Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0159 - Deep Learning and High-Resolution Anoscopy: Assessing the Impact of Staining and Overcoming the Impact Therapeutic Anal Manipulation in the Automated Detection and Differentiation of Anal Squamous Cell Cancer Precursors
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Miguel Mascarenhas, MD
Centro Hospitalar São João
Porto, Porto, Portugal
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Miguel Mascarenhas, MD1, Lucas Spindler, MD2, Nadia Fathallah, MD2, Tiago Ribeiro, MD1, João PL. Afonso, MD3, Pedro Cardoso, MD1, Francisco Mendes, MD1, Miguel Martins, MD1, João Ferreira, PhD4, Guilherme Macedo, MD, PhD3, Vincent De Parades, MD, PhD2
1Centro Hospitalar São João, Porto, Porto, Portugal; 2Hospital Paris Saint Joseph, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; 3Centro Hospitalar de São João, Porto, Porto, Portugal; 4University of Porto-FEUP, Porto, Porto, Portugal
Introduction: High-resolution anoscopy (HRA) is the gold standard for detecting anal squamous cell cancer (ASCC) precursors. It has shown superiority over cytology for detecting high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL). Nevertheless, the visual characterization of these lesions remains challenging. Preliminary studies on applying deep learning models to HRA have revealed promising results. The impact of staining techniques and anal manipulation for the treatment of precursor lesions on the effectiveness of these algorithms has not been evaluated.
Our aim was to develop a deep learning system for automatic detection and differentiation of HSIL versus low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL) in HRA images in different subsets of patients (non-stained, acetic acid, Lugol, and after manipulation).
Methods: A convolutional neural network (CNN) was developed based on 102 HRA exams from 88 patients from a Proctology high-volume center (GH Paris Saint-Joseph, Paris, France). A total of 27,770 images were included, 19,114 images containing HSIL and 8,656 LSIL. A patient-split five-fold cross-validation analysis was performed to assess the network's performance. Partial subanalyses were performed to evaluate the performance of the CNN in the subset of images with no staining (n=2,820), acetic acid (n=13,378), lugol (n=2,195), and after treatment of the anal canal (n=9,377). For these subanalyses, training, and testing datasets comprised 90% and 10% of each class's total number of images. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values, and area under the curve (AUC) were calculated.
Results: The overall accuracy of the CNN in distinguishing HSIL from LSIL during the testing stage was 98.3%. The algorithm had an overall sensitivity and specificity of 97.4% and 99.2%, respectively. The accuracy of the CNN for detecting HSIL vs. LSIL varied between 91.5% (post-manipulation) and 100% (Lugol) for the four categories of subanalysis. The AUC ranged between 0.95 and 1.00.
Discussion: The introduction of AI algorithms to HRA may enhance the early diagnosis of ASCC precursors, improving these patients' therapeutic course and prognosis. Staining techniques are essential during HRA exams. Our algorithm showed excellent performance for staining with both Lugol and acetic acid and in the post-manipulation/treatment images subset. This is particularly relevant as real-time AI models during HRA exams may help guide local treatment or detect relapsing disease.

Disclosures:
Miguel Mascarenhas, MD1, Lucas Spindler, MD2, Nadia Fathallah, MD2, Tiago Ribeiro, MD1, João PL. Afonso, MD3, Pedro Cardoso, MD1, Francisco Mendes, MD1, Miguel Martins, MD1, João Ferreira, PhD4, Guilherme Macedo, MD, PhD3, Vincent De Parades, MD, PhD2. P0159 - Deep Learning and High-Resolution Anoscopy: Assessing the Impact of Staining and Overcoming the Impact Therapeutic Anal Manipulation in the Automated Detection and Differentiation of Anal Squamous Cell Cancer Precursors, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Miguel Mascarenhas, MD1, Lucas Spindler, MD2, Nadia Fathallah, MD2, Tiago Ribeiro, MD1, João PL. Afonso, MD3, Pedro Cardoso, MD1, Francisco Mendes, MD1, Miguel Martins, MD1, João Ferreira, PhD4, Guilherme Macedo, MD, PhD3, Vincent De Parades, MD, PhD2
1Centro Hospitalar São João, Porto, Porto, Portugal; 2Hospital Paris Saint Joseph, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; 3Centro Hospitalar de São João, Porto, Porto, Portugal; 4University of Porto-FEUP, Porto, Porto, Portugal
Introduction: High-resolution anoscopy (HRA) is the gold standard for detecting anal squamous cell cancer (ASCC) precursors. It has shown superiority over cytology for detecting high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (HSIL). Nevertheless, the visual characterization of these lesions remains challenging. Preliminary studies on applying deep learning models to HRA have revealed promising results. The impact of staining techniques and anal manipulation for the treatment of precursor lesions on the effectiveness of these algorithms has not been evaluated.
Our aim was to develop a deep learning system for automatic detection and differentiation of HSIL versus low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSIL) in HRA images in different subsets of patients (non-stained, acetic acid, Lugol, and after manipulation).
Methods: A convolutional neural network (CNN) was developed based on 102 HRA exams from 88 patients from a Proctology high-volume center (GH Paris Saint-Joseph, Paris, France). A total of 27,770 images were included, 19,114 images containing HSIL and 8,656 LSIL. A patient-split five-fold cross-validation analysis was performed to assess the network's performance. Partial subanalyses were performed to evaluate the performance of the CNN in the subset of images with no staining (n=2,820), acetic acid (n=13,378), lugol (n=2,195), and after treatment of the anal canal (n=9,377). For these subanalyses, training, and testing datasets comprised 90% and 10% of each class's total number of images. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values, and area under the curve (AUC) were calculated.
Results: The overall accuracy of the CNN in distinguishing HSIL from LSIL during the testing stage was 98.3%. The algorithm had an overall sensitivity and specificity of 97.4% and 99.2%, respectively. The accuracy of the CNN for detecting HSIL vs. LSIL varied between 91.5% (post-manipulation) and 100% (Lugol) for the four categories of subanalysis. The AUC ranged between 0.95 and 1.00.
Discussion: The introduction of AI algorithms to HRA may enhance the early diagnosis of ASCC precursors, improving these patients' therapeutic course and prognosis. Staining techniques are essential during HRA exams. Our algorithm showed excellent performance for staining with both Lugol and acetic acid and in the post-manipulation/treatment images subset. This is particularly relevant as real-time AI models during HRA exams may help guide local treatment or detect relapsing disease.

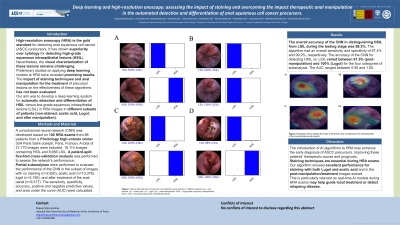
Figure: Fig. 1 Output obtained after running the convolutional neural network in different subsets: (a) – non-stained; (b) – acetic acid; (c) – Lugol; (d) – post-manipulation. HSIL – high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; LSIL - low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion.
Disclosures:
Miguel Mascarenhas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lucas Spindler indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nadia Fathallah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tiago Ribeiro indicated no relevant financial relationships.
João Afonso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pedro Cardoso indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Francisco Mendes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Martins indicated no relevant financial relationships.
João Ferreira indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Guilherme Macedo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vincent De Parades indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Mascarenhas, MD1, Lucas Spindler, MD2, Nadia Fathallah, MD2, Tiago Ribeiro, MD1, João PL. Afonso, MD3, Pedro Cardoso, MD1, Francisco Mendes, MD1, Miguel Martins, MD1, João Ferreira, PhD4, Guilherme Macedo, MD, PhD3, Vincent De Parades, MD, PhD2. P0159 - Deep Learning and High-Resolution Anoscopy: Assessing the Impact of Staining and Overcoming the Impact Therapeutic Anal Manipulation in the Automated Detection and Differentiation of Anal Squamous Cell Cancer Precursors, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

