Monday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P2629 - Duodenal Neoplasms in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO
Methodist Dallas Medical Center
Dallas, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO1, Nihal Ijaz Khan, MD2, Mahir Qureshi, MD3, Shahab R. Khan, MBBS4, Talia F.. Malik, MD5, Smit S.. Deliwala, MD6, Rami Musallam, MD7, Noor Fatima, MD8, Saurabh Chandan, MD9, Babu Mohan, MD, MS10, Douglas G. Adler, MD11
1Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 2AdventHealth, Orlando, FL; 3Cooper University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 4Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 5Chicago Medical School at Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago, IL; 6Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 7Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH; 8Nazareth Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 9Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE; 10University of Utah Health School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 11Center for Advanced Therapeutic (CATE), Centura Health, Porter Adventist Hospital, Peak Gastroenterology, Denver, CO
Introduction: While the association between Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) and an increased risk of colon cancer is well known, recent literature has highlighted an increased incidence of extracolonic cancer in patients with FAP. The mechanism behind this increased incidence is still unclear. In these patients, duodenal cancer is the second most common cause of death. This meta-analysis reports on the pooled rates of duodenal dysplasia in patients with FAP.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature from MEDLINE, EMBASE and Scopus was conducted from inception to October 2022, for studies reporting on upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopic findings (polyps and neoplasms) in patients with FAP. Outcome of interest was the pooled proportion of duodenal neoplasms in patients with FAP. Standard meta-analysis methods were followed using the random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2% statistics.
Results: Eighteen studies were included that reported on 1,357 patients with FAP. Of these patients, 51.7% were male and 48.3% were female, with an average age of 34 years old. All studies were retrospective in nature, with one being a multi-center study and the remaining seventeen being single-center studies.
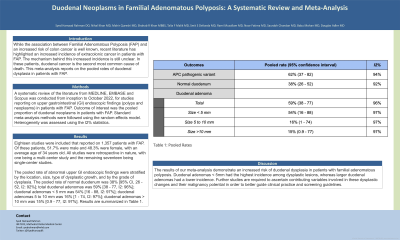
The pooled rate of abnormal upper GI endoscopic findings were stratified by the location, size, type of dysplastic growth, and by the grade of dysplasia. The pooled rate of normal duodenum was 38% [95% CI, 26 - 52, I2: 92%]; total duodenal adenomas was 59% [38 - 77, I2: 96%]; duodenal adenomas < 5 mm was 54% [16 - 88, I2: 97%]; duodenal adenomas 5 to 10 mm was 16% [1 - 74, I2: 97%]; duodenal adenomas > 10 mm was 15% [0.9 - 77, I2: 97%]. Results are summarized in Table 1.
Discussion: The results of our meta-analysis demonstrate an increased risk of duodenal dysplasia in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Duodenal adenomas < 5mm had the highest incidence among dysplastic lesions, whereas larger duodenal adenomas had a lower incidence. Further studies are required to ascertain contributing variables involved in these dysplastic changes and their malignancy potential in order to better guide clinical practice and screening guidelines.

Disclosures:
Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO1, Nihal Ijaz Khan, MD2, Mahir Qureshi, MD3, Shahab R. Khan, MBBS4, Talia F.. Malik, MD5, Smit S.. Deliwala, MD6, Rami Musallam, MD7, Noor Fatima, MD8, Saurabh Chandan, MD9, Babu Mohan, MD, MS10, Douglas G. Adler, MD11. P2629 - Duodenal Neoplasms in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Methodist Dallas Medical Center, Dallas, TX; 2AdventHealth, Orlando, FL; 3Cooper University Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 4Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA; 5Chicago Medical School at Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science, North Chicago, IL; 6Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA; 7Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, Cleveland, OH; 8Nazareth Hospital, Philadelphia, PA; 9Creighton University School of Medicine, Omaha, NE; 10University of Utah Health School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 11Center for Advanced Therapeutic (CATE), Centura Health, Porter Adventist Hospital, Peak Gastroenterology, Denver, CO
Introduction: While the association between Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) and an increased risk of colon cancer is well known, recent literature has highlighted an increased incidence of extracolonic cancer in patients with FAP. The mechanism behind this increased incidence is still unclear. In these patients, duodenal cancer is the second most common cause of death. This meta-analysis reports on the pooled rates of duodenal dysplasia in patients with FAP.
Methods: A systematic review of the literature from MEDLINE, EMBASE and Scopus was conducted from inception to October 2022, for studies reporting on upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopic findings (polyps and neoplasms) in patients with FAP. Outcome of interest was the pooled proportion of duodenal neoplasms in patients with FAP. Standard meta-analysis methods were followed using the random-effects model. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2% statistics.
Results: Eighteen studies were included that reported on 1,357 patients with FAP. Of these patients, 51.7% were male and 48.3% were female, with an average age of 34 years old. All studies were retrospective in nature, with one being a multi-center study and the remaining seventeen being single-center studies.
The pooled rate of abnormal upper GI endoscopic findings were stratified by the location, size, type of dysplastic growth, and by the grade of dysplasia. The pooled rate of normal duodenum was 38% [95% CI, 26 - 52, I2: 92%]; total duodenal adenomas was 59% [38 - 77, I2: 96%]; duodenal adenomas < 5 mm was 54% [16 - 88, I2: 97%]; duodenal adenomas 5 to 10 mm was 16% [1 - 74, I2: 97%]; duodenal adenomas > 10 mm was 15% [0.9 - 77, I2: 97%]. Results are summarized in Table 1.
Discussion: The results of our meta-analysis demonstrate an increased risk of duodenal dysplasia in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Duodenal adenomas < 5mm had the highest incidence among dysplastic lesions, whereas larger duodenal adenomas had a lower incidence. Further studies are required to ascertain contributing variables involved in these dysplastic changes and their malignancy potential in order to better guide clinical practice and screening guidelines.

Figure: Table 1: Pooled Rates
Disclosures:
Syed Hamaad Rahman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nihal Ijaz Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahir Qureshi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shahab Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Talia Malik indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Smit Deliwala indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rami Musallam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Noor Fatima indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Saurabh Chandan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Babu Mohan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Douglas Adler indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Syed Hamaad Rahman, DO1, Nihal Ijaz Khan, MD2, Mahir Qureshi, MD3, Shahab R. Khan, MBBS4, Talia F.. Malik, MD5, Smit S.. Deliwala, MD6, Rami Musallam, MD7, Noor Fatima, MD8, Saurabh Chandan, MD9, Babu Mohan, MD, MS10, Douglas G. Adler, MD11. P2629 - Duodenal Neoplasms in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
