Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1489 - Candida in Infected Peri-Pancreatic Fluid Collections - A Case Series
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- RA
Robinder Abrol, DO
University of Texas Medical Branch-Galveston
Galveston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Robinder Abrol, DO1, Muhammad Mushtaq, DO1, Kanana Aburayyan, MD2, Kumar Pallav, MBBS, FACG3, Irfan Masood, MD1, Joshua Person, MD1, Sreeram Parupudi, MD, FACG1
1University of Texas Medical Branch-Galveston, Galveston, TX; 2University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Galveston, TX; 3University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX
Introduction: Pancreatic Fluid Collections (PFC) can develop as a consequence of severe pancreatitis. Signs of infection are an indication for prompt drainage to assist in tailoring of antimicrobial therapy. Gastrointestinal flora are usually the isolated organisms in culture positive collections. Although, Candida spp. have been isolated as contaminants, symptomatic fungal infections are rare in the absence of immunocompromised states. Here we present a series of 3 immunocompetent patients with symptomatic infected PFC.
Case Description/Methods: Case 1:
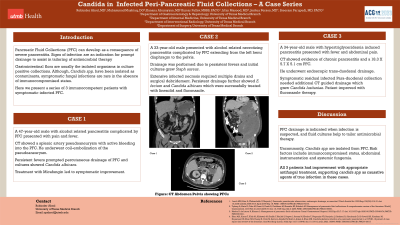
A 33-year-old male presented with alcohol related necrotizing pancreatitis complicated by PFC extending from the left hemidiaphragm to the pelvis. Drainage was performed due to persistent fevers and initial cultures grew Staph aureus that was treated. Extensive infected necrosis needed multiple drains and surgical debridement. Persistent drainage further showed E. fecium and Candida albicans which were successfully treated with linezolid and fluconazole.
Case 2:
A 34-year-old male with hypertriglyceridemia induced pancreatitis presented with fever and abdominal pain. CT showed evidence of chronic pancreatitis and a 18.3 X 5.7 X 5.1 cm PFC. He underwent endoscopic cysto-duodenal stenting. Symptomatic residual infected paraduodenal collection needed additional CT guided drainage which grew Candida lusitaniae. Patient improved with fluconazole therapy.
Case 3:
A 47-year-old male with alcohol related pancreatitis complicated by PFC presented with pain and fever. CT showed a splenic artery pseudoaneurysm with active bleeding into the PFC. He underwent coil-embolization of the pseudoaneurysm. Persistent fevers prompted percutaneous drainage of PFC and cultures showed Candida albicans. Treatment with Micafungin led to symptomatic improvement.
Discussion: PFC drainage is indicated when infection is suspected, and fluid cultures help to tailor antimicrobial therapy. Uncommonly, Candida spp are isolated from PFC. Risk factors include immunocompromised status, abdominal instrumentation and systemic fungemia. Here, we present 3 cases of PFCs growing Candida spp post instrumentation that were successfully treated with antimicrobial therapy.
Disclosures:
Robinder Abrol, DO1, Muhammad Mushtaq, DO1, Kanana Aburayyan, MD2, Kumar Pallav, MBBS, FACG3, Irfan Masood, MD1, Joshua Person, MD1, Sreeram Parupudi, MD, FACG1. P1489 - Candida in Infected Peri-Pancreatic Fluid Collections - A Case Series, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Texas Medical Branch-Galveston, Galveston, TX; 2University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, Galveston, TX; 3University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX
Introduction: Pancreatic Fluid Collections (PFC) can develop as a consequence of severe pancreatitis. Signs of infection are an indication for prompt drainage to assist in tailoring of antimicrobial therapy. Gastrointestinal flora are usually the isolated organisms in culture positive collections. Although, Candida spp. have been isolated as contaminants, symptomatic fungal infections are rare in the absence of immunocompromised states. Here we present a series of 3 immunocompetent patients with symptomatic infected PFC.
Case Description/Methods: Case 1:
A 33-year-old male presented with alcohol related necrotizing pancreatitis complicated by PFC extending from the left hemidiaphragm to the pelvis. Drainage was performed due to persistent fevers and initial cultures grew Staph aureus that was treated. Extensive infected necrosis needed multiple drains and surgical debridement. Persistent drainage further showed E. fecium and Candida albicans which were successfully treated with linezolid and fluconazole.
Case 2:
A 34-year-old male with hypertriglyceridemia induced pancreatitis presented with fever and abdominal pain. CT showed evidence of chronic pancreatitis and a 18.3 X 5.7 X 5.1 cm PFC. He underwent endoscopic cysto-duodenal stenting. Symptomatic residual infected paraduodenal collection needed additional CT guided drainage which grew Candida lusitaniae. Patient improved with fluconazole therapy.
Case 3:
A 47-year-old male with alcohol related pancreatitis complicated by PFC presented with pain and fever. CT showed a splenic artery pseudoaneurysm with active bleeding into the PFC. He underwent coil-embolization of the pseudoaneurysm. Persistent fevers prompted percutaneous drainage of PFC and cultures showed Candida albicans. Treatment with Micafungin led to symptomatic improvement.
Discussion: PFC drainage is indicated when infection is suspected, and fluid cultures help to tailor antimicrobial therapy. Uncommonly, Candida spp are isolated from PFC. Risk factors include immunocompromised status, abdominal instrumentation and systemic fungemia. Here, we present 3 cases of PFCs growing Candida spp post instrumentation that were successfully treated with antimicrobial therapy.
Disclosures:
Robinder Abrol indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Mushtaq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kanana Aburayyan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kumar Pallav indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Irfan Masood indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Person indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sreeram Parupudi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Robinder Abrol, DO1, Muhammad Mushtaq, DO1, Kanana Aburayyan, MD2, Kumar Pallav, MBBS, FACG3, Irfan Masood, MD1, Joshua Person, MD1, Sreeram Parupudi, MD, FACG1. P1489 - Candida in Infected Peri-Pancreatic Fluid Collections - A Case Series, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
