Monday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P1773 - Comparing Sessile Serrated Adenoma/Polyp Detection Rate Between Water Exchange and Computer-Aided Detection Colonoscopy Using Pooled Data From Randomized Controlled Trials
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Paul P. Shao, MD
Stanford University
Redwood City, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Paul P. Shao, MD1, Jonathan Kuo, MS2, Changhan R. Shao, MBBS3, Felix W. Leung, MD, FACG4
1Stanford University, Redwood City, CA; 2Touro University Nevada, Henderson, NV; 3Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan City, Taoyuan, Taiwan; 4Sepulveda ACC/VAGLAHS/UCLA, North Hills, CA
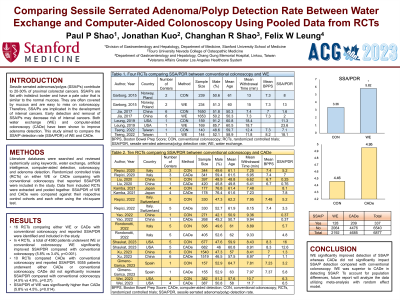
Introduction: Sessile serrated adenomas/polyps (SSA/Ps) contribute to 20-30% of proximal colorectal cancers. SSA/Ps are flat with indistinct border and have a pale color that is similar to the normal mucosa. They are often covered by mucous and are easy to miss on colonoscopy. Therefore, SSA/Ps are implicated in the development of interval cancers. Early detection and removal of SSA/Ps may decrease risk of interval cancers. Both water exchange (WE) and computer-aided colonoscopy (CADe) have been shown to improve adenoma detection. This study aimed to compare the SSA/P detection rate (SSA/PDR) of WE and CADe.
Methods: Literature databases were searched and reviewed systemically using keywords, water exchange, artificial intelligence, computer-aided detection, colonoscopy, and adenoma detection. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on either WE or CADe comparing with conventional colonoscopy that reported SSA/PDR were included in the study. Data from included RCTs were extracted and pooled together. SSA/PDR of WE and CADe were compared against their respective control cohorts and each other using the chi-square test.
Results: 14 RCTs comparing WE or CADe with conventional colonoscopy were identified from the literature search and included in our study. A total of 4380 patients underwent WE or conventional colonoscopy in 4 RCTs. WE significantly improved SSA/PDR compared with conventional colonoscopy (5.8% vs 3.4%, p< 0.001). In another 10 RCTs, 9355 patients underwent CADe or conventional colonoscopy. SSAP/DR of CADe was not significantly different from that of conventional colonoscopy (4.5% vs. 4.9%, p=0.27). SSA/PDR of WE was significantly higher than CADe (5.8% vs. 4.5%, p=0.029).
Discussion: WE significantly improved detection of SSA/P whereas CADe did not significantly impact SSA/P detection compared with conventional colonoscopy. WE was superior to CADe in detection of SSA/P.
Disclosures:
Paul P. Shao, MD1, Jonathan Kuo, MS2, Changhan R. Shao, MBBS3, Felix W. Leung, MD, FACG4. P1773 - Comparing Sessile Serrated Adenoma/Polyp Detection Rate Between Water Exchange and Computer-Aided Detection Colonoscopy Using Pooled Data From Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Stanford University, Redwood City, CA; 2Touro University Nevada, Henderson, NV; 3Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan City, Taoyuan, Taiwan; 4Sepulveda ACC/VAGLAHS/UCLA, North Hills, CA
Introduction: Sessile serrated adenomas/polyps (SSA/Ps) contribute to 20-30% of proximal colorectal cancers. SSA/Ps are flat with indistinct border and have a pale color that is similar to the normal mucosa. They are often covered by mucous and are easy to miss on colonoscopy. Therefore, SSA/Ps are implicated in the development of interval cancers. Early detection and removal of SSA/Ps may decrease risk of interval cancers. Both water exchange (WE) and computer-aided colonoscopy (CADe) have been shown to improve adenoma detection. This study aimed to compare the SSA/P detection rate (SSA/PDR) of WE and CADe.
Methods: Literature databases were searched and reviewed systemically using keywords, water exchange, artificial intelligence, computer-aided detection, colonoscopy, and adenoma detection. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on either WE or CADe comparing with conventional colonoscopy that reported SSA/PDR were included in the study. Data from included RCTs were extracted and pooled together. SSA/PDR of WE and CADe were compared against their respective control cohorts and each other using the chi-square test.
Results: 14 RCTs comparing WE or CADe with conventional colonoscopy were identified from the literature search and included in our study. A total of 4380 patients underwent WE or conventional colonoscopy in 4 RCTs. WE significantly improved SSA/PDR compared with conventional colonoscopy (5.8% vs 3.4%, p< 0.001). In another 10 RCTs, 9355 patients underwent CADe or conventional colonoscopy. SSAP/DR of CADe was not significantly different from that of conventional colonoscopy (4.5% vs. 4.9%, p=0.27). SSA/PDR of WE was significantly higher than CADe (5.8% vs. 4.5%, p=0.029).
Discussion: WE significantly improved detection of SSA/P whereas CADe did not significantly impact SSA/P detection compared with conventional colonoscopy. WE was superior to CADe in detection of SSA/P.
Disclosures:
Paul Shao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jonathan Kuo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Changhan Shao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Felix Leung indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paul P. Shao, MD1, Jonathan Kuo, MS2, Changhan R. Shao, MBBS3, Felix W. Leung, MD, FACG4. P1773 - Comparing Sessile Serrated Adenoma/Polyp Detection Rate Between Water Exchange and Computer-Aided Detection Colonoscopy Using Pooled Data From Randomized Controlled Trials, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
