Sunday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P0067 - Metastasis Pancreatic Melanoma First Presenting as Asymptomatic Isolated Elevation of Alkaline Phosphatase Level
Sunday, October 22, 2023
3:30 PM - 7:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- MS
Mohammed Saleh, DO
Danbury Hospital
Danbury, Connecticut
Presenting Author(s)
Prabasha Weeraddana, MD, Mohammed Saleh, DO, Rella Vincent, MD
Danbury Hospital, Danbury, CT
Introduction: Metastatic pancreatic tumors are rare and represent 2 % of all pancreatic malignancies. It’s less common for melanoma to metastasize to the pancreas. We present a case of metastatic pancreatic melanoma detected by imaging studies for further workup of asymptomatic elevation of alkaline phosphates level.
Case Description/Methods: We present an 82-year-old male with a past medical history of atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and superficial melanoma removed from his left shoulder two years ago found to have elevated alkaline phosphatase at 193 U/L on annual physical and repeated labs in 6 months revealed further elevation at 278 U/L without other liver function abnormalities. The patient denied abdominal pain, weight loss, or changes in bowel habits. This prompted an ultrasound scan of the abdomen which showed an ill-defined hypoechoic mass of 6.8 x 6.1 cm in the pancreatic head. A Follow-up CT scan revealed a lobulated shape 6.9 x 4.2 cm mass along the superior margin of the pancreatic head without pancreatic ductal dilatation. The patient underwent a EUS with fine needle aspiration of pancreatic mass, consistent with malignant melanoma. MRI brain was without evidence for enhancing intracranial metastatic disease. PET scan showed disseminated malignancy with PET avid lesions within bilateral lungs, right hilum, and liver. There were large PET avid masses in the pancreatic head region and PET avid lymphadenopathy in the porta hepatis, the para-aortic region, and the external iliac region. His genomic testing did not reveal any targetable mutations, and the patient was started on Opdualag therapy.
Discussion: Malignant melanoma with distant metastasis has a poor prognosis with a median survival of less than one year. Alkaline phosphatase is an isoenzyme; most of its serum is commonly released from the liver, bone, and intestine. In asymptomatic patients with isolated elevation of serum alkaline phosphatase, it is essential to identify the underlying source of abnormality. Our patient underwent US abdomen and leading to the diagnosis of pancreatic mass. Malignant melanoma was confirmed by EUS with FNA of pancreatic mass. Isolated pancreatic melanomas can be treated by surgical resection with IFN therapy. Immunocheck point inhibitors such as Ipilimumab and the nivolumab novel agent have improved progression-free survival in previously untreated metastatic melanomas. As our patient had disseminated metastasis of malignant melanoma, he was started with combination therapy with nivolumab/relatlimab.

Disclosures:
Prabasha Weeraddana, MD, Mohammed Saleh, DO, Rella Vincent, MD. P0067 - Metastasis Pancreatic Melanoma First Presenting as Asymptomatic Isolated Elevation of Alkaline Phosphatase Level, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Danbury Hospital, Danbury, CT
Introduction: Metastatic pancreatic tumors are rare and represent 2 % of all pancreatic malignancies. It’s less common for melanoma to metastasize to the pancreas. We present a case of metastatic pancreatic melanoma detected by imaging studies for further workup of asymptomatic elevation of alkaline phosphates level.
Case Description/Methods: We present an 82-year-old male with a past medical history of atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and superficial melanoma removed from his left shoulder two years ago found to have elevated alkaline phosphatase at 193 U/L on annual physical and repeated labs in 6 months revealed further elevation at 278 U/L without other liver function abnormalities. The patient denied abdominal pain, weight loss, or changes in bowel habits. This prompted an ultrasound scan of the abdomen which showed an ill-defined hypoechoic mass of 6.8 x 6.1 cm in the pancreatic head. A Follow-up CT scan revealed a lobulated shape 6.9 x 4.2 cm mass along the superior margin of the pancreatic head without pancreatic ductal dilatation. The patient underwent a EUS with fine needle aspiration of pancreatic mass, consistent with malignant melanoma. MRI brain was without evidence for enhancing intracranial metastatic disease. PET scan showed disseminated malignancy with PET avid lesions within bilateral lungs, right hilum, and liver. There were large PET avid masses in the pancreatic head region and PET avid lymphadenopathy in the porta hepatis, the para-aortic region, and the external iliac region. His genomic testing did not reveal any targetable mutations, and the patient was started on Opdualag therapy.
Discussion: Malignant melanoma with distant metastasis has a poor prognosis with a median survival of less than one year. Alkaline phosphatase is an isoenzyme; most of its serum is commonly released from the liver, bone, and intestine. In asymptomatic patients with isolated elevation of serum alkaline phosphatase, it is essential to identify the underlying source of abnormality. Our patient underwent US abdomen and leading to the diagnosis of pancreatic mass. Malignant melanoma was confirmed by EUS with FNA of pancreatic mass. Isolated pancreatic melanomas can be treated by surgical resection with IFN therapy. Immunocheck point inhibitors such as Ipilimumab and the nivolumab novel agent have improved progression-free survival in previously untreated metastatic melanomas. As our patient had disseminated metastasis of malignant melanoma, he was started with combination therapy with nivolumab/relatlimab.

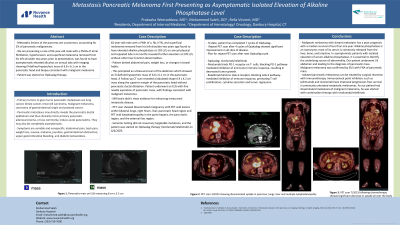
Figure: A- PET scan showed large PET avid masses in the region of the pancreatic head B- PET CT showed approximately 7.7 cm pancreatic head region mass
Disclosures:
Prabasha Weeraddana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mohammed Saleh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rella Vincent indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prabasha Weeraddana, MD, Mohammed Saleh, DO, Rella Vincent, MD. P0067 - Metastasis Pancreatic Melanoma First Presenting as Asymptomatic Isolated Elevation of Alkaline Phosphatase Level, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
