Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3561 - Outcomes and Predictors of Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Ese Uwagbale, MD
Rochester General Hospital
Rochester, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Ese Uwagbale, MD1, Faisaluddin Mohammed, MD1, Solomon Agbroko, MD2, Sheza Malik, MD1, Nida Khalid, MD1, Dileepa Chathuranga, MD1, Dasha Moza, MD1, Karin Dunnigan, MD1, Patrick Okolo, MD, MPH, FACG1
1Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY; 2Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) led to significant mortality worldwide. Outcomes in patients with Covid-19 are suspected to be more severe in patients with comorbid conditions. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. This study aims to investigate the outcomes of Covid -19 in patients with IBD and the predictors of mortality in Covid-19 patients with IBD.
Methods: Using the National inpatient sample (NIS) database from January 1st, 2020, to December 31st, 2020, we identified patients 18 years and older with a primary diagnosis of COVID-19 using ICD 10 codes. We had a total of 1,050,040 patients, out of which 5750 patients (0.55%) had IBD (51.4% had Crohn’s disease, and 48.6% had ulcerative colitis). The primary outcomes were mortality, length of hospital stay, positive predictors of mortality, and cost.
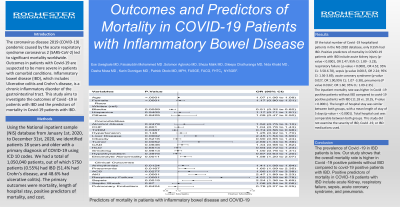
Results: Of the total number of Covid -19 hospitalized patients in the NIS 2020 database, only 0.55% had IBD. Positive predictors of mortality in COVID-19 patients with IBD include acute kidney injury (p-value < 0.0001, OR 2.47; 95% CI: 1.89 - 3.23), respiratory failure ( p-value < 0.0001, OR 4.52; 95% CL: 3.58-6.78), sepsis (p-value 0.0015, OR 2.24; 95% CI: 1.36-3.69), acute coronary syndrome (p-value 0.027, OR 1.90;95% CL: 1.07 -3.38), pneumonia (P value 0.0167, OR 1.60; 95% CL: 1.09-2.35)
The inpatient mortality rate was higher in Covid -19 positive patients without IBD compared to covid-19 positive patients with IBD (11.18 vs. 10.35, P value < 0.0001). The length of hospital stay was similar between both groups, with a mean length of stay of 5 days (p-value < < 0.0001). Total hospital cost was comparable between both groups. This study did not examine the severity of IBD, Covid -19, or IBD medications used.
Discussion: The prevalence of Covid -19 in IBD patients is low. Our study shows that the overall mortality rate is higher in Covid -19 positive patients without IBD compared to covid-19 positive patients with IBD. Positive predictors of mortality in COVID-19 patients with IBD include acute Kidney, respiratory failure, sepsis, acute coronary syndrome, and pneumonia.

Disclosures:
Ese Uwagbale, MD1, Faisaluddin Mohammed, MD1, Solomon Agbroko, MD2, Sheza Malik, MD1, Nida Khalid, MD1, Dileepa Chathuranga, MD1, Dasha Moza, MD1, Karin Dunnigan, MD1, Patrick Okolo, MD, MPH, FACG1. P3561 - Outcomes and Predictors of Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY; 2Maimonides Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY
Introduction: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) led to significant mortality worldwide. Outcomes in patients with Covid-19 are suspected to be more severe in patients with comorbid conditions. Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. This study aims to investigate the outcomes of Covid -19 in patients with IBD and the predictors of mortality in Covid-19 patients with IBD.
Methods: Using the National inpatient sample (NIS) database from January 1st, 2020, to December 31st, 2020, we identified patients 18 years and older with a primary diagnosis of COVID-19 using ICD 10 codes. We had a total of 1,050,040 patients, out of which 5750 patients (0.55%) had IBD (51.4% had Crohn’s disease, and 48.6% had ulcerative colitis). The primary outcomes were mortality, length of hospital stay, positive predictors of mortality, and cost.
Results: Of the total number of Covid -19 hospitalized patients in the NIS 2020 database, only 0.55% had IBD. Positive predictors of mortality in COVID-19 patients with IBD include acute kidney injury (p-value < 0.0001, OR 2.47; 95% CI: 1.89 - 3.23), respiratory failure ( p-value < 0.0001, OR 4.52; 95% CL: 3.58-6.78), sepsis (p-value 0.0015, OR 2.24; 95% CI: 1.36-3.69), acute coronary syndrome (p-value 0.027, OR 1.90;95% CL: 1.07 -3.38), pneumonia (P value 0.0167, OR 1.60; 95% CL: 1.09-2.35)
The inpatient mortality rate was higher in Covid -19 positive patients without IBD compared to covid-19 positive patients with IBD (11.18 vs. 10.35, P value < 0.0001). The length of hospital stay was similar between both groups, with a mean length of stay of 5 days (p-value < < 0.0001). Total hospital cost was comparable between both groups. This study did not examine the severity of IBD, Covid -19, or IBD medications used.
Discussion: The prevalence of Covid -19 in IBD patients is low. Our study shows that the overall mortality rate is higher in Covid -19 positive patients without IBD compared to covid-19 positive patients with IBD. Positive predictors of mortality in COVID-19 patients with IBD include acute Kidney, respiratory failure, sepsis, acute coronary syndrome, and pneumonia.

Figure: Predictors of mortality in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and COVID-19
Disclosures:
Ese Uwagbale indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Faisaluddin Mohammed indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Solomon Agbroko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sheza Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nida Khalid indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dileepa Chathuranga indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Dasha Moza indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karin Dunnigan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Patrick Okolo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ese Uwagbale, MD1, Faisaluddin Mohammed, MD1, Solomon Agbroko, MD2, Sheza Malik, MD1, Nida Khalid, MD1, Dileepa Chathuranga, MD1, Dasha Moza, MD1, Karin Dunnigan, MD1, Patrick Okolo, MD, MPH, FACG1. P3561 - Outcomes and Predictors of Mortality in COVID-19 Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
