Monday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P2525 - Metastatic Liver Abscess Secondary to Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Tooba Laeeq, MD
University of Nevada, Las Vegas
Henderson, NV
Presenting Author(s)
Tooba Laeeq, MD1, Kyaw Min Tun, DO2, Zahra Dossaji, DO2, Shanon McCarthy, DO3
1University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Henderson, NV; 2Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at UNLV, Las Vegas, NV; 3University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: HvKp induced liver abscess is an emerging cause of pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) worldwide requiring immediate attention. It can cause multi-organ infection and is associated with high morbidity and mortality in immunocompetent hosts. We present a unique case initially presenting as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) unmasking itself with septic emboli to the lungs and the brain secondary to hvKp PLA.
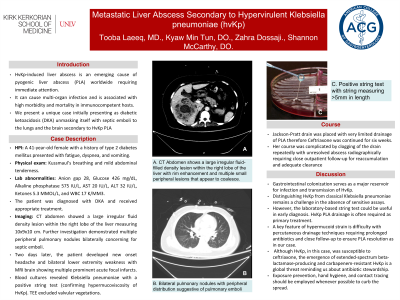
Case Description/Methods: 41 year old female with history of type 2 diabetes mellitus presented with fatigue, dyspnea and vomiting. Physical exam was significant for Kussmaul breathing and mild abdominal tenderness. Lab abnormalities included anion gap 28, Glucose 426 mg/dL, Alkaline phosphatase 575 IU/L, AST 20 IU/L, ALT 32 IU/L, Ketones 5.3 MMOL/L, and WBC 17 K/MM3. Patient was diagnosed with DKA and received appropriate treatment. CT abdomen showed a large irregular fluid density lesion within the right lobe of the liver measuring 10x9x10 cm. Further investigation demonstrated multiple peripheral pulmonary nodules bilaterally concerning for septic emboli. Two days later, patient developed new onset headache and bilateral lower extremity weakness with MRI brain showing multiple prominent acute focal infarcts. Blood cultures revealed Klebsiella pneumoniae with positive string test (confirming hypermucoviscosity of hvKp). TEE excluded valvular vegetations. Jackson-pratt drain was placed with very limited drainage of PLA therefore Ceftriaxone was continued for six weeks. Her course was complicated by clogging of the drain repeatedly with unresolved abscess radiographically requiring close outpatient follow up for reaccumulation and adequate clearance.
Discussion: Gastrointestinal colonization serves as a major reservoir for infection and transmission of hvKp. Distinguishing hvKp from classical Klebsiella pneumoniae remains a challenge in the absence of sensitive assays. However, the laboratory-based string test could be useful in early diagnosis. HvKp PLA drainage is often required as primary treatment. A key feature of hyper mucoid strain is difficulty with percutaneous drainage techniques requiring prolonged antibiotics and close follow up to ensure PLA resolution as in our case. Although hvKp in this case was susceptible to ceftriaxone, emergence of extended spectrum beta lactamase producing and carbapenem resistant hvKp is a global threat reminding us about antibiotic stewardship. Exposure prevention, hand hygiene and contact tracing should be employed whenever possible to curb the spread.

Disclosures:
Tooba Laeeq, MD1, Kyaw Min Tun, DO2, Zahra Dossaji, DO2, Shanon McCarthy, DO3. P2525 - Metastatic Liver Abscess Secondary to Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Henderson, NV; 2Kirk Kerkorian School of Medicine at UNLV, Las Vegas, NV; 3University of Nevada, Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV
Introduction: HvKp induced liver abscess is an emerging cause of pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) worldwide requiring immediate attention. It can cause multi-organ infection and is associated with high morbidity and mortality in immunocompetent hosts. We present a unique case initially presenting as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) unmasking itself with septic emboli to the lungs and the brain secondary to hvKp PLA.
Case Description/Methods: 41 year old female with history of type 2 diabetes mellitus presented with fatigue, dyspnea and vomiting. Physical exam was significant for Kussmaul breathing and mild abdominal tenderness. Lab abnormalities included anion gap 28, Glucose 426 mg/dL, Alkaline phosphatase 575 IU/L, AST 20 IU/L, ALT 32 IU/L, Ketones 5.3 MMOL/L, and WBC 17 K/MM3. Patient was diagnosed with DKA and received appropriate treatment. CT abdomen showed a large irregular fluid density lesion within the right lobe of the liver measuring 10x9x10 cm. Further investigation demonstrated multiple peripheral pulmonary nodules bilaterally concerning for septic emboli. Two days later, patient developed new onset headache and bilateral lower extremity weakness with MRI brain showing multiple prominent acute focal infarcts. Blood cultures revealed Klebsiella pneumoniae with positive string test (confirming hypermucoviscosity of hvKp). TEE excluded valvular vegetations. Jackson-pratt drain was placed with very limited drainage of PLA therefore Ceftriaxone was continued for six weeks. Her course was complicated by clogging of the drain repeatedly with unresolved abscess radiographically requiring close outpatient follow up for reaccumulation and adequate clearance.
Discussion: Gastrointestinal colonization serves as a major reservoir for infection and transmission of hvKp. Distinguishing hvKp from classical Klebsiella pneumoniae remains a challenge in the absence of sensitive assays. However, the laboratory-based string test could be useful in early diagnosis. HvKp PLA drainage is often required as primary treatment. A key feature of hyper mucoid strain is difficulty with percutaneous drainage techniques requiring prolonged antibiotics and close follow up to ensure PLA resolution as in our case. Although hvKp in this case was susceptible to ceftriaxone, emergence of extended spectrum beta lactamase producing and carbapenem resistant hvKp is a global threat reminding us about antibiotic stewardship. Exposure prevention, hand hygiene and contact tracing should be employed whenever possible to curb the spread.

Figure: A. Bilateral pulmonary nodules with peripheral distribution suggestive of pulmonary emboli
B. CT Abdomen showing large irregular fluid fluid density lesion within the right lobe of the liver with rim enhancement and multiple small peripheral lesions which appear to coalesce.
C. Positive string test with string measuring >5mm in length
B. CT Abdomen showing large irregular fluid fluid density lesion within the right lobe of the liver with rim enhancement and multiple small peripheral lesions which appear to coalesce.
C. Positive string test with string measuring >5mm in length
Disclosures:
Tooba Laeeq indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kyaw Min Tun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zahra Dossaji indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shanon McCarthy indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tooba Laeeq, MD1, Kyaw Min Tun, DO2, Zahra Dossaji, DO2, Shanon McCarthy, DO3. P2525 - Metastatic Liver Abscess Secondary to Hypervirulent Klebsiella Pneumoniae, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
