Monday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P2234 - Systemic Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematous Related to Golimumab: Report of a Rare Case and Review of the Literature
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Michael Gianarakis, MD
University of Illinois at Chicago
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Michael Gianarakis, MD, Elie Ghoulam, MD, Sandra Naffouj, MD, Mina Al-Awqati, MD, Itishree Trivedi, MD, MS
University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Drug-induced lupus erythematous (DILE) is a lupus-like syndrome associated with continuous drug exposure and resolves with drug discontinuation. DILE has been reported with anti-TNF agents, with most cases in infliximab, adalimumab, and etanercept use. Its pathogenesis is poorly understood. While the induction of autoantibodies in anti-TNF treated patients is common, DILE is rare, with an estimated incidence of 0.5-1% and a mean onset of 40.6 weeks.
DILE is divided into systemic (SDILE), subacute cutaneous (DISCLE) and chronic cutaneous. DISCLE is the most common, characterized by a milder photosensitive rash than idiopathic SCLE. SDILE resembles a mild form of idiopathic SLE, with arthralgias, myalgias and fever. SDILE related to anti-TNF drugs has distinct characteristics, including higher incidence in women, and is more likely to have cutaneous involvement and positive anti-dsDNA Ab. We present a case of SDILE related to golimumab in an ulcerative colitis (UC) patient. To date, no cases of golimumab-induced SDILE have been reported.
Case Description/Methods: A 25-year-old female with a 10-year history of UC and inflammatory arthritis, well-controlled with golimumab 100 mg/month for 46 months, presented with 3 weeks of severe arthralgias, painless subcutaneous nodules over her hands, oral ulcers, and fatigue. Blood count and metabolic panel were normal. Serological studies showed positive antinuclear Ab (homogenous, titer >1:2650), elevated anti-histone Ab at 3.3 U (strong positive), and positive anti-dsDNA Ab (titer 1:80). CRP, anti-Ro, anti-La, anti-RNP, anti-Smith antibodies, C3 and C4 levels were normal. Our patient was diagnosed with DILE related to golimumab and commenced on prednisone 10 mg/daily. Golimumab was discontinued. The patient was switched to 45 mg upadacitinib for management of UC and inflammatory arthritis. One month after starting treatment, the patient's arthralgias resolved.
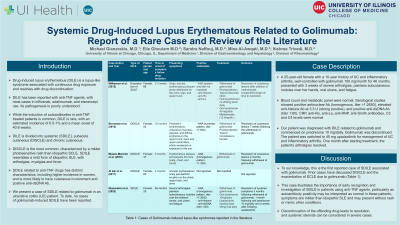
Discussion: To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of SDILE associated with golimumab. Prior cases have discussed DISCLE and the exacerbation of SCLE due to golimumab (Table 1). This case illustrates the importance of early recognition and investigation of SDILE in patients using anti-TNF agents, particularly as autoantibody positivity may be interpreted as normal in these patients, symptoms are milder than idiopathic SLE and may present without rash or mimic other conditions. Discontinuation of the offending drug leads to resolution, and systemic steroids can be considered in severe cases.
Disclosures:
Michael Gianarakis, MD, Elie Ghoulam, MD, Sandra Naffouj, MD, Mina Al-Awqati, MD, Itishree Trivedi, MD, MS. P2234 - Systemic Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematous Related to Golimumab: Report of a Rare Case and Review of the Literature, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Drug-induced lupus erythematous (DILE) is a lupus-like syndrome associated with continuous drug exposure and resolves with drug discontinuation. DILE has been reported with anti-TNF agents, with most cases in infliximab, adalimumab, and etanercept use. Its pathogenesis is poorly understood. While the induction of autoantibodies in anti-TNF treated patients is common, DILE is rare, with an estimated incidence of 0.5-1% and a mean onset of 40.6 weeks.
DILE is divided into systemic (SDILE), subacute cutaneous (DISCLE) and chronic cutaneous. DISCLE is the most common, characterized by a milder photosensitive rash than idiopathic SCLE. SDILE resembles a mild form of idiopathic SLE, with arthralgias, myalgias and fever. SDILE related to anti-TNF drugs has distinct characteristics, including higher incidence in women, and is more likely to have cutaneous involvement and positive anti-dsDNA Ab. We present a case of SDILE related to golimumab in an ulcerative colitis (UC) patient. To date, no cases of golimumab-induced SDILE have been reported.
Case Description/Methods: A 25-year-old female with a 10-year history of UC and inflammatory arthritis, well-controlled with golimumab 100 mg/month for 46 months, presented with 3 weeks of severe arthralgias, painless subcutaneous nodules over her hands, oral ulcers, and fatigue. Blood count and metabolic panel were normal. Serological studies showed positive antinuclear Ab (homogenous, titer >1:2650), elevated anti-histone Ab at 3.3 U (strong positive), and positive anti-dsDNA Ab (titer 1:80). CRP, anti-Ro, anti-La, anti-RNP, anti-Smith antibodies, C3 and C4 levels were normal. Our patient was diagnosed with DILE related to golimumab and commenced on prednisone 10 mg/daily. Golimumab was discontinued. The patient was switched to 45 mg upadacitinib for management of UC and inflammatory arthritis. One month after starting treatment, the patient's arthralgias resolved.
Discussion: To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of SDILE associated with golimumab. Prior cases have discussed DISCLE and the exacerbation of SCLE due to golimumab (Table 1). This case illustrates the importance of early recognition and investigation of SDILE in patients using anti-TNF agents, particularly as autoantibody positivity may be interpreted as normal in these patients, symptoms are milder than idiopathic SLE and may present without rash or mimic other conditions. Discontinuation of the offending drug leads to resolution, and systemic steroids can be considered in severe cases.
Disclosures:
Michael Gianarakis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Elie Ghoulam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sandra Naffouj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mina Al-Awqati indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Itishree Trivedi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Gianarakis, MD, Elie Ghoulam, MD, Sandra Naffouj, MD, Mina Al-Awqati, MD, Itishree Trivedi, MD, MS. P2234 - Systemic Drug-Induced Lupus Erythematous Related to Golimumab: Report of a Rare Case and Review of the Literature, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
