Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P2290 - Racial Disparities in All-Cause Inpatient Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in the United States: How Important Is Race?
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Ramaswamy Sundararajan, MBBS
Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Presenting Author(s)
Dushyant Singh. Dahiya, MD1, Ramaswamy Sundararajan, MBBS2, Saurabh Chandan, MD3, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD4, Muhammad Aziz, MD5, Andrew Canakis, DO6, Daryl Ramai, MD7, Jay Bapaye, MBBS, MD8, Babu Mohan, MD, MS9, Amandeep Singh, MD10, Chin-I Cheng, PhD11, Sumant Inamdar, MD12, Madhusudhan R.. Sanaka, MD10, Neil Sharma, MD13, Mohammad Al-Haddad, MD14
1University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 2Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA; 3Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE; 4University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 5University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 6University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD; 7University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 8Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY; 9University of Utah Health School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 10Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 11Central Michigan University, Mount Pleasant, MI; 12University of Arkansas, Toledo, OH; 13Parkview Health, Fort Wayne, IN; 14Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN
Introduction: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has evolved into a vital endoscopic technique for managing numerous pancreaticobiliary disorders. Studies have reported higher rates of adverse outcomes and post-ERCP complications in ethnic minorities, making race an important risk factor for ERCP utilization. In this study, we aimed to identify the influence of race on clinical outcomes of all-cause inpatient ERCPs in the United States (US).
Methods: We used the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) to identify all adult (≥18 years) hospitalizations that underwent ERCP in the US from 2007–2019. The study population was further subdivided into 3 groups based on race (Whites, Blacks, and Hispanics). Hospitalization characteristics and clinical outcomes were highlighted and compared. p-values ≤0.05 were considered statistically significant.
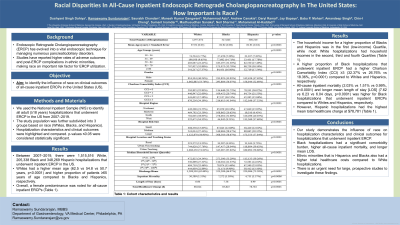
Results: Between 2007–2019, there were 1,515,516 White, 205,338 Black and 348,269 Hispanic hospitalizations that underwent inpatient ERCP in the US. Whites had a higher mean age (62.5 vs 54.8 vs 50.7 years, p< 0.0001) and higher proportion of patients ≥65 years of age compared to Blacks and Hispanics, respectively. Overall, a female predominance was noted for all-cause inpatient ERCPs (Table 1).
The household income for a higher proportion of Blacks and Hispanics was in the first (low-income) Quartile, while most White hospitalizations had household incomes in the second, third and fourth Quartiles (Table 1). A higher proportion of Black hospitalizations that underwent inpatient ERCP had a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) ≥3 (32.37% vs 26.76% vs 18.36%, p< 0.0001) compared to Whites and Hispanics, respectively.
All-cause inpatient mortality (2.03% vs 1.51% vs 0.99%, p< 0.0001) and longer mean length of stay [LOS] (7.62 vs 6.23 vs 6.04 days, p< 0.0001) was higher for Black hospitalizations that underwent inpatient ERCPs compared to Whites and Hispanics, respectively. However, Hispanic hospitalizations had the highest mean total healthcare charge at $80,569 (Table 1).
Discussion: Our study demonstrates the influence of race on hospitalization characteristics and clinical outcomes for hospitalizations that underwent inpatient ERCP. Black hospitalizations had a significant comorbidity burden, higher all-cause inpatient mortality, and longer mean LOS. Ethnic minorities i.e. Hispanics and Blacks also had a higher total healthcare charge compare to White hospitalizations. There is an urgent need for large, prospective studies to investigate these findings.
Disclosures:
Dushyant Singh. Dahiya, MD1, Ramaswamy Sundararajan, MBBS2, Saurabh Chandan, MD3, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD4, Muhammad Aziz, MD5, Andrew Canakis, DO6, Daryl Ramai, MD7, Jay Bapaye, MBBS, MD8, Babu Mohan, MD, MS9, Amandeep Singh, MD10, Chin-I Cheng, PhD11, Sumant Inamdar, MD12, Madhusudhan R.. Sanaka, MD10, Neil Sharma, MD13, Mohammad Al-Haddad, MD14. P2290 - Racial Disparities in All-Cause Inpatient Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in the United States: How Important Is Race?, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Kansas School of Medicine, Kansas City, KS; 2Corporal Michael J. Crescenz VA Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA; 3Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE; 4University of Toledo Medical Center, Toledo, OH; 5University of Toledo, Toledo, OH; 6University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD; 7University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 8Rochester General Hospital, Rochester, NY; 9University of Utah Health School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 10Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH; 11Central Michigan University, Mount Pleasant, MI; 12University of Arkansas, Toledo, OH; 13Parkview Health, Fort Wayne, IN; 14Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN
Introduction: Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has evolved into a vital endoscopic technique for managing numerous pancreaticobiliary disorders. Studies have reported higher rates of adverse outcomes and post-ERCP complications in ethnic minorities, making race an important risk factor for ERCP utilization. In this study, we aimed to identify the influence of race on clinical outcomes of all-cause inpatient ERCPs in the United States (US).
Methods: We used the National Inpatient Sample (NIS) to identify all adult (≥18 years) hospitalizations that underwent ERCP in the US from 2007–2019. The study population was further subdivided into 3 groups based on race (Whites, Blacks, and Hispanics). Hospitalization characteristics and clinical outcomes were highlighted and compared. p-values ≤0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results: Between 2007–2019, there were 1,515,516 White, 205,338 Black and 348,269 Hispanic hospitalizations that underwent inpatient ERCP in the US. Whites had a higher mean age (62.5 vs 54.8 vs 50.7 years, p< 0.0001) and higher proportion of patients ≥65 years of age compared to Blacks and Hispanics, respectively. Overall, a female predominance was noted for all-cause inpatient ERCPs (Table 1).
The household income for a higher proportion of Blacks and Hispanics was in the first (low-income) Quartile, while most White hospitalizations had household incomes in the second, third and fourth Quartiles (Table 1). A higher proportion of Black hospitalizations that underwent inpatient ERCP had a higher Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) ≥3 (32.37% vs 26.76% vs 18.36%, p< 0.0001) compared to Whites and Hispanics, respectively.
All-cause inpatient mortality (2.03% vs 1.51% vs 0.99%, p< 0.0001) and longer mean length of stay [LOS] (7.62 vs 6.23 vs 6.04 days, p< 0.0001) was higher for Black hospitalizations that underwent inpatient ERCPs compared to Whites and Hispanics, respectively. However, Hispanic hospitalizations had the highest mean total healthcare charge at $80,569 (Table 1).
Discussion: Our study demonstrates the influence of race on hospitalization characteristics and clinical outcomes for hospitalizations that underwent inpatient ERCP. Black hospitalizations had a significant comorbidity burden, higher all-cause inpatient mortality, and longer mean LOS. Ethnic minorities i.e. Hispanics and Blacks also had a higher total healthcare charge compare to White hospitalizations. There is an urgent need for large, prospective studies to investigate these findings.
Disclosures:
Dushyant Dahiya indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ramaswamy Sundararajan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saurabh Chandan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manesh Kumar Gangwani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhammad Aziz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Canakis indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Daryl Ramai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jay Bapaye indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Babu Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amandeep Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chin-I Cheng indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sumant Inamdar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhusudhan Sanaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neil Sharma: Boston Scientific – Consultant. Mauna Kea – Consultant. Medtronic – Consultant. Olympus – Consultant. Steria – Consultant.
Mohammad Al-Haddad: Amplified Sciences – Grant/Research Support. Creatics, LLC – Grant/Research Support. Interpace diagnostics – Consultant.
Dushyant Singh. Dahiya, MD1, Ramaswamy Sundararajan, MBBS2, Saurabh Chandan, MD3, Manesh Kumar Gangwani, MD4, Muhammad Aziz, MD5, Andrew Canakis, DO6, Daryl Ramai, MD7, Jay Bapaye, MBBS, MD8, Babu Mohan, MD, MS9, Amandeep Singh, MD10, Chin-I Cheng, PhD11, Sumant Inamdar, MD12, Madhusudhan R.. Sanaka, MD10, Neil Sharma, MD13, Mohammad Al-Haddad, MD14. P2290 - Racial Disparities in All-Cause Inpatient Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in the United States: How Important Is Race?, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
