Monday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P1930 - Dupilumab Improves Treatment-Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis at 2 Months: A Longitudinal Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Outcome Case Report
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Quan M. Nhu, MD, PhD
Scripps Clinic & Scripps Research Institute
La Jolla, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Quan M.. Nhu, MD, PhD
Scripps Clinic & Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, type 2 (T2) immune-mediated disease that progresses to fibrostenotic EoE. Dupilumab inhibits T2 inflammation and is FDA-approved for EoE, having demonstrated “deep remission” with sustained clinical and endoscopic improvement and histologic remission at weeks 24 and 52. Herein, we present a case of EoE, refractory to proton-pump inhibitor (PPI), topical corticosteroid (TCS) and six-food elimination diet (SFED) therapies, that responded to dupilumab with histologic response, endoscopic and clinical improvement at as early as 2 months.
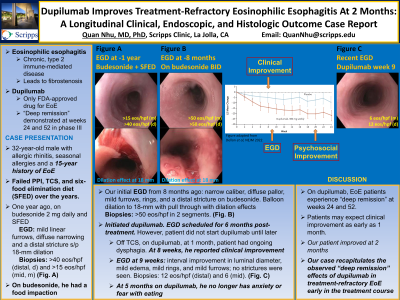
Case Description/Methods: A 32-year-old-male with allergic rhinitis and seasonal allergies presented with a 15-year history of EoE with solid-food dysphagia. On PPI, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) from 8 years ago showed concentric esophageal narrowing with diffuse rings; a distal stricture was dilated to 13-mm. Biopsies showed 100 eosinophils (eos)/hpf. On high-dose fluticasone, EGD from 5 years ago showed 80 eos/hpf. Patient failed PPI, TCS, and six-food elimination diet (SFED) combination therapies 2 years ago. One year ago, on budesonide 2 mg daily and SFED, EGD showed mild linear furrows. A distal stricture was dilated to 18 mm. Distal and middle esophageal biopsies had >40 and >15 eos/hpf. On budesonide, he had a food impaction.
Our initial EGD from 8 months ago showed diffuse pallor, mild furrows and mild rings on budesonide. Balloon dilation to 18-mm with pull through had dilation effects in the distal and middle esophagus. Biopsies showed >50 eos/hpf in 2 segments. Patient was initiated on dupilumab but did not start it until 5 months ago. Off TCS, on dupilumab, at 1 month, patient had ongoing dysphagia. At 8 weeks, he reported clinical improvement. EGD at 9 weeks showed interval improvement in luminal diameter, mild edema, mild rings, and mild furrows; no strictures were seen. Distal and middle esophagus had 12 and 6 eos/hpf. At 5 months on dupilumab, he no longer has anxiety or fear with eating.
Discussion: On dupilumab, EoE patients experience “deep remission” at weeks 24 and 52. Patients may expect clinical improvement as early as 1 month. Our patient felt clinical improvement at week 8 and had histologic response for the first time in his EoE treatment history at as early as 9 weeks on dupilumab. Our case recapitulates the observed “deep remission” effects of dupilumab in treatment-refractory EoE and provides longitudinal clinical, endoscopic, and histologic outcomes early in the treatment course.
Disclosures:
Quan M.. Nhu, MD, PhD. P1930 - Dupilumab Improves Treatment-Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis at 2 Months: A Longitudinal Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Outcome Case Report, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Scripps Clinic & Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, CA
Introduction: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, type 2 (T2) immune-mediated disease that progresses to fibrostenotic EoE. Dupilumab inhibits T2 inflammation and is FDA-approved for EoE, having demonstrated “deep remission” with sustained clinical and endoscopic improvement and histologic remission at weeks 24 and 52. Herein, we present a case of EoE, refractory to proton-pump inhibitor (PPI), topical corticosteroid (TCS) and six-food elimination diet (SFED) therapies, that responded to dupilumab with histologic response, endoscopic and clinical improvement at as early as 2 months.
Case Description/Methods: A 32-year-old-male with allergic rhinitis and seasonal allergies presented with a 15-year history of EoE with solid-food dysphagia. On PPI, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) from 8 years ago showed concentric esophageal narrowing with diffuse rings; a distal stricture was dilated to 13-mm. Biopsies showed 100 eosinophils (eos)/hpf. On high-dose fluticasone, EGD from 5 years ago showed 80 eos/hpf. Patient failed PPI, TCS, and six-food elimination diet (SFED) combination therapies 2 years ago. One year ago, on budesonide 2 mg daily and SFED, EGD showed mild linear furrows. A distal stricture was dilated to 18 mm. Distal and middle esophageal biopsies had >40 and >15 eos/hpf. On budesonide, he had a food impaction.
Our initial EGD from 8 months ago showed diffuse pallor, mild furrows and mild rings on budesonide. Balloon dilation to 18-mm with pull through had dilation effects in the distal and middle esophagus. Biopsies showed >50 eos/hpf in 2 segments. Patient was initiated on dupilumab but did not start it until 5 months ago. Off TCS, on dupilumab, at 1 month, patient had ongoing dysphagia. At 8 weeks, he reported clinical improvement. EGD at 9 weeks showed interval improvement in luminal diameter, mild edema, mild rings, and mild furrows; no strictures were seen. Distal and middle esophagus had 12 and 6 eos/hpf. At 5 months on dupilumab, he no longer has anxiety or fear with eating.
Discussion: On dupilumab, EoE patients experience “deep remission” at weeks 24 and 52. Patients may expect clinical improvement as early as 1 month. Our patient felt clinical improvement at week 8 and had histologic response for the first time in his EoE treatment history at as early as 9 weeks on dupilumab. Our case recapitulates the observed “deep remission” effects of dupilumab in treatment-refractory EoE and provides longitudinal clinical, endoscopic, and histologic outcomes early in the treatment course.
Disclosures:
Quan Nhu: Regeneron – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Sanofi – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Speakers Bureau. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Quan M.. Nhu, MD, PhD. P1930 - Dupilumab Improves Treatment-Refractory Eosinophilic Esophagitis at 2 Months: A Longitudinal Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histologic Outcome Case Report, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
