Monday Poster Session
Category: Stomach
P2759 - Vonoprazan May Increase the Risk of Fractures
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
.jpg)
Nishant Aggarwal, MD
William Beaumont Hospital-Royal Oak
Royal Oak, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Nishant Aggarwal, MD1, Achintya D. Singh, MD, MBBS2, Tusar K.. Desai, MD3
1William Beaumont Hospital-Royal Oak, Royal Oak, MI; 2MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH; 3Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital, Royal Oak, MI
Introduction: Potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCABs) are novel and more potent inhibitors of gastric acid secretion than proton pump inhibitors (PPI). A recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 1,024 patients reported almost 3 fold higher incidence of fractures with vonoprazan vs PPI.1 We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the risk of fracture with vonoprazan vs PPIs.
Methods: We queried the databases of PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library from 2013 to March 20, 2023 for RCTs that compared vonoprazan vs PPI treatment. The primary outcome was the relative risk of fracture in vonoprazan group vs PPI. Statistical analysis was performed in STATA.
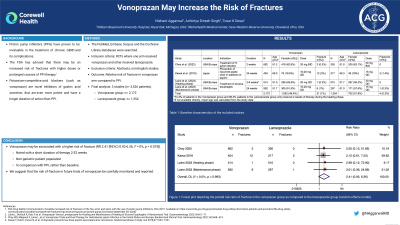
Results: Only 3 RCTs reported the incidence of fracture in the PPI or vonoprazan groups (table 1).1–3 There were 3,526 patients across three studies- 2,172 in the vonoprazan group and 1,354 in the lansoprazole group. The duration of treatment ranged from 2-32 weeks. Using the random effects model, the pooled relative risk (RR) of fracture with vonoprazan was 2.41 (95%CI 0.92-6.36, I2= 0%, figure 1). Repeating the same analysis using a fixed effects model, RR 2.8 (95%CI 0.98-8.09, I2 = 0%) was obtained. In the RCT by Laine et al. after a 2-8 week healing phase, patients were re-randomized into a 24 week maintenance phase of either vonoprazan or lansoprazole. Therefore, there is a 50% chance that the one patient who developed a fracture on lansoprazole in the maintenance phase received vonoprazan in the healing phase.1
Discussion: The higher risk of fracture with vonoprazan was just short of statistical significance, but this was observed with < 32 weeks of vonoprazan in a non-geriatric patient population. Further, this was not in comparison to baseline but rather to PPI, which themselves carry an FDA warning regarding possible increased risk of fracture. The risk of fracture in future trials of vonoprazan must be carefully monitored and reported.
References:
1. Laine L, DeVault K, Katz P, et al. Vonoprazan Versus Lansoprazole for Healing and Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis: A Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology 2023;164:61–71.
2. Chey WD, Mégraud F, Laine L, et al. Vonoprazan Triple and Dual Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Infection in the United States and Europe: Randomized Clinical Trial. Gastroenterology 2022;163:608–619.
3. Kawai T, Oda K, Funao N, et al. Vonoprazan prevents low-dose aspirin-associated ulcer recurrence: randomised phase 3 study. Gut 2018;67:1033–1041.

Disclosures:
Nishant Aggarwal, MD1, Achintya D. Singh, MD, MBBS2, Tusar K.. Desai, MD3. P2759 - Vonoprazan May Increase the Risk of Fractures, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1William Beaumont Hospital-Royal Oak, Royal Oak, MI; 2MetroHealth Medical Center, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH; 3Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital, Royal Oak, MI
Introduction: Potassium-competitive acid blockers (PCABs) are novel and more potent inhibitors of gastric acid secretion than proton pump inhibitors (PPI). A recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 1,024 patients reported almost 3 fold higher incidence of fractures with vonoprazan vs PPI.1 We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the risk of fracture with vonoprazan vs PPIs.
Methods: We queried the databases of PubMed, Embase, Scopus, and the Cochrane Library from 2013 to March 20, 2023 for RCTs that compared vonoprazan vs PPI treatment. The primary outcome was the relative risk of fracture in vonoprazan group vs PPI. Statistical analysis was performed in STATA.
Results: Only 3 RCTs reported the incidence of fracture in the PPI or vonoprazan groups (table 1).1–3 There were 3,526 patients across three studies- 2,172 in the vonoprazan group and 1,354 in the lansoprazole group. The duration of treatment ranged from 2-32 weeks. Using the random effects model, the pooled relative risk (RR) of fracture with vonoprazan was 2.41 (95%CI 0.92-6.36, I2= 0%, figure 1). Repeating the same analysis using a fixed effects model, RR 2.8 (95%CI 0.98-8.09, I2 = 0%) was obtained. In the RCT by Laine et al. after a 2-8 week healing phase, patients were re-randomized into a 24 week maintenance phase of either vonoprazan or lansoprazole. Therefore, there is a 50% chance that the one patient who developed a fracture on lansoprazole in the maintenance phase received vonoprazan in the healing phase.1
Discussion: The higher risk of fracture with vonoprazan was just short of statistical significance, but this was observed with < 32 weeks of vonoprazan in a non-geriatric patient population. Further, this was not in comparison to baseline but rather to PPI, which themselves carry an FDA warning regarding possible increased risk of fracture. The risk of fracture in future trials of vonoprazan must be carefully monitored and reported.
References:
1. Laine L, DeVault K, Katz P, et al. Vonoprazan Versus Lansoprazole for Healing and Maintenance of Healing of Erosive Esophagitis: A Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology 2023;164:61–71.
2. Chey WD, Mégraud F, Laine L, et al. Vonoprazan Triple and Dual Therapy for Helicobacter pylori Infection in the United States and Europe: Randomized Clinical Trial. Gastroenterology 2022;163:608–619.
3. Kawai T, Oda K, Funao N, et al. Vonoprazan prevents low-dose aspirin-associated ulcer recurrence: randomised phase 3 study. Gut 2018;67:1033–1041.

Figure: Figure 1: Forest plot depicting the pooled risk ratio of fracture in the vonoprazan group as compared to the lansoprazole group
Disclosures:
Nishant Aggarwal indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Achintya Singh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tusar Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nishant Aggarwal, MD1, Achintya D. Singh, MD, MBBS2, Tusar K.. Desai, MD3. P2759 - Vonoprazan May Increase the Risk of Fractures, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
