Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Functional Bowel Disease
P3365 - Zemedy 2.0: A CBT Smartphone App Improves HRQL, GI Symptoms and Underlying Psychological Mechanisms for IBS Patients
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Melissa G. Hunt, PhD
University of Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Melissa G.. Hunt, PhD1, Simay I. Ipek, BA2, Sophia G.. Glinski, BA1
1University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; 2Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
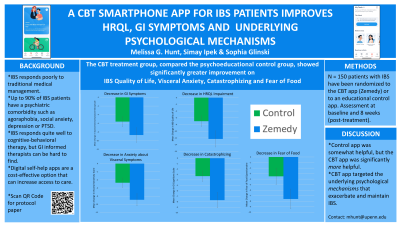
Introduction: Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) responds poorly to traditional medical management, and up to 90% of treatment seeking IBS patients have at least one psychiatric co-morbidity. Integrative behavioral care including working with a GI knowledgeable psychotherapist with expertise in cognitive behavioral therapy or hypnotherapy results in far better outcomes. Unfortunately there are not enough providers to meet the need and funding pathways (e.g. insurance coverage) is a limiting factor. Self-help approaches, including books and smart phone apps show great promise and are a novel way to disseminate evidence based treatment for IBS while increasing access and reducing health disparities. The Zemedy App provides self-help CBT for IBS. Version 1.0 of the app was tested in a clinical trial and resulted in improved HRQL and reduced GI symptoms compared to a waitlist control. The current study compares Version 2.0 of the app to an active educational and relaxation training control app.
Methods: This is a two arm, randomized controlled clinical trial with a cross over design and longitudinal follow-up. Participants are recruited from multiple sources (doctor referrals, social media, clinical trial sites) and are randomized to the Zemedy app or the control app. Post-treatment data is collected at 8 weeks. Primary outcomes include IBS specific HRQL and GI symptoms. Secondary outcome measures include fear of food, visceral anxiety, and catastrophizing about GI symptoms.
Results: Participants using Zemedy showed significant improvement on all measures from pre to post treatment [all paired samples t-tests t(48) > 3.70, all p < .001]. They also improved significantly more than the control group on fear of food, anxiety about visceral symptoms and catastrophizing about GI symptoms [all F(1,177) > 4.2, all p < .05].
Discussion: Zemedy 2.0 resulted in significant improvement in both primary outcome measures of GI symptoms and IBS specific HRQL. Moreover, it resulted in a significantly greater change in underlying psychological maintaining factors in IBS, such as fear of food, anxiety about visceral symptoms and catastrophizing about GI symptoms than a credible active control app. The Zemedy app is an affordable, accessible and effective way to deliver CBT to patients with IBS.
Disclosures:
Melissa G.. Hunt, PhD1, Simay I. Ipek, BA2, Sophia G.. Glinski, BA1. P3365 - Zemedy 2.0: A CBT Smartphone App Improves HRQL, GI Symptoms and Underlying Psychological Mechanisms for IBS Patients, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; 2Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA
Introduction: Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) responds poorly to traditional medical management, and up to 90% of treatment seeking IBS patients have at least one psychiatric co-morbidity. Integrative behavioral care including working with a GI knowledgeable psychotherapist with expertise in cognitive behavioral therapy or hypnotherapy results in far better outcomes. Unfortunately there are not enough providers to meet the need and funding pathways (e.g. insurance coverage) is a limiting factor. Self-help approaches, including books and smart phone apps show great promise and are a novel way to disseminate evidence based treatment for IBS while increasing access and reducing health disparities. The Zemedy App provides self-help CBT for IBS. Version 1.0 of the app was tested in a clinical trial and resulted in improved HRQL and reduced GI symptoms compared to a waitlist control. The current study compares Version 2.0 of the app to an active educational and relaxation training control app.
Methods: This is a two arm, randomized controlled clinical trial with a cross over design and longitudinal follow-up. Participants are recruited from multiple sources (doctor referrals, social media, clinical trial sites) and are randomized to the Zemedy app or the control app. Post-treatment data is collected at 8 weeks. Primary outcomes include IBS specific HRQL and GI symptoms. Secondary outcome measures include fear of food, visceral anxiety, and catastrophizing about GI symptoms.
Results: Participants using Zemedy showed significant improvement on all measures from pre to post treatment [all paired samples t-tests t(48) > 3.70, all p < .001]. They also improved significantly more than the control group on fear of food, anxiety about visceral symptoms and catastrophizing about GI symptoms [all F(1,177) > 4.2, all p < .05].
Discussion: Zemedy 2.0 resulted in significant improvement in both primary outcome measures of GI symptoms and IBS specific HRQL. Moreover, it resulted in a significantly greater change in underlying psychological maintaining factors in IBS, such as fear of food, anxiety about visceral symptoms and catastrophizing about GI symptoms than a credible active control app. The Zemedy app is an affordable, accessible and effective way to deliver CBT to patients with IBS.
Disclosures:
Melissa Hunt indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Simay Ipek indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sophia Glinski indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Melissa G.. Hunt, PhD1, Simay I. Ipek, BA2, Sophia G.. Glinski, BA1. P3365 - Zemedy 2.0: A CBT Smartphone App Improves HRQL, GI Symptoms and Underlying Psychological Mechanisms for IBS Patients, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
