Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P2918 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis in the Settings of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Case Report
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Aryanna Sousa, MD, MPH
Roger Williams Medical Center
Providence, RI
Presenting Author(s)
Aryanna Sousa, MD, MPH1, Adderly Toribio, MD2, Nabil Toubia, MD1
1Roger Williams Medical Center, Providence, RI; 2Roger Willams Medical Center, Boston, MA
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory disease affecting several organs. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is a type of IgG4-RD affecting the bile ducts and is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP). A patient with IgG4-SC had underlying autoimmune pancreatitis. However, ruling out primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) was pivotal for an effective treatment.
Case Description/Methods: A 59-year-old male with type 2 diabetes mellitus and choledocholithiasis status post cholecystectomy presented complaining of a 2-week history of pruritus and an 8/10 diffuse, non-radiating abdominal pain. He lost 30 pounds in 2 months unintentionally. His abdomen was soft and non-distended, with mild epigastrium tenderness but no guarding or rebound. Direct bilirubin was 0.3mg/dL, AST/ALT 211/352U/L, and alkaline phosphatase 739U/L. Serologies for HIV, TB, and Hepatitis were negative. Abdominal CT showed intrahepatic biliary dilatation of the common bile duct (CBD), suspicious of malignancy. CA 19-9 level was normal. Extensive autoimmune workup was negative, but IgG4 was elevated. PSC was ruled out. MRCP showed an enlarged pancreatic head and moderate intra and extrahepatic duct dilatation. ERCP showed a stricture in the distal CBD. A stent was placed. Biopsies of the CBD and the head of the pancreas ruled out malignancy. The patient was started on steroids. An FNA biopsy of a submandibular lymph node showed an IgG4/IgG plasma cell ratio above 40%. The diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis with IgG-4-related Sclerosing Cholangitis was established.
Discussion: IgG4-SC is a chronic inflammatory disease presenting obstructive jaundice, pruritus, cholangitis, weight loss, and abdominal pain. IgG4-RD involves the pancreas in 41% of the cases. IgG4-SC can be misdiagnosed by CCA. Histology is the gold standard for diagnosing IgG4-SC. Irregular storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and lymphoplasmacytic infiltration are hallmarks. In our patient, the biopsy from the ERCP ruled out CCA. The IgG staining from the submandibular lymph node was suboptimal, but the high IgG4/IgG plasma cell ratio confirmed that IgG4-RD caused the SC. Additionally, the CD3, CD10, CD20, BCL2, BCL6 and Ki67 staining ruled out lymphoma. Due to numerous relapses, the patient was successfully started on Rituximab. Immunomodulatory drugs are the choice for refractory for IgG4-RD.

Disclosures:
Aryanna Sousa, MD, MPH1, Adderly Toribio, MD2, Nabil Toubia, MD1. P2918 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis in the Settings of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Case Report, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Roger Williams Medical Center, Providence, RI; 2Roger Willams Medical Center, Boston, MA
Introduction: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory disease affecting several organs. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) is a type of IgG4-RD affecting the bile ducts and is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP). A patient with IgG4-SC had underlying autoimmune pancreatitis. However, ruling out primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) was pivotal for an effective treatment.
Case Description/Methods: A 59-year-old male with type 2 diabetes mellitus and choledocholithiasis status post cholecystectomy presented complaining of a 2-week history of pruritus and an 8/10 diffuse, non-radiating abdominal pain. He lost 30 pounds in 2 months unintentionally. His abdomen was soft and non-distended, with mild epigastrium tenderness but no guarding or rebound. Direct bilirubin was 0.3mg/dL, AST/ALT 211/352U/L, and alkaline phosphatase 739U/L. Serologies for HIV, TB, and Hepatitis were negative. Abdominal CT showed intrahepatic biliary dilatation of the common bile duct (CBD), suspicious of malignancy. CA 19-9 level was normal. Extensive autoimmune workup was negative, but IgG4 was elevated. PSC was ruled out. MRCP showed an enlarged pancreatic head and moderate intra and extrahepatic duct dilatation. ERCP showed a stricture in the distal CBD. A stent was placed. Biopsies of the CBD and the head of the pancreas ruled out malignancy. The patient was started on steroids. An FNA biopsy of a submandibular lymph node showed an IgG4/IgG plasma cell ratio above 40%. The diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis with IgG-4-related Sclerosing Cholangitis was established.
Discussion: IgG4-SC is a chronic inflammatory disease presenting obstructive jaundice, pruritus, cholangitis, weight loss, and abdominal pain. IgG4-RD involves the pancreas in 41% of the cases. IgG4-SC can be misdiagnosed by CCA. Histology is the gold standard for diagnosing IgG4-SC. Irregular storiform fibrosis, obliterative phlebitis, and lymphoplasmacytic infiltration are hallmarks. In our patient, the biopsy from the ERCP ruled out CCA. The IgG staining from the submandibular lymph node was suboptimal, but the high IgG4/IgG plasma cell ratio confirmed that IgG4-RD caused the SC. Additionally, the CD3, CD10, CD20, BCL2, BCL6 and Ki67 staining ruled out lymphoma. Due to numerous relapses, the patient was successfully started on Rituximab. Immunomodulatory drugs are the choice for refractory for IgG4-RD.

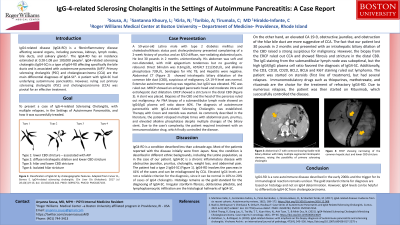
Figure: Figure 1: Abdominal CT with contrast (left) showing mild biliary dilation with likely multiple segmental intrahepatic stenoses, raising the suspicion for primary sclerosing cholangitis. ERCP (right) showing narrowing of the common hepatic duct and lower CBD stricture
Disclosures:
Aryanna Sousa indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adderly Toribio indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nabil Toubia indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Aryanna Sousa, MD, MPH1, Adderly Toribio, MD2, Nabil Toubia, MD1. P2918 - IgG4-Related Sclerosing Cholangitis in the Settings of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Case Report, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
