Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1442 - Diagnostic Yield of Cholangioscopy-Guided Biopsies for Biliary Strictures Using SpyGlass DS II and SpyBite Max
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- CP
Christopher Paiji, MD
UCLA
Los Angeles, California
Presenting Author(s)
Christopher Paiji, MD, Stephen Kim, MD, Adarsh Thaker, MD, Danny Issa, MD, Alireza Sedarat, MD, V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, MAS
UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Obtaining an accurate pathologic diagnosis is essential for management of biliary strictures. ERCP with brush cytology, intraductal forceps biopsy and EUS with FNA have found to be suboptimal in excluding malignancy. Bile duct biopsies utilizing the first digital single-operator cholangioscopy system (SpyGlass DS) in conjunction with biopsy forceps (SpyBite) is associated with higher sensitivity for diagnosis of malignancy compared to prior methods. An updated system (SpyGlass DS II) with increased image resolution and an enhanced biopsy forceps (SpyBite Max) that offers increased tissue acquisition have since been introduced. The improvement of diagnostic yield with SpyGlass DS II and SpyBite Max have yet to be fully described.
Methods: Consecutive adult patients who underwent cholangioscopy-guided biopsies for undiagnosed biliary strictures at 2 tertiary referral centers between 2015 to 2022 were included in this retrospective study. Patients with less than 6 months of post-procedure follow-up were excluded. Specific criteria were used to determine if the final diagnosis of the biliary stricture was malignant or benign. Primary outcomes included overall diagnostic yield of cholangioscopy-guided biopsies and differences in sensitivity for diagnosis of malignancy based on the version of cholangioscopy system and forceps used. Comparisons of sensitivity between the different versions were performed using Pearson’s chi-squared test.
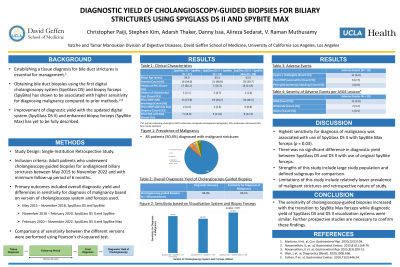
Results: A total of 164 patients who underwent 220 cholangioscopy-guided biopsy procedures were included in this study. Eighty three patients (50.6%) were diagnosed with malignant strictures. Overall, cholangioscopy-guided biopsies had a diagnostic accuracy of 85.0% and sensitivity for diagnosis of malignancy of 69.1%. The sensitivity of biopsies using SpyGlass DS II with SpyBite Max was significantly higher than sensitivities of biopsies using SpyGlass DS with SpyBite and SpyGlass DS II with SpyBite (80.9% vs 73.7% vs 68.4%, P = 0.03). There was no significant difference in sensitivity of endoscopists’ visual impression between SpyGlass DS and SpyGlass DS II (88.9% vs 90.4%, P = 1.00). Mean follow-up period was 23.5 months.
Discussion: In this study, sensitivity of cholangioscopy-guided biopsies increased with transition to SpyBite Max forceps while diagnostic yield between SpyGlass DS and SpyGlass DS II visualization systems were similar. Further studies in a prospective manner are necessary to confirm the higher sensitivity of biopsies using SpyBite Max.

Disclosures:
Christopher Paiji, MD, Stephen Kim, MD, Adarsh Thaker, MD, Danny Issa, MD, Alireza Sedarat, MD, V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, MAS. P1442 - Diagnostic Yield of Cholangioscopy-Guided Biopsies for Biliary Strictures Using SpyGlass DS II and SpyBite Max, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Obtaining an accurate pathologic diagnosis is essential for management of biliary strictures. ERCP with brush cytology, intraductal forceps biopsy and EUS with FNA have found to be suboptimal in excluding malignancy. Bile duct biopsies utilizing the first digital single-operator cholangioscopy system (SpyGlass DS) in conjunction with biopsy forceps (SpyBite) is associated with higher sensitivity for diagnosis of malignancy compared to prior methods. An updated system (SpyGlass DS II) with increased image resolution and an enhanced biopsy forceps (SpyBite Max) that offers increased tissue acquisition have since been introduced. The improvement of diagnostic yield with SpyGlass DS II and SpyBite Max have yet to be fully described.
Methods: Consecutive adult patients who underwent cholangioscopy-guided biopsies for undiagnosed biliary strictures at 2 tertiary referral centers between 2015 to 2022 were included in this retrospective study. Patients with less than 6 months of post-procedure follow-up were excluded. Specific criteria were used to determine if the final diagnosis of the biliary stricture was malignant or benign. Primary outcomes included overall diagnostic yield of cholangioscopy-guided biopsies and differences in sensitivity for diagnosis of malignancy based on the version of cholangioscopy system and forceps used. Comparisons of sensitivity between the different versions were performed using Pearson’s chi-squared test.
Results: A total of 164 patients who underwent 220 cholangioscopy-guided biopsy procedures were included in this study. Eighty three patients (50.6%) were diagnosed with malignant strictures. Overall, cholangioscopy-guided biopsies had a diagnostic accuracy of 85.0% and sensitivity for diagnosis of malignancy of 69.1%. The sensitivity of biopsies using SpyGlass DS II with SpyBite Max was significantly higher than sensitivities of biopsies using SpyGlass DS with SpyBite and SpyGlass DS II with SpyBite (80.9% vs 73.7% vs 68.4%, P = 0.03). There was no significant difference in sensitivity of endoscopists’ visual impression between SpyGlass DS and SpyGlass DS II (88.9% vs 90.4%, P = 1.00). Mean follow-up period was 23.5 months.
Discussion: In this study, sensitivity of cholangioscopy-guided biopsies increased with transition to SpyBite Max forceps while diagnostic yield between SpyGlass DS and SpyGlass DS II visualization systems were similar. Further studies in a prospective manner are necessary to confirm the higher sensitivity of biopsies using SpyBite Max.

Figure: Sensitivity for Diagnosis of Malignancy based on Visualization System and Biopsy Forceps Utilized
Disclosures:
Christopher Paiji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephen Kim: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Exact sciences – Consultant.
Adarsh Thaker: Apollo Endosurgery – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Boston Scientific Corporation – Consultant, Speakers Bureau. Neptune Medical – Consultant. Steris – Consultant.
Danny Issa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alireza Sedarat: Boston Scientific – Consultant.
V. Raman Muthusamy: Boston Scientific – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Capsovision – Stock Options. Endogastric Solutions – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Motus GI – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Christopher Paiji, MD, Stephen Kim, MD, Adarsh Thaker, MD, Danny Issa, MD, Alireza Sedarat, MD, V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, MAS. P1442 - Diagnostic Yield of Cholangioscopy-Guided Biopsies for Biliary Strictures Using SpyGlass DS II and SpyBite Max, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
