Sunday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P0313 - Colonic Ganglioneuroma: A Special Type of Pedunculated Polyp
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- DC
David L. Cheung, MD
UC Irvine
Orange, CA
Presenting Author(s)
David L. Cheung, MD1, Andy Lin, MD2, Amirali Tavangar, MD2, Jaehyun Kim, MD2, Joshua Kwon, MD2, Jason Samarasena, MD2, Nimisha Parekh, MD2
1UC Irvine, Orange, CA; 2University of California Irvine, Orange, CA
Introduction: Ganglioneuroma (GN) is a rare, benign neurogenic tumor that originates from undifferentiated neuro crest cells within the neuroepithelium and often seen within the head, neck, or adrenal glands. We present a rare case of a polypoid GN within the colon on average risk colonoscopy screening in a patient with incidental cutaneous lipomas in the extremities.
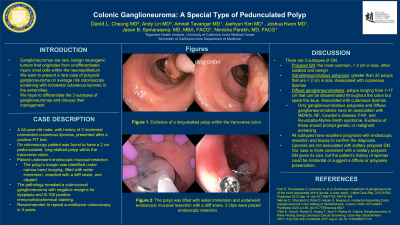
Case Description/Methods: A 54 male presents for routine colonoscopy after a positive FIT test. The patient denies any gastrointestinal symptoms but does report a history of three unresected lipomas. On colonoscopy, the patient was found to have a total of five sessile polyps within the transverse, ascending, and sigmoid colon with resection, with 2 polyps consistent for tubular adenomas on pathology. The patient was also found to have a large 2 cm pedunculated, long-stalked polyp within the transverse colon (Image A/B). Due to its extensive nature, the patient underwent repeat colonoscopy with endoscopic mucosal resection (Image C). The polyp’s margin was identified under NBI, lifted with water immersion, resected with a stiff snare, and clipped (Image D). The pathology revealed a submucosal ganglioneuroma with negative margins for dysplasia and S-100 positive immunohistochemical staining. The patient will follow up for repeat surveillance colonoscopy in 3 years.
Discussion: There are 3 subtypes of GNs that can be found within the colon: polypoid GN, ganglioneuromatous polyposis, and diffuse ganglioneuromatosis. Polypoid GNs are the most common, < 2 cm in size, often isolated and benign, and are not normally associated with cutaneous lipomas. Ganglioneuromatous polyposis is usually present with greater than 20 polyps that are < 2 cm in size. Diffuse ganglioneuromatosis present with polyps ranging from 1-17 cm that can be disseminated throughout the colon but spare the ileus. Ganglioneuromatous polyposis and diffuse ganglioneuromatosis are often associated with cutaneous lipomas and have an association with MENIIb, NF, Cowden’s disease, FAP, and Ruvalcaba-Myhre-Smith syndrome. These findings should prompt genetic screening for these potential syndromes or for malignancy. All subtypes have excellent prognosis with endoscopic resection and biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. Within the literature, lipomas have not been reported to be present with solitary polypoid GN. Our case is more consistent with a solitary polypoid GN given its size, but the patient’s history of lipomas could be incidental or suggest a diffuse or polyposis presentation.

Disclosures:
David L. Cheung, MD1, Andy Lin, MD2, Amirali Tavangar, MD2, Jaehyun Kim, MD2, Joshua Kwon, MD2, Jason Samarasena, MD2, Nimisha Parekh, MD2. P0313 - Colonic Ganglioneuroma: A Special Type of Pedunculated Polyp, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UC Irvine, Orange, CA; 2University of California Irvine, Orange, CA
Introduction: Ganglioneuroma (GN) is a rare, benign neurogenic tumor that originates from undifferentiated neuro crest cells within the neuroepithelium and often seen within the head, neck, or adrenal glands. We present a rare case of a polypoid GN within the colon on average risk colonoscopy screening in a patient with incidental cutaneous lipomas in the extremities.
Case Description/Methods: A 54 male presents for routine colonoscopy after a positive FIT test. The patient denies any gastrointestinal symptoms but does report a history of three unresected lipomas. On colonoscopy, the patient was found to have a total of five sessile polyps within the transverse, ascending, and sigmoid colon with resection, with 2 polyps consistent for tubular adenomas on pathology. The patient was also found to have a large 2 cm pedunculated, long-stalked polyp within the transverse colon (Image A/B). Due to its extensive nature, the patient underwent repeat colonoscopy with endoscopic mucosal resection (Image C). The polyp’s margin was identified under NBI, lifted with water immersion, resected with a stiff snare, and clipped (Image D). The pathology revealed a submucosal ganglioneuroma with negative margins for dysplasia and S-100 positive immunohistochemical staining. The patient will follow up for repeat surveillance colonoscopy in 3 years.
Discussion: There are 3 subtypes of GNs that can be found within the colon: polypoid GN, ganglioneuromatous polyposis, and diffuse ganglioneuromatosis. Polypoid GNs are the most common, < 2 cm in size, often isolated and benign, and are not normally associated with cutaneous lipomas. Ganglioneuromatous polyposis is usually present with greater than 20 polyps that are < 2 cm in size. Diffuse ganglioneuromatosis present with polyps ranging from 1-17 cm that can be disseminated throughout the colon but spare the ileus. Ganglioneuromatous polyposis and diffuse ganglioneuromatosis are often associated with cutaneous lipomas and have an association with MENIIb, NF, Cowden’s disease, FAP, and Ruvalcaba-Myhre-Smith syndrome. These findings should prompt genetic screening for these potential syndromes or for malignancy. All subtypes have excellent prognosis with endoscopic resection and biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. Within the literature, lipomas have not been reported to be present with solitary polypoid GN. Our case is more consistent with a solitary polypoid GN given its size, but the patient’s history of lipomas could be incidental or suggest a diffuse or polyposis presentation.

Figure: A and B) long stalked polyp within the transverse colon.
C) Polyp lifted with water immersion that underwent endoscopic mucosal resection with stiff snare.
D) Placement of clips after endoscopic mucosal resection
C) Polyp lifted with water immersion that underwent endoscopic mucosal resection with stiff snare.
D) Placement of clips after endoscopic mucosal resection
Disclosures:
David Cheung indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andy Lin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amirali Tavangar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jaehyun Kim indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Kwon indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jason Samarasena: Applied Medical – Advisor or Review Panel Member. Boston Scientific – Consultant. Conmed – Consultant. Cook – Educational Grant. Neptune Medical – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. Steris – Consultant.
Nimisha Parekh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David L. Cheung, MD1, Andy Lin, MD2, Amirali Tavangar, MD2, Jaehyun Kim, MD2, Joshua Kwon, MD2, Jason Samarasena, MD2, Nimisha Parekh, MD2. P0313 - Colonic Ganglioneuroma: A Special Type of Pedunculated Polyp, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
