Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P1646 - Expanding the Differential: A Case of Primary Ileocecal Valve Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- OA
Osama Alshakhatreh, MD
Albany Medical Center
Albany, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Osama Alshakhatreh, MD, Ethan Pearlstein, MD, Hasan B. Aydin, MD, Xiaoyan Huang, MD, Asra Batool, MD
Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY
Introduction: Primary gastrointestinal (GI) lymphomas represent 1-4% of GI malignancies. Primary ileocecal (IC) valve lymphoma is an uncommon presentation. We report the case of a previously healthy 27-year-old male who presented with symptoms concerning for IBD but was found to have a primary IC valve mass presenting as stage IV Non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma.
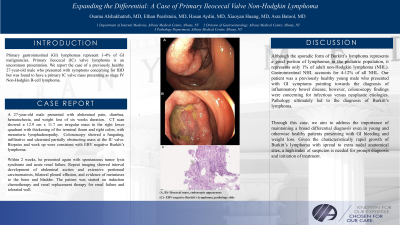
Case Description/Methods: A 27-year-old male with no comorbidities presented with abdominal pain, diarrhea, hematochezia, and weight loss of six weeks duration. CT scan showed a 12.9 cm x 11.7 cm irregular mass in the right lower quadrant with thickening of the terminal ileum and right colon, with mesenteric lymphadenopathy. Colonoscopy showed a fungating, infiltrative and ulcerated partially obstructing mass at the IC valve. Biopsies were consistent with an aggressive B-cell lymphoma with monoclonal proliferation of CD10+ cells. Serology for EBV and HIV was negative. Based on the workup, he was diagnosed with EBV negative Burkitt’s lymphoma.
Within 2 weeks, he presented again with spontaneous tumor lysis syndrome and acute renal failure. Repeat imaging showed interval development of abdominal ascites and extensive peritoneal carcinomatosis, bilateral pleural effusion, and evidence of metastases to the bone and bladder. Flow cytometry studies revealed no bone marrow or peripheral blood involvement. Pleural fluid cytology was consistent with B-cell lymphoma. The patient was started on induction chemotherapy and renal replacement therapy for renal failure and tolerated well.
Discussion: Although the sporadic form of Burkitt’s lymphoma represents a good portion of lymphomas in the pediatric population, it represents only 1% of adult non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Gastrointestinal NHL accounts for 4-12% of all NHL. Our patient was a previously healthy young male who presented with GI symptoms pointing towards the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease, however, colonoscopy findings were concerning for infectious versus neoplastic etiologies. Pathology ultimately led to the diagnosis of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Through this case, we aim to address the importance of maintaining a broad differential diagnosis even in young and otherwise healthy patients presenting with GI bleeding and weight loss. Given the characteristically rapid growth of Burkitt’s lymphoma with spread to extra nodal anatomical sites, a high index of suspicion is needed for prompt diagnosis and initiation of treatment.

Disclosures:
Osama Alshakhatreh, MD, Ethan Pearlstein, MD, Hasan B. Aydin, MD, Xiaoyan Huang, MD, Asra Batool, MD. P1646 - Expanding the Differential: A Case of Primary Ileocecal Valve Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Albany Medical Center, Albany, NY
Introduction: Primary gastrointestinal (GI) lymphomas represent 1-4% of GI malignancies. Primary ileocecal (IC) valve lymphoma is an uncommon presentation. We report the case of a previously healthy 27-year-old male who presented with symptoms concerning for IBD but was found to have a primary IC valve mass presenting as stage IV Non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma.
Case Description/Methods: A 27-year-old male with no comorbidities presented with abdominal pain, diarrhea, hematochezia, and weight loss of six weeks duration. CT scan showed a 12.9 cm x 11.7 cm irregular mass in the right lower quadrant with thickening of the terminal ileum and right colon, with mesenteric lymphadenopathy. Colonoscopy showed a fungating, infiltrative and ulcerated partially obstructing mass at the IC valve. Biopsies were consistent with an aggressive B-cell lymphoma with monoclonal proliferation of CD10+ cells. Serology for EBV and HIV was negative. Based on the workup, he was diagnosed with EBV negative Burkitt’s lymphoma.
Within 2 weeks, he presented again with spontaneous tumor lysis syndrome and acute renal failure. Repeat imaging showed interval development of abdominal ascites and extensive peritoneal carcinomatosis, bilateral pleural effusion, and evidence of metastases to the bone and bladder. Flow cytometry studies revealed no bone marrow or peripheral blood involvement. Pleural fluid cytology was consistent with B-cell lymphoma. The patient was started on induction chemotherapy and renal replacement therapy for renal failure and tolerated well.
Discussion: Although the sporadic form of Burkitt’s lymphoma represents a good portion of lymphomas in the pediatric population, it represents only 1% of adult non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). Gastrointestinal NHL accounts for 4-12% of all NHL. Our patient was a previously healthy young male who presented with GI symptoms pointing towards the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease, however, colonoscopy findings were concerning for infectious versus neoplastic etiologies. Pathology ultimately led to the diagnosis of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Through this case, we aim to address the importance of maintaining a broad differential diagnosis even in young and otherwise healthy patients presenting with GI bleeding and weight loss. Given the characteristically rapid growth of Burkitt’s lymphoma with spread to extra nodal anatomical sites, a high index of suspicion is needed for prompt diagnosis and initiation of treatment.

Figure: (A,B)- Ileocecal mass, endoscopic appearance. (C)- EBV-negative Burkitt's lymphoma, pathology slide.
Disclosures:
Osama Alshakhatreh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ethan Pearlstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hasan Aydin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Xiaoyan Huang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Asra Batool indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Osama Alshakhatreh, MD, Ethan Pearlstein, MD, Hasan B. Aydin, MD, Xiaoyan Huang, MD, Asra Batool, MD. P1646 - Expanding the Differential: A Case of Primary Ileocecal Valve Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
