Sunday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P1330 - A Rare Case of Concurrent Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma and Gastric Tubular Adenoma
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- HR
Harini Rathinamanickam, MD
SIU School of Medicine
Springfield, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Harini Rathinamanickam, MD
SIU School of Medicine, Springfield, IL
Introduction: Primary duodenal follicular lymphoma (DFL) is rare comprising 1-3.6% of Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (NHL) with gastrointestinal (GI) involvement. We present a 73 y/o woman with iron deficiency anemia (IDA) who was found to have a DFL. She also had concurrent gastric adenoma (GA) which was removed by endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Concurrent DFL and GA have never been reported.
Case Description/Methods: 73 y/o Caucasian woman with HTN, OSA, RA, and breast cancer in remission presents with IDA. She denies abdominal pain or overt bleeding or weight loss. She denies smoking. She drinks alcohol a few days a week. She denies family h/o colon or stomach cancer. Her Hb-11.2, Iron-58, TIBC 349, and ferritin-76 on iron supplement. EGD revealed an erythematous fold in the 2nd portion of the duodenum. Biopsies revealed a low-grade DFL. She also had a 10 mm nodule with a superficial ulcer in the gastric antrum. Biopsy revealed a tubular adenoma with low-grade dysplasia in the background of focal intestinal metaplasia. The biopsy for H.pylori was negative. Colonoscopy revealed tubular adenomatous polyps. Bone marrow biopsy was negative. A PET scan showed indeterminate activity in the small bowel loops. She is scheduled for a repeat scan and f/u with oncology. Meanwhile, the gastric nodule was removed by EMR using a band ligator. Pathology revealed complete resection with negative margins.
Discussion: DFLs are diagnosed in 1:3000-7000 EGDs and are a rare primary GI malignancy. DFLs occur predominantly in middle-aged women. DFLs are most commonly found in the descending duodenum and 81% are associated with synchronous lesions in the jejunum or ileum. The most common endoscopic appearance is white granular or nodular lesions. Most patients are asymptomatic. DFLs have an indolent course with a median survival of up to 10 years after diagnosis. Management includes watchful observation, radiation, or chemotherapy.
GAs are precancerous lesions occurring most commonly in men in the 6th decade. GAs are rare accounting for 10% of gastric polyps. The 4 types of GAs are the intestinal, foveolar, pyloric, and oxyntic types. Intestinal GAs are the most common type and are often associated with gastritis. Microscopically Intestinal GAs may have tubular, villous, or sessile morphology. Endoscopically GAs may present as a polyp or flat lesion. Neoplastic progression is higher with flat lesions, high-grade dysplasia, and intestinal type of GAs. Endoscopic resection of GAs with surveillance EGD at 1 year is recommended.

Disclosures:
Harini Rathinamanickam, MD. P1330 - A Rare Case of Concurrent Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma and Gastric Tubular Adenoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
SIU School of Medicine, Springfield, IL
Introduction: Primary duodenal follicular lymphoma (DFL) is rare comprising 1-3.6% of Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (NHL) with gastrointestinal (GI) involvement. We present a 73 y/o woman with iron deficiency anemia (IDA) who was found to have a DFL. She also had concurrent gastric adenoma (GA) which was removed by endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Concurrent DFL and GA have never been reported.
Case Description/Methods: 73 y/o Caucasian woman with HTN, OSA, RA, and breast cancer in remission presents with IDA. She denies abdominal pain or overt bleeding or weight loss. She denies smoking. She drinks alcohol a few days a week. She denies family h/o colon or stomach cancer. Her Hb-11.2, Iron-58, TIBC 349, and ferritin-76 on iron supplement. EGD revealed an erythematous fold in the 2nd portion of the duodenum. Biopsies revealed a low-grade DFL. She also had a 10 mm nodule with a superficial ulcer in the gastric antrum. Biopsy revealed a tubular adenoma with low-grade dysplasia in the background of focal intestinal metaplasia. The biopsy for H.pylori was negative. Colonoscopy revealed tubular adenomatous polyps. Bone marrow biopsy was negative. A PET scan showed indeterminate activity in the small bowel loops. She is scheduled for a repeat scan and f/u with oncology. Meanwhile, the gastric nodule was removed by EMR using a band ligator. Pathology revealed complete resection with negative margins.
Discussion: DFLs are diagnosed in 1:3000-7000 EGDs and are a rare primary GI malignancy. DFLs occur predominantly in middle-aged women. DFLs are most commonly found in the descending duodenum and 81% are associated with synchronous lesions in the jejunum or ileum. The most common endoscopic appearance is white granular or nodular lesions. Most patients are asymptomatic. DFLs have an indolent course with a median survival of up to 10 years after diagnosis. Management includes watchful observation, radiation, or chemotherapy.
GAs are precancerous lesions occurring most commonly in men in the 6th decade. GAs are rare accounting for 10% of gastric polyps. The 4 types of GAs are the intestinal, foveolar, pyloric, and oxyntic types. Intestinal GAs are the most common type and are often associated with gastritis. Microscopically Intestinal GAs may have tubular, villous, or sessile morphology. Endoscopically GAs may present as a polyp or flat lesion. Neoplastic progression is higher with flat lesions, high-grade dysplasia, and intestinal type of GAs. Endoscopic resection of GAs with surveillance EGD at 1 year is recommended.

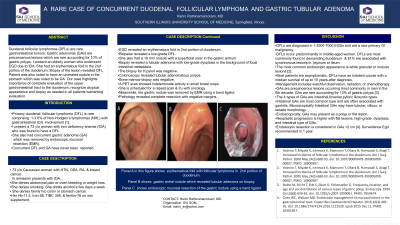
Figure: Panel A in this figure shows the erythematous fold with follicular lymphoma in the 2nd portion of duodenum. Panel B shows the gastric antral nodule which revealed tubular adenoma on biopsy. Panel C of the figure shows endoscopic mucosal resection of the gastric nodule using a band ligator device.
Disclosures:
Harini Rathinamanickam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Harini Rathinamanickam, MD. P1330 - A Rare Case of Concurrent Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma and Gastric Tubular Adenoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
