Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3031 - Implementation of Artificial Intelligence Device for Polyp Detection During Colonoscopy at an Academic County Hospital System
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Anthony Xu, MD
Baylor College of Medicine
Houston, TX
Presenting Author(s)
Anthony Xu, MD, Vanessa V. Catania, BA, Thien-Bao P. Nguyen, MD, Shivani Kastuar, MD, Loan Ho, APRN, DNP, Jordan Sparkman, MD, Robert J. Sealock, MD
Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Studies have shown that a higher adenoma detection rate (ADR) decreases the incidence of interval colorectal cancer diagnosis. Artificial intelligence (AI) in colonoscopy is an emerging tool to increase ADR, sessile serrated lesion (SSLs) detection rate and polyp detection rate (PDR).
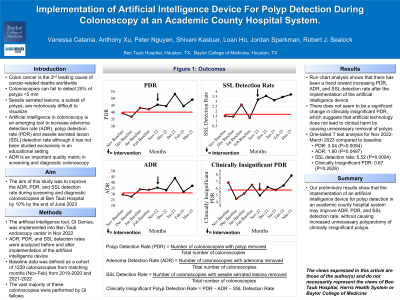
Methods: The AI device, GI Genius by Medtronic, was obtained through the Health Equity Assistance Program from the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. The AI device was implemented in the endoscopy center in November 2022. Given colonoscopies at the academic county hospital are performed by gastroenterology fellows, attempting to account for increasing colonoscopy proficiency throughout training and significant disruptions of endoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic, the baseline data was defined using a composite of 8 months between 2019 and 2022. The ADR, PDR, and SSL detection rates were collected from baseline data and after implementation of the AI device. Clinically insignificant PDR was defined as the PDR minus ADR and SSL detection rates.
Results: The baseline PDR was 40.3%, ADR was 31.1%, SSL detection rate was 1.7% and the clinically insignificant PDR was 7.5%. After implementation of the artificial intelligence device, the mean PDR was 47.5%, ADR was 36.4%, SSL detection rate was 3.4% and clinically insignificant PDR was 7.6%. Run chart analysis showed that there was a trend toward increasing PDR, ADR, and SSL detection rate and no significant change in clinically insignificant PDR. A two-sample t-test between baseline PDR, ADR, SSL detection rates and clinically insignificant PDR and after implementation of the AI device showed there was a significant increase in PDR (p=0.02), ADR (p=0.01), SSL detection rate (p=0.0009) and no significant increase in clinically insignificant PDR (p=0.53).
Discussion: The aim of this quality improvement project was to improve the ADR, PDR, and SSL detection rate during screening and diagnostic colonoscopies at the academic county hospital by 10% through the implementation of an AI device during colonoscopy. Our results suggest that AI devices can improve the PDR, ADR, and SSL detection rates for gastroenterology trainees. A potential harm in these AI polyp detection devices is detection of non-precancerous polyps/tissue however our data shows that there was no increase in the clinically insignificant PDR which suggests that the device does not increase unnecessary polypectomy.

Disclosures:
Anthony Xu, MD, Vanessa V. Catania, BA, Thien-Bao P. Nguyen, MD, Shivani Kastuar, MD, Loan Ho, APRN, DNP, Jordan Sparkman, MD, Robert J. Sealock, MD. P3031 - Implementation of Artificial Intelligence Device for Polyp Detection During Colonoscopy at an Academic County Hospital System, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Introduction: Studies have shown that a higher adenoma detection rate (ADR) decreases the incidence of interval colorectal cancer diagnosis. Artificial intelligence (AI) in colonoscopy is an emerging tool to increase ADR, sessile serrated lesion (SSLs) detection rate and polyp detection rate (PDR).
Methods: The AI device, GI Genius by Medtronic, was obtained through the Health Equity Assistance Program from the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. The AI device was implemented in the endoscopy center in November 2022. Given colonoscopies at the academic county hospital are performed by gastroenterology fellows, attempting to account for increasing colonoscopy proficiency throughout training and significant disruptions of endoscopy during the COVID-19 pandemic, the baseline data was defined using a composite of 8 months between 2019 and 2022. The ADR, PDR, and SSL detection rates were collected from baseline data and after implementation of the AI device. Clinically insignificant PDR was defined as the PDR minus ADR and SSL detection rates.
Results: The baseline PDR was 40.3%, ADR was 31.1%, SSL detection rate was 1.7% and the clinically insignificant PDR was 7.5%. After implementation of the artificial intelligence device, the mean PDR was 47.5%, ADR was 36.4%, SSL detection rate was 3.4% and clinically insignificant PDR was 7.6%. Run chart analysis showed that there was a trend toward increasing PDR, ADR, and SSL detection rate and no significant change in clinically insignificant PDR. A two-sample t-test between baseline PDR, ADR, SSL detection rates and clinically insignificant PDR and after implementation of the AI device showed there was a significant increase in PDR (p=0.02), ADR (p=0.01), SSL detection rate (p=0.0009) and no significant increase in clinically insignificant PDR (p=0.53).
Discussion: The aim of this quality improvement project was to improve the ADR, PDR, and SSL detection rate during screening and diagnostic colonoscopies at the academic county hospital by 10% through the implementation of an AI device during colonoscopy. Our results suggest that AI devices can improve the PDR, ADR, and SSL detection rates for gastroenterology trainees. A potential harm in these AI polyp detection devices is detection of non-precancerous polyps/tissue however our data shows that there was no increase in the clinically insignificant PDR which suggests that the device does not increase unnecessary polypectomy.

Figure: Run charts of polyp detection rate, adenoma detection rate, sessile serrated lesion detection rate and clinically insignificant poly detection rate during baseline and after implementation of AI device during colonoscopy
Disclosures:
Anthony Xu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vanessa Catania indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Thien-Bao Nguyen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shivani Kastuar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Loan Ho indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jordan Sparkman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Robert Sealock: Abbvie – Grant/Research Support. Ambu – Consultant. ConMed – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Anthony Xu, MD, Vanessa V. Catania, BA, Thien-Bao P. Nguyen, MD, Shivani Kastuar, MD, Loan Ho, APRN, DNP, Jordan Sparkman, MD, Robert J. Sealock, MD. P3031 - Implementation of Artificial Intelligence Device for Polyp Detection During Colonoscopy at an Academic County Hospital System, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
