Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Liver
P3997 - Elevated Liver Enzymes Due to Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor-Induced Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
.jpg)
Caroline Wang, MD
Rush University Medical Center
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Caroline Wang, MD, Manavi Bhagwat, MD, Joshua Moran, MD, Zoë Post, MD, Sujit Janardhan, MD, PhD
Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL
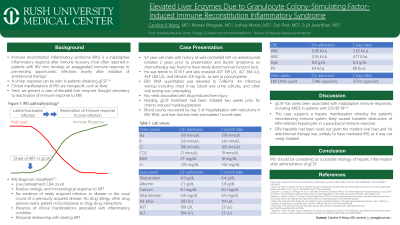
Introduction: Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) is a maladaptive inflammatory response after immune recovery, most often reported in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) who develop an exaggerated immune response to pre-existing opportunistic infections shortly after initiation of antiretroviral therapy. A similar hyper-response has been seen in patients that achieve immune restoration through marrow-stimulating agents such as granulocyte colony stimulating factor (gCSF). Clinical manifestations of IRIS usually represent foci of previous opportunistic infections, but many present with nonspecific symptoms like fever. In this report, we present a case of elevated liver enzymes thought to be secondary to reactivation of immune response to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Case Description/Methods: A 52-year-old male with past medical history of well-controlled HIV on antiretrovirals initiated 2 years prior to presentation and Burkitt lymphoma of a right iliopsoas mass on chemotherapy was found to have newly abnormal liver function tests. He was febrile to 101.8 F and laboratory studies revealed AST 109 U/L, ALT 384 U/L, alkaline phosphatase 260 U/L, and bilirubin 0.8 mg/dL, as well as pancytopenia (neutrophils 550/uL, lymphocytes 400/uL, hemoglobin 8.0 g/dL, platelets 122 k/uL). EBV DNA quantitation was elevated to 7346/mL. An infectious workup including chest X-ray, blood and urine cultures, and other viral serologic testing was unrevealing. No medications associated with drug-induced liver injury, including the patient’s chemotherapy, were identified. Notably, gCSF treatment had been initiated two weeks prior for chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression. His blood cell lineages recovered by day 3 of hospitalization, and liver function tests normalized 1 month later. Repeat EBV RNA was 3724/mL 3 days after the initial EBV quantification date.
Discussion: gCSF has rarely been associated with maladaptive immune responses, including acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with COVID-19. However, this is the first documented evidence to support a hepatic clinical manifestation whereby the patient’s reconstituting immune system likely caused transient destruction of EBV-infected hepatocytes in a paradoxical immune response. EBV-hepatitis had been ruled out given the modest viral load and his antiretroviral therapy was unlikely to have mediated IRIS as it was not newly initiated. IRIS should thus be considered as a possible etiology of hepatic inflammation after administration of gCSF.
Disclosures:
Caroline Wang, MD, Manavi Bhagwat, MD, Joshua Moran, MD, Zoë Post, MD, Sujit Janardhan, MD, PhD. P3997 - Elevated Liver Enzymes Due to Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor-Induced Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) is a maladaptive inflammatory response after immune recovery, most often reported in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) who develop an exaggerated immune response to pre-existing opportunistic infections shortly after initiation of antiretroviral therapy. A similar hyper-response has been seen in patients that achieve immune restoration through marrow-stimulating agents such as granulocyte colony stimulating factor (gCSF). Clinical manifestations of IRIS usually represent foci of previous opportunistic infections, but many present with nonspecific symptoms like fever. In this report, we present a case of elevated liver enzymes thought to be secondary to reactivation of immune response to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).
Case Description/Methods: A 52-year-old male with past medical history of well-controlled HIV on antiretrovirals initiated 2 years prior to presentation and Burkitt lymphoma of a right iliopsoas mass on chemotherapy was found to have newly abnormal liver function tests. He was febrile to 101.8 F and laboratory studies revealed AST 109 U/L, ALT 384 U/L, alkaline phosphatase 260 U/L, and bilirubin 0.8 mg/dL, as well as pancytopenia (neutrophils 550/uL, lymphocytes 400/uL, hemoglobin 8.0 g/dL, platelets 122 k/uL). EBV DNA quantitation was elevated to 7346/mL. An infectious workup including chest X-ray, blood and urine cultures, and other viral serologic testing was unrevealing. No medications associated with drug-induced liver injury, including the patient’s chemotherapy, were identified. Notably, gCSF treatment had been initiated two weeks prior for chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression. His blood cell lineages recovered by day 3 of hospitalization, and liver function tests normalized 1 month later. Repeat EBV RNA was 3724/mL 3 days after the initial EBV quantification date.
Discussion: gCSF has rarely been associated with maladaptive immune responses, including acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with COVID-19. However, this is the first documented evidence to support a hepatic clinical manifestation whereby the patient’s reconstituting immune system likely caused transient destruction of EBV-infected hepatocytes in a paradoxical immune response. EBV-hepatitis had been ruled out given the modest viral load and his antiretroviral therapy was unlikely to have mediated IRIS as it was not newly initiated. IRIS should thus be considered as a possible etiology of hepatic inflammation after administration of gCSF.
Disclosures:
Caroline Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Manavi Bhagwat indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joshua Moran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zoë Post indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sujit Janardhan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Caroline Wang, MD, Manavi Bhagwat, MD, Joshua Moran, MD, Zoë Post, MD, Sujit Janardhan, MD, PhD. P3997 - Elevated Liver Enzymes Due to Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor-Induced Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
