Monday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P2087 - Conquering Millions of Platelets: Hydroxyurea's Cytoreduction Cures Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Karan B. Singh, MD
University of South Alabama
Mobile, AL
Presenting Author(s)
Karan B. Singh, MD1, Mary C. Marshall, MD2
1University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL; 2USA Health University Hospital, Mobile, AL
Introduction: Essential thrombocythemia (ET), a myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN), presents with a platelet count of >450,000/uL and encompasses a diverse range of clinical manifestations. Notably, platelet counts >1,000,000/uL are associated with a heightened bleeding risk, while counts < 1,000,000/uL predispose thrombotic events. In this case, we demonstrate ET resulting in lower gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) caused by arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
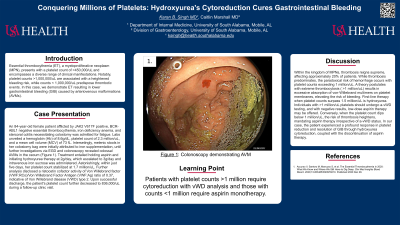
Case Description/Methods: An 84-year-old female patient afflicted by JAK2 V617F positive, BCR-ABL1 negative essential thrombocythemia, iron deficiency anemia, and stercoral colitis necessitating colostomy was admitted for fatigue. Labs unveiled a hemoglobin (Hb) of 8.6g/dL, platelet count of 2.3 million/uL, and a mean cell volume (MCV) of 73 fL. Intersetingly, melenic stools in her colostomy bag were initially attributed to iron supplementation, until further investigations via EGD and colonoscopy revealed colossal AVMs in the cecum (Figure 1). Treatment entailed holding aspirin and initiating hydroxyurea therapy at 2g/day, which escalated to 3g/day and intravenous iron sucrose was administered. Astonishingly, within just five days, her platelet count stabilized at 1.7 million/uL. Further analysis disclosed a ristocetin cofactor activity of Von Willebrand factor (VWF:RCo)/Von Willebrand Factor Antigen (VWF:Ag) ratio of 0.37, indicative of Von Willebrand disease (VWD) type 2. Upon successful discharge, the patient's platelet count further decreased to 836,000/uL during a follow-up clinic visit.
Discussion: Within the kingdom of MPNs, thrombosis reigns supreme, affecting approximately 20% of patients. While thrombosis predominates, the paradoxical risk of hemorrhage occurs with platelet counts exceeding 1 million/uL. A theory postulates with extreme thrombocytosis ( >1 million/uL) results in excessive absorption of von-Willebrand multimers on platelet membranes, elevating the risk of bleeding. First-line therapy when platelet counts surpass 1.5 million/uL is hydroxyurea. Individuals with >1 million/uL platelets should undergo a-vWD testing, and with negative results, low-dose aspirin therapy may be offered. Conversely, when the platelet count dips below 1 million/uL, the risk of thrombosis heightens, mandating aspirin therapy irrespective of a-vWD status. In our case, the patient experienced a profound response in platelet reduction and resolution of GIB through hydroxyurea cytoreduction, coupled with the discontinuation of aspirin therapy.

Disclosures:
Karan B. Singh, MD1, Mary C. Marshall, MD2. P2087 - Conquering Millions of Platelets: Hydroxyurea's Cytoreduction Cures Gastrointestinal Bleeding, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of South Alabama, Mobile, AL; 2USA Health University Hospital, Mobile, AL
Introduction: Essential thrombocythemia (ET), a myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN), presents with a platelet count of >450,000/uL and encompasses a diverse range of clinical manifestations. Notably, platelet counts >1,000,000/uL are associated with a heightened bleeding risk, while counts < 1,000,000/uL predispose thrombotic events. In this case, we demonstrate ET resulting in lower gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) caused by arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
Case Description/Methods: An 84-year-old female patient afflicted by JAK2 V617F positive, BCR-ABL1 negative essential thrombocythemia, iron deficiency anemia, and stercoral colitis necessitating colostomy was admitted for fatigue. Labs unveiled a hemoglobin (Hb) of 8.6g/dL, platelet count of 2.3 million/uL, and a mean cell volume (MCV) of 73 fL. Intersetingly, melenic stools in her colostomy bag were initially attributed to iron supplementation, until further investigations via EGD and colonoscopy revealed colossal AVMs in the cecum (Figure 1). Treatment entailed holding aspirin and initiating hydroxyurea therapy at 2g/day, which escalated to 3g/day and intravenous iron sucrose was administered. Astonishingly, within just five days, her platelet count stabilized at 1.7 million/uL. Further analysis disclosed a ristocetin cofactor activity of Von Willebrand factor (VWF:RCo)/Von Willebrand Factor Antigen (VWF:Ag) ratio of 0.37, indicative of Von Willebrand disease (VWD) type 2. Upon successful discharge, the patient's platelet count further decreased to 836,000/uL during a follow-up clinic visit.
Discussion: Within the kingdom of MPNs, thrombosis reigns supreme, affecting approximately 20% of patients. While thrombosis predominates, the paradoxical risk of hemorrhage occurs with platelet counts exceeding 1 million/uL. A theory postulates with extreme thrombocytosis ( >1 million/uL) results in excessive absorption of von-Willebrand multimers on platelet membranes, elevating the risk of bleeding. First-line therapy when platelet counts surpass 1.5 million/uL is hydroxyurea. Individuals with >1 million/uL platelets should undergo a-vWD testing, and with negative results, low-dose aspirin therapy may be offered. Conversely, when the platelet count dips below 1 million/uL, the risk of thrombosis heightens, mandating aspirin therapy irrespective of a-vWD status. In our case, the patient experienced a profound response in platelet reduction and resolution of GIB through hydroxyurea cytoreduction, coupled with the discontinuation of aspirin therapy.

Figure: Figure 1: Area of arteriovenous malformation (blue arrow) on colonoscopy.
Disclosures:
Karan Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mary Marshall indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Karan B. Singh, MD1, Mary C. Marshall, MD2. P2087 - Conquering Millions of Platelets: Hydroxyurea's Cytoreduction Cures Gastrointestinal Bleeding, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
