Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3601 - Impact of Tofacitinib Maintenance Therapy on Key Ulcerative Colitis Patient-Reported Outcomes of Fatigue, Urgency, Abdominal Pain, and Sexual Dysfunction Using IBDQ and SF-36 Individual Items as Proxies
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Marla C. Dubinsky, MD
Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Hospital
New York, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Marla C. Dubinsky, MD1, Sean Gardiner, 2, Peter Hur, 2, Xiang Guo, 3, Jerome Paulissen, 2, Joseph C. Cappelleri, 4, Andrew G. Bushmakin, 4, Julian Panés, MD, PhD5
1Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Hospital, New York, NY; 2Pfizer Inc., New York, NY; 3Pfizer Inc., Collegeville, PA; 4Pfizer Inc., Groton, CT; 5Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, IDIBAPS, CIBERehd, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain
Introduction: Tofacitinib is an oral small molecule Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC). This novel analysis evaluated tofacitinib outcomes using items from the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire-32 (IBDQ) and Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36) as proxies for key UC patient (pt)-reported outcomes (PROs) over 52 weeks of maintenance treatment.
Methods: Data from 593 pts with UC in OCTAVE Sustain (NCT01458574) were included.1 PROs were assessed via self-reported proxy items for each UC symptom/dysfunction of interest in the IBDQ and SF-36. A longitudinal mixed-effects model compared tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg twice daily (BID) vs placebo up to 52 weeks for change from baseline (CFB). Least squares (LS) mean differences and standardized effect sizes (ES; [LS mean difference]/[standard deviation (SD) of baseline scores]) were calculated for tofacitinib vs placebo; ES of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8 were trivial, small, medium, and large, respectively, with ES categorization intervals defined as the midpoints between these absolute values.2 LS means and ES ([LS mean]/[SD of baseline scores]) for both tofacitinib doses and placebo at Week 52 vs baseline were calculated. p < 0.05 denoted statistical significance.
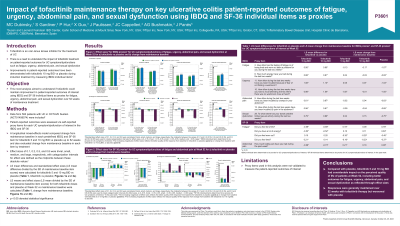
Results: At Week 52, all IBDQ proxies were improved with tofacitinib vs placebo, with significant LS mean differences. Large ES were reported for fatigue and urgency proxies (Figure A); abdominal pain and sexual dysfunction proxies had medium ES (Figure B). For SF-36 proxies, LS mean differences vs placebo were significant at Week 52, except for some fatigue proxies. Small to large ES were reported for fatigue proxies; the abdominal pain proxy had medium to large ES (Figure C). Regarding CFB, patients receiving tofacitinib maintained responses in IBDQ and SF-36 proxies at Week 52. LS mean CFB in IBDQ items were generally not significant with tofacitinib; this was not as evident for SF-36 items. Trivial to small ES were reported for tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID, and medium to large ES for placebo. Significant worsening was observed with placebo for all items of interest.
Discussion: Compared with placebo, tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID had better IBDQ and SF-36 proxy item responses at Week 52. Responses were maintained over 52 weeks with tofacitinib therapy, but worsened with placebo. Proxy items have not been validated to measure the symptom PROs of interest.
References
1. Sandborn et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1723–36
2. Dubinsky et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2021;27:983–93

Disclosures:
Marla C. Dubinsky, MD1, Sean Gardiner, 2, Peter Hur, 2, Xiang Guo, 3, Jerome Paulissen, 2, Joseph C. Cappelleri, 4, Andrew G. Bushmakin, 4, Julian Panés, MD, PhD5. P3601 - Impact of Tofacitinib Maintenance Therapy on Key Ulcerative Colitis Patient-Reported Outcomes of Fatigue, Urgency, Abdominal Pain, and Sexual Dysfunction Using IBDQ and SF-36 Individual Items as Proxies, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mount Sinai Kravis Children’s Hospital, New York, NY; 2Pfizer Inc., New York, NY; 3Pfizer Inc., Collegeville, PA; 4Pfizer Inc., Groton, CT; 5Hospital Clínic de Barcelona, IDIBAPS, CIBERehd, Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain
Introduction: Tofacitinib is an oral small molecule Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC). This novel analysis evaluated tofacitinib outcomes using items from the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire-32 (IBDQ) and Short Form-36 Health Survey (SF-36) as proxies for key UC patient (pt)-reported outcomes (PROs) over 52 weeks of maintenance treatment.
Methods: Data from 593 pts with UC in OCTAVE Sustain (NCT01458574) were included.1 PROs were assessed via self-reported proxy items for each UC symptom/dysfunction of interest in the IBDQ and SF-36. A longitudinal mixed-effects model compared tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg twice daily (BID) vs placebo up to 52 weeks for change from baseline (CFB). Least squares (LS) mean differences and standardized effect sizes (ES; [LS mean difference]/[standard deviation (SD) of baseline scores]) were calculated for tofacitinib vs placebo; ES of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8 were trivial, small, medium, and large, respectively, with ES categorization intervals defined as the midpoints between these absolute values.2 LS means and ES ([LS mean]/[SD of baseline scores]) for both tofacitinib doses and placebo at Week 52 vs baseline were calculated. p < 0.05 denoted statistical significance.
Results: At Week 52, all IBDQ proxies were improved with tofacitinib vs placebo, with significant LS mean differences. Large ES were reported for fatigue and urgency proxies (Figure A); abdominal pain and sexual dysfunction proxies had medium ES (Figure B). For SF-36 proxies, LS mean differences vs placebo were significant at Week 52, except for some fatigue proxies. Small to large ES were reported for fatigue proxies; the abdominal pain proxy had medium to large ES (Figure C). Regarding CFB, patients receiving tofacitinib maintained responses in IBDQ and SF-36 proxies at Week 52. LS mean CFB in IBDQ items were generally not significant with tofacitinib; this was not as evident for SF-36 items. Trivial to small ES were reported for tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID, and medium to large ES for placebo. Significant worsening was observed with placebo for all items of interest.
Discussion: Compared with placebo, tofacitinib 5 and 10 mg BID had better IBDQ and SF-36 proxy item responses at Week 52. Responses were maintained over 52 weeks with tofacitinib therapy, but worsened with placebo. Proxy items have not been validated to measure the symptom PROs of interest.
References
1. Sandborn et al. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1723–36
2. Dubinsky et al. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2021;27:983–93

Figure: Figure. ES[a] for A) IBDQ Proxies[b] of Fatigue and Urgency; B) IBDQ Proxies[b] of Abdominal Pain and Sexual Dysfunction; and C) SF-36 Proxies[c] of Fatigue and Abdominal Pain at Week 52 for Tofacitinib vs Placebo.
[a]Standardized ES of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8 were considered trivial, small, medium, and large, respectively; midpoints between values of 0.1 and 0.2 (0.15), 0.2 and 0.5 (0.35), and 0.5 and 0.8 (0.65) were used to create categorization intervals for ES, ie 0–0.15, trivial; > 0.15–0.35, small; > 0.35–0.65, medium; > 0.65, large[2].
[b]IBDQ individual items determined to be proxies for UC symptoms of interest.
[c]SF-36 individual items determined to be proxies for UC symptoms of interest.
[d]The increasing magnitude of ES reflects the better quality of life response from baseline for tofacitinib vs placebo.
BID, twice daily; ES, effect size; IBDQ, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire-32; SF-36, Short Form-36 Health Survey; UC, ulcerative colitis.
[a]Standardized ES of 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 0.8 were considered trivial, small, medium, and large, respectively; midpoints between values of 0.1 and 0.2 (0.15), 0.2 and 0.5 (0.35), and 0.5 and 0.8 (0.65) were used to create categorization intervals for ES, ie 0–0.15, trivial; > 0.15–0.35, small; > 0.35–0.65, medium; > 0.65, large[2].
[b]IBDQ individual items determined to be proxies for UC symptoms of interest.
[c]SF-36 individual items determined to be proxies for UC symptoms of interest.
[d]The increasing magnitude of ES reflects the better quality of life response from baseline for tofacitinib vs placebo.
BID, twice daily; ES, effect size; IBDQ, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire-32; SF-36, Short Form-36 Health Survey; UC, ulcerative colitis.
Disclosures:
Marla Dubinsky: AbbVie – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Arena Pharmaceuticals – Consultant. Astra Zeneca – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Genentech Inc. – Consultant. Gilead Sciences – Consultant. Janssen – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Merck – Consultant. Pfizer – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus Biosciences – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Prometheus Labs – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Consultant, Licensing fees. Thabor – Consultant. Trellus Health – Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds). UCB Pharma – Consultant.
Sean Gardiner: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Shareholder.
Peter Hur: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Shareholder.
Xiang Guo: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Shareholder.
Jerome Paulissen: Eli Lilly – contractor. Pfizer Inc – Paid Contractor. Syneos Health – Employee.
Joseph C. Cappelleri: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Shareholder.
Andrew Bushmakin: Pfizer Inc – Employee, Shareholder.
Julian Panés: AbbVie – Grant/Research Support, Personal fees. Arena – Consultant. Athos – Consultant. Atomwise – Consultant. Boehringer Ingelheim – Consultant. Celgene – Consultant. Celltrion – Consultant. Ferring – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Galapagos – Consultant. Genentech/Roche – Consultant. GlaxoSmithKline – Consultant. Immunic – Personal fees. Janssen – Consultant, payment for development of educational presentations. Mirum – Consultant. Morphic – Consultant. Origo – Consultant. Pandion – Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Grant/Research Support, payment for development of educational presentations. Progenity – Consultant. Revolo – Consultant. Takeda – payment for development of educational presentations. Theravance – Consultant. Wasserman – Consultant.
Marla C. Dubinsky, MD1, Sean Gardiner, 2, Peter Hur, 2, Xiang Guo, 3, Jerome Paulissen, 2, Joseph C. Cappelleri, 4, Andrew G. Bushmakin, 4, Julian Panés, MD, PhD5. P3601 - Impact of Tofacitinib Maintenance Therapy on Key Ulcerative Colitis Patient-Reported Outcomes of Fatigue, Urgency, Abdominal Pain, and Sexual Dysfunction Using IBDQ and SF-36 Individual Items as Proxies, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
