Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3987 - Intrahepatic Arteriovenous Fistulas as Rare Cause of Portal Hypertension and Liver Cirrhosis
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Marko Kozyk, MD
Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital
Royal Oak, MI
Presenting Author(s)
Marko Kozyk, MD1, Kateryna Strubchevska, MD1, Hanna Dorogavtseva, MD2
1Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital, Royal Oak, MI; 2Klinichna Likarnya Feofaniya, Kyiv, Kyyiv, Ukraine
Introduction: Intrahepatic arterioportal fistulas are pathological communications between arterial and venous systems, which may result in the development of portal hypertension and liver cirrhosis.
Case Description/Methods: We report a case of a 33-year-old male without any significant past medical history who presented with fever up to 102.2 °F, mouth ulcers, abdominal distension, and fatigue. The patient had multiple painful ulcers in his mouth and enlarged submandibular and axillary lymph nodes up to 2 cm. The abdomen was enlarged due to ascites. The liver had uneven contour and was easily palpated. The spleen was also enlarged. The patient had pitting edema of his lower extremities.
Laboratory tests results were significant for a hemoglobin of 7.4 g/dL, white blood cells count of 0.9 bil/L, ESR of 62 mm/h, alkaline phosphatase of 743 U/L, ALT of 33 U/L, AST of 22 U/L, GGT of 218 U/L, LDH of 264 IU/L, total bilirubin of 27 mg/dL, direct bilirubin of 14 mg/dL. All serum electrolytes were normal. Tests for HIV, viral hepatitides, HSV-1, HSV-2, and EBV were negative. Autoimmune hepatitis and Wilson’s disease were also excluded. The patient denied alcohol abuse or hereditary liver diseases.
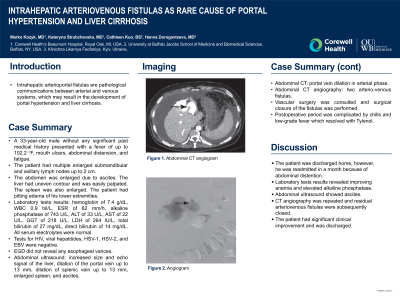
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy did not reveal any esophageal varices. Abdominal ultrasound showed increased size and echo signal of the liver, dilation of the portal vein up to 13 mm, dilation of splenic vein up to 13 mm, enlarged spleen, and ascites. Abdominal CT scan was remarkable for portal vein dilation in arterial phase. Abdominal CT angiography revealed two arterio-venous fistulas. Vascular surgery was consulted and surgical closure of the fistulas was performed. Postoperative period was complicated by chills and low-grade fever which resolved with Tylenol.
The patient was discharged home, however, he was readmitted in a month because of abdominal distention. Laboratory tests results revealed improving anemia and elevated alkaline phosphatase. Abdominal ultrasound showed ascites. CT angiography was repeated and residual arteriovenous fistulas were subsequently closed. The patient had significant clinical improvement and was discharged.
Discussion: This clinical case demonstrates a rare cause of portal hypertension – intrahepatic arteriovenous malformation which results in inadequate blood supply of the liver. In our case, the patient developed severe portal hypertension complicated by ascites, hepatorenal syndrome, bicytopenia, and splenomegaly.

Disclosures:
Marko Kozyk, MD1, Kateryna Strubchevska, MD1, Hanna Dorogavtseva, MD2. P3987 - Intrahepatic Arteriovenous Fistulas as Rare Cause of Portal Hypertension and Liver Cirrhosis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital, Royal Oak, MI; 2Klinichna Likarnya Feofaniya, Kyiv, Kyyiv, Ukraine
Introduction: Intrahepatic arterioportal fistulas are pathological communications between arterial and venous systems, which may result in the development of portal hypertension and liver cirrhosis.
Case Description/Methods: We report a case of a 33-year-old male without any significant past medical history who presented with fever up to 102.2 °F, mouth ulcers, abdominal distension, and fatigue. The patient had multiple painful ulcers in his mouth and enlarged submandibular and axillary lymph nodes up to 2 cm. The abdomen was enlarged due to ascites. The liver had uneven contour and was easily palpated. The spleen was also enlarged. The patient had pitting edema of his lower extremities.
Laboratory tests results were significant for a hemoglobin of 7.4 g/dL, white blood cells count of 0.9 bil/L, ESR of 62 mm/h, alkaline phosphatase of 743 U/L, ALT of 33 U/L, AST of 22 U/L, GGT of 218 U/L, LDH of 264 IU/L, total bilirubin of 27 mg/dL, direct bilirubin of 14 mg/dL. All serum electrolytes were normal. Tests for HIV, viral hepatitides, HSV-1, HSV-2, and EBV were negative. Autoimmune hepatitis and Wilson’s disease were also excluded. The patient denied alcohol abuse or hereditary liver diseases.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy did not reveal any esophageal varices. Abdominal ultrasound showed increased size and echo signal of the liver, dilation of the portal vein up to 13 mm, dilation of splenic vein up to 13 mm, enlarged spleen, and ascites. Abdominal CT scan was remarkable for portal vein dilation in arterial phase. Abdominal CT angiography revealed two arterio-venous fistulas. Vascular surgery was consulted and surgical closure of the fistulas was performed. Postoperative period was complicated by chills and low-grade fever which resolved with Tylenol.
The patient was discharged home, however, he was readmitted in a month because of abdominal distention. Laboratory tests results revealed improving anemia and elevated alkaline phosphatase. Abdominal ultrasound showed ascites. CT angiography was repeated and residual arteriovenous fistulas were subsequently closed. The patient had significant clinical improvement and was discharged.
Discussion: This clinical case demonstrates a rare cause of portal hypertension – intrahepatic arteriovenous malformation which results in inadequate blood supply of the liver. In our case, the patient developed severe portal hypertension complicated by ascites, hepatorenal syndrome, bicytopenia, and splenomegaly.

Figure: Abdominal CT angiogram
Disclosures:
Marko Kozyk indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kateryna Strubchevska indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hanna Dorogavtseva indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marko Kozyk, MD1, Kateryna Strubchevska, MD1, Hanna Dorogavtseva, MD2. P3987 - Intrahepatic Arteriovenous Fistulas as Rare Cause of Portal Hypertension and Liver Cirrhosis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
