Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1528 - Unusual Presentation of Cholangitis in a Patient With IgG4-RD and Extreme Hypereosinophilia
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- GS
Gurpal Singh, MD
Kern Medical Center
Bakersfield, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Gurpal Singh, MD, Vishal Narang, MD, Cesar Aranguri, MD, Shikha Mishra, MD, Ishaan Kalha, MD
Kern Medical Center, Bakersfield, CA
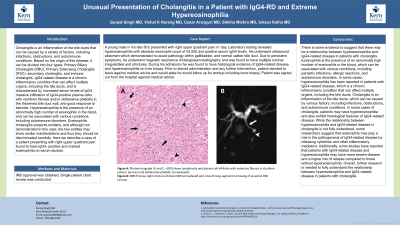
Introduction: Cholangitis is an inflammation of bile ducts that can be caused by multiple factors, including infections, obstructions, and autoimmune conditions. IgG4-related disease is a condition that can affect many organs, including the bile ducts, and is characterized by elevated serum IgG4 levels and histological features of inflammation/fibrosis. Hypereosinophilia is the presence of abnormally high eosinophils in the blood, and can be associated with various conditions, including autoimmune disorders. Here we describe a case of a patient presenting with RUQ pain found to have IgG4- positive and marked eosinophilia on serum studies.
Case Description/Methods: 30 male presented with RUQ abdominal pain. Lab testing revealed hypereosinophilia with absolute eosinophil count of 43000 and positive serum IgG4 levels. Ultrasound abdomen demonstrated no acute pathology within gallbladder. Due to persistent symptoms, he underwent MRCP and was found to have multiple luminal irregularities. He was found to have histological evidence of IgG4-related disease and hypereosinophilia on liver biopsy. Patient decided to leave against medical advice before any further intervention, but stated he would follow up for workup including bone biopsy.
Discussion: There is evidence to suggest that there may be a relationship between hypereosinophilia and IgG4-related disease in patients with cholangitis. In some cases, hypereosinophilia has been reported in patients with IgG4-related disease, a chronic inflammatory condition that can affect multiple organs, including the bile ducts. Cholangitis is an inflammation of the bile ducts, which can be caused by various factors, including infections, obstructions, and autoimmune conditions. In some cases of cholangitis, patients may have hypereosinophilia and also exhibit histological features of IgG4-related disease. While the relationship between hypereosinophilia and IgG4-related disease in cholangitis is not fully understood, some researchers suggest that eosinophils may play a role in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease by releasing cytokines and other inflammatory mediators. Additionally, some studies have reported that patients with IgG4-related disease and hypereosinophilia may have more severe disease and a higher risk of relapse compared to those without hypereosinophilia. Overall, further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between hypereosinophilia and IgG4-related disease in patients with cholangitis.
Disclosures:
Gurpal Singh, MD, Vishal Narang, MD, Cesar Aranguri, MD, Shikha Mishra, MD, Ishaan Kalha, MD. P1528 - Unusual Presentation of Cholangitis in a Patient With IgG4-RD and Extreme Hypereosinophilia, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Kern Medical Center, Bakersfield, CA
Introduction: Cholangitis is an inflammation of bile ducts that can be caused by multiple factors, including infections, obstructions, and autoimmune conditions. IgG4-related disease is a condition that can affect many organs, including the bile ducts, and is characterized by elevated serum IgG4 levels and histological features of inflammation/fibrosis. Hypereosinophilia is the presence of abnormally high eosinophils in the blood, and can be associated with various conditions, including autoimmune disorders. Here we describe a case of a patient presenting with RUQ pain found to have IgG4- positive and marked eosinophilia on serum studies.
Case Description/Methods: 30 male presented with RUQ abdominal pain. Lab testing revealed hypereosinophilia with absolute eosinophil count of 43000 and positive serum IgG4 levels. Ultrasound abdomen demonstrated no acute pathology within gallbladder. Due to persistent symptoms, he underwent MRCP and was found to have multiple luminal irregularities. He was found to have histological evidence of IgG4-related disease and hypereosinophilia on liver biopsy. Patient decided to leave against medical advice before any further intervention, but stated he would follow up for workup including bone biopsy.
Discussion: There is evidence to suggest that there may be a relationship between hypereosinophilia and IgG4-related disease in patients with cholangitis. In some cases, hypereosinophilia has been reported in patients with IgG4-related disease, a chronic inflammatory condition that can affect multiple organs, including the bile ducts. Cholangitis is an inflammation of the bile ducts, which can be caused by various factors, including infections, obstructions, and autoimmune conditions. In some cases of cholangitis, patients may have hypereosinophilia and also exhibit histological features of IgG4-related disease. While the relationship between hypereosinophilia and IgG4-related disease in cholangitis is not fully understood, some researchers suggest that eosinophils may play a role in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related disease by releasing cytokines and other inflammatory mediators. Additionally, some studies have reported that patients with IgG4-related disease and hypereosinophilia may have more severe disease and a higher risk of relapse compared to those without hypereosinophilia. Overall, further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between hypereosinophilia and IgG4-related disease in patients with cholangitis.
Disclosures:
Gurpal Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vishal Narang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Cesar Aranguri indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shikha Mishra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishaan Kalha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gurpal Singh, MD, Vishal Narang, MD, Cesar Aranguri, MD, Shikha Mishra, MD, Ishaan Kalha, MD. P1528 - Unusual Presentation of Cholangitis in a Patient With IgG4-RD and Extreme Hypereosinophilia, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
