be the probable reason While acute life-threatening events such as DVT, P.E, MI, and stroke have been frequently reported, Portal Vein Thrombosis (PVT) has not been described much. The most common predisposing conditions are cirrhosis, hepatobiliary malignancy, major infectious or inflammatory abdominal disease, myeloproliferative disorders. This diagnosis is often overlooked because it mimics COVID’s gastrointestinal symptoms. Intestinal infarction, perforation, shock, and multi-organ failure leading to death are some of the horrific complications of untreated portal vein thrombosis. Therefore timely diagnosis and initiation of treatment are of prime importance to reduce morbidity and mortality. MRI is the most sensitive and specific test followed by ultrasonography with Doppler imaging. The duration of treatment in COVID patients is not well studied. In PVT patients, regardless of COVID infection, symptoms and systemic inflammation improve after initiation of anticoagulation. Our patient did not have any risk factors besides being unvaccinated against COVID and having COVID. In consultation with Hematology Department, patient was recommended three months of anticoagulation therapy.

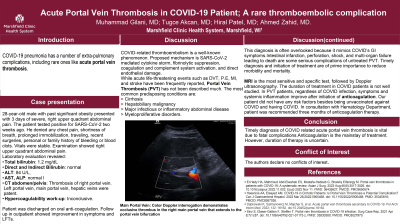
Figure: Main Portal Vein: Color Doppler interrogation demonstrates occlusive thrombus in the right main portal
vein that extends to the portal vein bifurcation
vein that extends to the portal vein bifurcation
Disclosures:
Muhammad Gilani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tugce Akcan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hiral Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ahmed Zahid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Gilani, MD, Tugce Akcan, MD, Hiral Patel, MD, Ahmed Zahid, MD. P3979 - Acute Portal Vein Thrombosis in COVID-19 Patient: A Rare Thromboembolic Complication, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
