Monday Poster Session
Category: Interventional Endoscopy
P2317 - Hemorrhagic Pancreatic Pseudocyst Managed With Endoscopic Cystogastrostomy With Great Outcome
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Kazi N. Khan, MD
Aurora Healthcare
Milwaukee, WI
Presenting Author(s)
Kazi Khan, MD1, Abdulaziz Siddiqui, MD1, Robert Marker, DO1, Mohammad Aasim Khan, MBBS2, Ahmed Akhter, MD1
1Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI; 2Khyber Medical College & Advocate Health Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center, Milwaukee, WI
Introduction:
Hemorrhagic pancreatitis, although rare, is due to recurrent pancreatitis and pseudocyst formation. Hemorrhagic pseudocysts can be extremely painful and life-threatening. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guided techniques have now become the standard of care, offering minimally invasive options such as cystogastrostomy. Our case discusses the successful management of a patient with a hemorrhagic pseudocyst through endoscopic cystogastrostomy with stent placement.
Case Description/Methods:
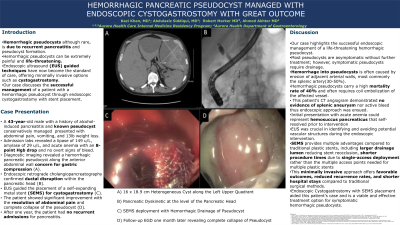
A 43-year-old male with a history of alcohol-induced pancreatitis presented with abdominal pain, vomiting, and weight loss. He had a known history of pseudocysts managed conservatively in previous hospitalizations. Admission labs revealed a lipase of 149 u/L, amylase of 29 u/L, and acute anemia with an 8-point Hgb drop and no overt signs of bleed. Diagnostic imaging revealed a hemorrhagic pancreatic pseudocyst along the anterior abdominal wall concern for gastric compression (A). Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography confirmed ductal disruption within the pancreatic head (B). EUS guided the placement of a self-expanding metal stent (SEMS) for cystogastrostomy (C). The patient showed significant improvement with the resolution of abdominal pain and complete collapse of the pseudocyst (D). After one year, the patient had no recurrent admissions for pancreatitis.
Discussion:Our case highlights the successful endoscopic management of a life-threatening hemorrhagic pseudocyst. Hemorrhage into pseudocysts is often caused by erosion of adjacent arterial walls, most commonly the splenic artery. Hemorrhagic pseudocysts carry a high mortality rate and may require coil embolization of the affected vessel. This patient's CT-angiogram demonstrated no evidence of splenic aneurysm nor active bleeding. EUS was crucial in identifying and avoiding potential vascular structures during the endoscopic intervention. This minimally invasive approach offers favorable outcomes, reduced recurrence rates, and shorter hospital stays compared to traditional surgical methods. Endoscopic cystogastrostomy with SEMS placement aided this patient's case and is a viable and effective treatment option for symptomatic hemorrhagic pseudocysts.
1Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI; 2Khyber Medical College & Advocate Health Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center, Milwaukee, WI
Introduction:
Hemorrhagic pancreatitis, although rare, is due to recurrent pancreatitis and pseudocyst formation. Hemorrhagic pseudocysts can be extremely painful and life-threatening. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guided techniques have now become the standard of care, offering minimally invasive options such as cystogastrostomy. Our case discusses the successful management of a patient with a hemorrhagic pseudocyst through endoscopic cystogastrostomy with stent placement.
Case Description/Methods:
A 43-year-old male with a history of alcohol-induced pancreatitis presented with abdominal pain, vomiting, and weight loss. He had a known history of pseudocysts managed conservatively in previous hospitalizations. Admission labs revealed a lipase of 149 u/L, amylase of 29 u/L, and acute anemia with an 8-point Hgb drop and no overt signs of bleed. Diagnostic imaging revealed a hemorrhagic pancreatic pseudocyst along the anterior abdominal wall concern for gastric compression (A). Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography confirmed ductal disruption within the pancreatic head (B). EUS guided the placement of a self-expanding metal stent (SEMS) for cystogastrostomy (C). The patient showed significant improvement with the resolution of abdominal pain and complete collapse of the pseudocyst (D). After one year, the patient had no recurrent admissions for pancreatitis.
Discussion:
Our case highlights the successful endoscopic management of a life-threatening hemorrhagic pseudocyst. Hemorrhage into pseudocysts is often caused by erosion of adjacent arterial walls, most commonly the splenic artery. Hemorrhagic pseudocysts carry a high mortality rate and may require coil embolization of the affected vessel. This patient's CT-angiogram demonstrated no evidence of splenic aneurysm nor active bleeding. EUS was crucial in identifying and avoiding potential vascular structures during the endoscopic intervention. This minimally invasive approach offers favorable outcomes, reduced recurrence rates, and shorter hospital stays compared to traditional surgical methods. Endoscopic cystogastrostomy with SEMS placement aided this patient's case and is a viable and effective treatment option for symptomatic hemorrhagic pseudocysts.

Figure: A) 16 x 18.9 cm heterogeneous cyst along the left upper quadrant
B) Pancreatic dyskinetic at the level of the pancreatic head
C) SEMS deployment with hemorrhagic drainage of pseudocyst
D) Follow-up EGD one month later revealing complete collapse of pseudocyst
Disclosures:
Kazi Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships. Abdulaziz Siddiqui indicated no relevant financial relationships. Robert Marker indicated no relevant financial relationships. Mohammad Aasim Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships. Ahmed Akhter indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kazi Khan, MD1, Abdulaziz Siddiqui, MD1, Robert Marker, DO1, Mohammad Aasim Khan, MBBS2, Ahmed Akhter, MD1. P2317 - Hemorrhagic Pancreatic Pseudocyst Managed With Endoscopic Cystogastrostomy With Great Outcome, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

B) Pancreatic dyskinetic at the level of the pancreatic head
C) SEMS deployment with hemorrhagic drainage of pseudocyst
D) Follow-up EGD one month later revealing complete collapse of pseudocyst
