Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0123 - An Accordion-Like Bile Duct in IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Rare Finding in an Elusive Diagnosis!
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- UC
Uche Chukwudumebi, DO
University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine
Tampa, FL
Presenting Author(s)
Chukwudumebi Uche, DO1, Pushpak Taunk, MD2, Danial Shaikh, MD2
1University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, FL; 2University of South Florida, Tampa, FL
Introduction: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease is an immune-mediated fibroinflammatory condition that can affect multiple organs, including the biliary tree. Diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is based on histopathologic, clinical, serologic, and radiographic findings. Radiologic findings include narrowing of the intra and extrahepatic bile ducts. We present a rare case of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis in which an “accordion-like” common bile duct (CBD) was found on cholangiography, a unique finding that has never been reported in the literature.
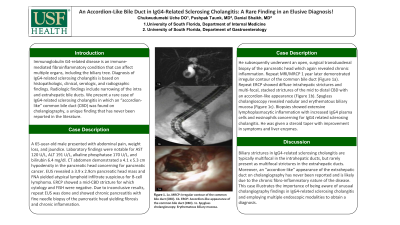
Case Description/Methods: A 65-year-old male presented with abdominal pain, weight loss, and jaundice. Laboratory findings were notable for AST 120 U/L, ALT 191 U/L, alkaline phosphatase 170 U/L, and bilirubin 6.4 mg/dl. CT abdomen demonstrated a 4.1 x 5.3 cm hypodensity in the pancreatic head concerning for pancreatic cancer. EUS revealed a 3.9 x 2.9cm pancreatic head mass and FNA yielded atypical lymphoid infiltrate suspicious for B-cell lymphoma. ERCP showed a mid-CBD stricture for which cytology and FISH were negative. Due to inconclusive results, repeat EUS was done and showed chronic pancreatitis with fine needle biopsy of the pancreatic head yielding fibrosis and chronic inflammation. He subsequently underwent an open, surgical transduodenal biopsy of the pancreatic head which again revealed chronic inflammation. Repeat MRI/MRCP 1 year later demonstrated irregular contour of the common bile duct (Figure 1a). Repeat ERCP showed diffuse intrahepatic strictures and multi-focal, stacked strictures of the mid to distal CBD with an accordion-like appearance (Figure 1b). Spyglass cholangioscopy revealed nodular and erythematous biliary mucosa (Figure 1c). Biopsies showed extensive lymphoplasmacytic inflammation with increased IgG4 plasma cells and eosinophils concerning for IgG4 related sclerosing cholangitis. He was given a steroid taper with improvement in symptoms and liver enzymes.
Discussion: Biliary strictures in IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis are typically multifocal in the intrahepatic ducts, but rarely present as multifocal strictures in the extrahepatic ducts. Moreover, an “accordion-like” appearance of the extrahepatic duct on cholangiography has never been reported and is likely due to the chronic fibro-inflammatory nature of the disease. This case illustrates the importance of being aware of unusual cholangiography findings in IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and employing multiple endoscopic modalities to obtain a diagnosis.

Disclosures:
Chukwudumebi Uche, DO1, Pushpak Taunk, MD2, Danial Shaikh, MD2. P0123 - An Accordion-Like Bile Duct in IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Rare Finding in an Elusive Diagnosis!, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of South Florida Morsani College of Medicine, Tampa, FL; 2University of South Florida, Tampa, FL
Introduction: Immunoglobulin G4-related disease is an immune-mediated fibroinflammatory condition that can affect multiple organs, including the biliary tree. Diagnosis of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis is based on histopathologic, clinical, serologic, and radiographic findings. Radiologic findings include narrowing of the intra and extrahepatic bile ducts. We present a rare case of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis in which an “accordion-like” common bile duct (CBD) was found on cholangiography, a unique finding that has never been reported in the literature.
Case Description/Methods: A 65-year-old male presented with abdominal pain, weight loss, and jaundice. Laboratory findings were notable for AST 120 U/L, ALT 191 U/L, alkaline phosphatase 170 U/L, and bilirubin 6.4 mg/dl. CT abdomen demonstrated a 4.1 x 5.3 cm hypodensity in the pancreatic head concerning for pancreatic cancer. EUS revealed a 3.9 x 2.9cm pancreatic head mass and FNA yielded atypical lymphoid infiltrate suspicious for B-cell lymphoma. ERCP showed a mid-CBD stricture for which cytology and FISH were negative. Due to inconclusive results, repeat EUS was done and showed chronic pancreatitis with fine needle biopsy of the pancreatic head yielding fibrosis and chronic inflammation. He subsequently underwent an open, surgical transduodenal biopsy of the pancreatic head which again revealed chronic inflammation. Repeat MRI/MRCP 1 year later demonstrated irregular contour of the common bile duct (Figure 1a). Repeat ERCP showed diffuse intrahepatic strictures and multi-focal, stacked strictures of the mid to distal CBD with an accordion-like appearance (Figure 1b). Spyglass cholangioscopy revealed nodular and erythematous biliary mucosa (Figure 1c). Biopsies showed extensive lymphoplasmacytic inflammation with increased IgG4 plasma cells and eosinophils concerning for IgG4 related sclerosing cholangitis. He was given a steroid taper with improvement in symptoms and liver enzymes.
Discussion: Biliary strictures in IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis are typically multifocal in the intrahepatic ducts, but rarely present as multifocal strictures in the extrahepatic ducts. Moreover, an “accordion-like” appearance of the extrahepatic duct on cholangiography has never been reported and is likely due to the chronic fibro-inflammatory nature of the disease. This case illustrates the importance of being aware of unusual cholangiography findings in IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and employing multiple endoscopic modalities to obtain a diagnosis.

Figure: 1a. MRCP: Irregular contour of the common bile duct (CBD). 1b. ERCP: Accordion-like appearance of the common bile duct (CBD). 1c. Spyglass cholangioscopy: Erythematous biliary mucosa.
Disclosures:
Chukwudumebi Uche indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pushpak Taunk indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Danial Shaikh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chukwudumebi Uche, DO1, Pushpak Taunk, MD2, Danial Shaikh, MD2. P0123 - An Accordion-Like Bile Duct in IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis: A Rare Finding in an Elusive Diagnosis!, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
