Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach
P2746 - PEG-Tube Conundrum: Identifying the Knowledge Gap and Creating Awareness Among Internal Medicine Residents Regarding Percutaneous Endoscopy Gastrostomy Tube Placement
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

David Okuampa, MD
LSU Health Sciences Center
Shreveport, LA
Presenting Author(s)
David Okuampa, MD, Nazar Hafiz, , Maryam Mubashir, MD, Sudha Pandit, MD, Aditya Vyas,
LSU Health Sciences Center, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Enteral feeding is the preferred and safest method to meet the body’s nutritional requirements in individuals with impaired oral intake. Percutaneous gastrostomy tube (PEG tube) can achieve this goal, not only safely but over extended periods of time. Between 160,000 - 200,000 gastrostomy tubes are placed endoscopically annually in the US. Complications range up to 35%. These are attributable to the lack of awareness of practitioners providing patient care. These can be avoided by identifying the knowledge gap and creating awareness regarding PEG tube care. We present a novel study highlighting the knowledge gap among the Internal Medicine Residents at a University Hospital and how a short educational session improved awareness.
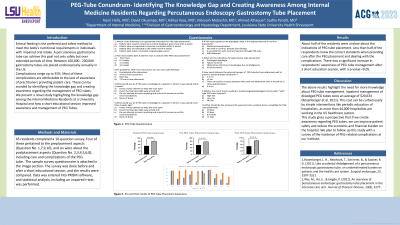
Methods: 45 residents completed a 10-question survey. Four of these pertained to the preplacement aspects (Question No. 1,7,9,10), and six were about the postplacement aspects (Question No. 2,3,4,5,6,8), including care and complications of the PEG tube. The sample survey questionnaire is attached in the image section. The survey was done before and after a short educational session, and the results were compared. Data was entered into PRISM software, and statistical analysis, including an unpaired t-test, was performed.
Results: About half of the residents were unclear about the indications of PEG tube placement. Less than half of the respondents knew the correct standards when providing care after the PEG placement and dealing with the complications. There was a significant increase in respondents' awareness of PEG tube management after a short education session, with a p-value < 0.05.
Discussion: The above results highlight the need for more knowledge about PEG tube management. Inpatient management of dislodged PEG tubes costs an average of $20,633 (Rosenberger et al. 2011). This cost can be curbed easily by simple interventions like periodic education of hospitalists, as more than 44,000 hospitalists are working in the US healthcare system.
This study gives a perspective that if we create awareness regarding PEG tubes, we can improve patient safety and reduce the economic and financial burden on the hospital. We plan to follow up this study with a survey of the incidence of PEG-related complications at our institute.

Disclosures:
David Okuampa, MD, Nazar Hafiz, , Maryam Mubashir, MD, Sudha Pandit, MD, Aditya Vyas, . P2746 - PEG-Tube Conundrum: Identifying the Knowledge Gap and Creating Awareness Among Internal Medicine Residents Regarding Percutaneous Endoscopy Gastrostomy Tube Placement, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
LSU Health Sciences Center, Shreveport, LA
Introduction: Enteral feeding is the preferred and safest method to meet the body’s nutritional requirements in individuals with impaired oral intake. Percutaneous gastrostomy tube (PEG tube) can achieve this goal, not only safely but over extended periods of time. Between 160,000 - 200,000 gastrostomy tubes are placed endoscopically annually in the US. Complications range up to 35%. These are attributable to the lack of awareness of practitioners providing patient care. These can be avoided by identifying the knowledge gap and creating awareness regarding PEG tube care. We present a novel study highlighting the knowledge gap among the Internal Medicine Residents at a University Hospital and how a short educational session improved awareness.
Methods: 45 residents completed a 10-question survey. Four of these pertained to the preplacement aspects (Question No. 1,7,9,10), and six were about the postplacement aspects (Question No. 2,3,4,5,6,8), including care and complications of the PEG tube. The sample survey questionnaire is attached in the image section. The survey was done before and after a short educational session, and the results were compared. Data was entered into PRISM software, and statistical analysis, including an unpaired t-test, was performed.
Results: About half of the residents were unclear about the indications of PEG tube placement. Less than half of the respondents knew the correct standards when providing care after the PEG placement and dealing with the complications. There was a significant increase in respondents' awareness of PEG tube management after a short education session, with a p-value < 0.05.
Discussion: The above results highlight the need for more knowledge about PEG tube management. Inpatient management of dislodged PEG tubes costs an average of $20,633 (Rosenberger et al. 2011). This cost can be curbed easily by simple interventions like periodic education of hospitalists, as more than 44,000 hospitalists are working in the US healthcare system.
This study gives a perspective that if we create awareness regarding PEG tubes, we can improve patient safety and reduce the economic and financial burden on the hospital. We plan to follow up this study with a survey of the incidence of PEG-related complications at our institute.

Figure: PEG Tube Questionnaire with Pre and Post-Educational Results
**** Indicate a p-value less than 0.05
**** Indicate a p-value less than 0.05
Disclosures:
David Okuampa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nazar Hafiz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Maryam Mubashir indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sudha Pandit indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aditya Vyas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
David Okuampa, MD, Nazar Hafiz, , Maryam Mubashir, MD, Sudha Pandit, MD, Aditya Vyas, . P2746 - PEG-Tube Conundrum: Identifying the Knowledge Gap and Creating Awareness Among Internal Medicine Residents Regarding Percutaneous Endoscopy Gastrostomy Tube Placement, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
