Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3621 - Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Among Adult Patients With Active Crohn’s Disease: A Single Center Experience
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- AS
Alexander Sheiban, MD
Blacktown Hospital
Blacktown, New South Wales, Australia
Presenting Author(s)
Alexander Sheiban, MD, Brook Maguire, BSN, Mark Ghali, MD, Nirodhi Premachandra, MD, Khizar Niazi, MD, Brandon Baraty, MBBS, Nikola Mitrev, MBBS, MPhil, Viraj Kariyawasam, MBBS, PhD
Blacktown Hospital, Blacktown, New South Wales, Australia
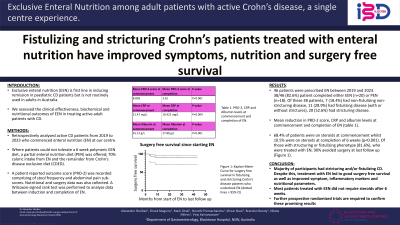
Introduction: Current medical management for Crohn’s disease (CD) utilises corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to induce and maintain remission. Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) is first line in inducing remission in paediatric CD patients but is not routinely used in adults in Australia. We assessed the clinical effectiveness, biochemical and nutritional outcomes of EEN in treating adult CD patients.
Methods: We retrospectively analysed active CD patients from 2019 to 2023 who commenced enteral nutrition (EN) at our centre. Local protocol entails that EN patients are seen weekly for 6 weeks. Where patients could not tolerate a polymeric EEN diet, a partial enteral nutrition diet (PEN) was offered; which we defined as at least 70% caloric intake from EN and the remainder from Crohn’s disease exclusion diet (CDED). Electronic medical records were reviewed and data collected. A patient reported outcome score (PRO-2) was recorded comprising of stool frequency and abdominal pain sub-scores. Medication exposures and bowel resections within 12 months were recorded. A Wilcoxon-signed rank test was performed to analyse data between induction and completion of EN.
Results: 46 patients were prescribed EN as part of their CD management between 2019 and 2023. 38/46 (82.6%) patients completed either EEN (n=20) or PEN (n=18). Of these 38 patients, 7 (18.4%) had non-fistulising non-stricturing disease, 11 (28.9%) had fistulising disease (with or without strictures), 20 (52.6%) had stricturing disease. PRO-2 scores reduced from a mean of 8.8 (SD 5.6, median 9) at induction to 3.6 (SD 3.9, median 3) at completion (p< 0.0001). CRP levels reduced from a mean 21.5 mg/L (SD 28.7, median 13) to 10.4 mg/L (SD 18.2, median 3) at completion (p< 0.001). Albumin levels increased from 35.1g/L (SD 7.7, median 35) to 37.9g/L (SD 5.6, median 39) p=0.004. 68.4% of patients were on steroids at commence while 10.5% were on steroids at completion of 6 weeks (p< 0.001). Of the 5 patients that had bowel resections over the following 12 months, only one was an emergency procedure.
Discussion: Our data suggests that adult CD patients treated with EEN had improved symptomatic scores and nutrition markers, high completion rates and reduced need for surgery. Most patients did not require ongoing steroids after 6 weeks. Steroid and other medication use may have confounded the beneficial effects of EEN in our study. Further prospective randomised trials are required to confirm these results.
Disclosures:
Alexander Sheiban, MD, Brook Maguire, BSN, Mark Ghali, MD, Nirodhi Premachandra, MD, Khizar Niazi, MD, Brandon Baraty, MBBS, Nikola Mitrev, MBBS, MPhil, Viraj Kariyawasam, MBBS, PhD. P3621 - Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Among Adult Patients With Active Crohn’s Disease: A Single Center Experience, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Blacktown Hospital, Blacktown, New South Wales, Australia
Introduction: Current medical management for Crohn’s disease (CD) utilises corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to induce and maintain remission. Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) is first line in inducing remission in paediatric CD patients but is not routinely used in adults in Australia. We assessed the clinical effectiveness, biochemical and nutritional outcomes of EEN in treating adult CD patients.
Methods: We retrospectively analysed active CD patients from 2019 to 2023 who commenced enteral nutrition (EN) at our centre. Local protocol entails that EN patients are seen weekly for 6 weeks. Where patients could not tolerate a polymeric EEN diet, a partial enteral nutrition diet (PEN) was offered; which we defined as at least 70% caloric intake from EN and the remainder from Crohn’s disease exclusion diet (CDED). Electronic medical records were reviewed and data collected. A patient reported outcome score (PRO-2) was recorded comprising of stool frequency and abdominal pain sub-scores. Medication exposures and bowel resections within 12 months were recorded. A Wilcoxon-signed rank test was performed to analyse data between induction and completion of EN.
Results: 46 patients were prescribed EN as part of their CD management between 2019 and 2023. 38/46 (82.6%) patients completed either EEN (n=20) or PEN (n=18). Of these 38 patients, 7 (18.4%) had non-fistulising non-stricturing disease, 11 (28.9%) had fistulising disease (with or without strictures), 20 (52.6%) had stricturing disease. PRO-2 scores reduced from a mean of 8.8 (SD 5.6, median 9) at induction to 3.6 (SD 3.9, median 3) at completion (p< 0.0001). CRP levels reduced from a mean 21.5 mg/L (SD 28.7, median 13) to 10.4 mg/L (SD 18.2, median 3) at completion (p< 0.001). Albumin levels increased from 35.1g/L (SD 7.7, median 35) to 37.9g/L (SD 5.6, median 39) p=0.004. 68.4% of patients were on steroids at commence while 10.5% were on steroids at completion of 6 weeks (p< 0.001). Of the 5 patients that had bowel resections over the following 12 months, only one was an emergency procedure.
Discussion: Our data suggests that adult CD patients treated with EEN had improved symptomatic scores and nutrition markers, high completion rates and reduced need for surgery. Most patients did not require ongoing steroids after 6 weeks. Steroid and other medication use may have confounded the beneficial effects of EEN in our study. Further prospective randomised trials are required to confirm these results.
Disclosures:
Alexander Sheiban indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brook Maguire indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mark Ghali indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nirodhi Premachandra indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Khizar Niazi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brandon Baraty indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nikola Mitrev indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Viraj Kariyawasam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Alexander Sheiban, MD, Brook Maguire, BSN, Mark Ghali, MD, Nirodhi Premachandra, MD, Khizar Niazi, MD, Brandon Baraty, MBBS, Nikola Mitrev, MBBS, MPhil, Viraj Kariyawasam, MBBS, PhD. P3621 - Exclusive Enteral Nutrition Among Adult Patients With Active Crohn’s Disease: A Single Center Experience, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
