Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3046 - Efficacy of Infliximab and Vedolizumab in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis: A Meta-Analysis
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Shaharyar Zuberi, MD
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Boston, MA
Presenting Author(s)
Shaharyar Zuberi, MD1, Kelsey Anderson, MD1, Rachel Porth, MD1, Vikas Taneja, MD2, Joseph D. Feuerstein, MD1
1Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Norwalk Hospital, Norwalk, CT
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized cancer management and have significantly improved survival outcomes. While these medications are effective at enhancing anti-tumor activity, they also cause several immune-related adverse effects including enterocolitis. Management of ICI colitis depends on the severity of disease ranging from dietary changes for mild (grade 1) disease to steroids and biologic therapy for moderate-severe (grade 2-4) disease. We performed a meta-analysis evaluating the use and efficacy of biologics, mainly infliximab and vedolizumab, for the treatment of refractory ICI colitis.
Methods: We performed a systematic review of the literature using PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane using search criteria including the different checkpoint inhibitors, colitis, diarrhea, infliximab, vedolizumab. We screened these studies to ensure they adhered to our inclusion criteria (adult humans, at least 10 patients, solid or heme malignancy receiving a dose of checkpoint inhibitor, treatment with biologic). Data was extracted by two reviewers. The primary outcome was response to biologic therapy with infliximab, vedolizumab, and both drugs combined. Statistical analysis was performed in R.
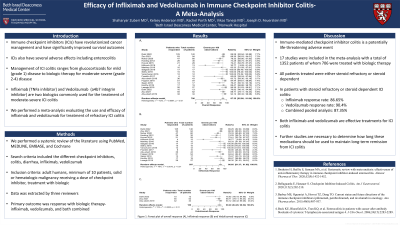
Results: A total of 214 studies were identified of which 17 were included in the meta-analysis. The total number of patients were 1352 of whom 706 were treated with biologics. Patients received checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy or combination checkpoint inhibitors. All patients treated with biologics were either steroid refractory or steroid dependent. Combined pooled analysis resulted in a response rate of 87.35% (95% CI 82.86 – 91.84%). In further subgroup analysis, treatment with infliximab led to a response rate of 86.65% (95% CI 81.37 - 91.92) and treatment with vedolizumab led to a response rate of 90.4% (95% CI 84.26 – 96.54).
Discussion: Immune-mediated checkpoint inhibitor colitis is a potentially life-threatening adverse event from the therapy. While steroids are the initial treatment of choice for moderate-severe colitis, both infliximab and vedolizumab are effective treatments for ICI colitis. Further studies are needed to determine how long these drugs should be used to maintain long-term remission from checkpoint inhibitor colitis.

Disclosures:
Shaharyar Zuberi, MD1, Kelsey Anderson, MD1, Rachel Porth, MD1, Vikas Taneja, MD2, Joseph D. Feuerstein, MD1. P3046 - Efficacy of Infliximab and Vedolizumab in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA; 2Norwalk Hospital, Norwalk, CT
Introduction: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionized cancer management and have significantly improved survival outcomes. While these medications are effective at enhancing anti-tumor activity, they also cause several immune-related adverse effects including enterocolitis. Management of ICI colitis depends on the severity of disease ranging from dietary changes for mild (grade 1) disease to steroids and biologic therapy for moderate-severe (grade 2-4) disease. We performed a meta-analysis evaluating the use and efficacy of biologics, mainly infliximab and vedolizumab, for the treatment of refractory ICI colitis.
Methods: We performed a systematic review of the literature using PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane using search criteria including the different checkpoint inhibitors, colitis, diarrhea, infliximab, vedolizumab. We screened these studies to ensure they adhered to our inclusion criteria (adult humans, at least 10 patients, solid or heme malignancy receiving a dose of checkpoint inhibitor, treatment with biologic). Data was extracted by two reviewers. The primary outcome was response to biologic therapy with infliximab, vedolizumab, and both drugs combined. Statistical analysis was performed in R.
Results: A total of 214 studies were identified of which 17 were included in the meta-analysis. The total number of patients were 1352 of whom 706 were treated with biologics. Patients received checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy or combination checkpoint inhibitors. All patients treated with biologics were either steroid refractory or steroid dependent. Combined pooled analysis resulted in a response rate of 87.35% (95% CI 82.86 – 91.84%). In further subgroup analysis, treatment with infliximab led to a response rate of 86.65% (95% CI 81.37 - 91.92) and treatment with vedolizumab led to a response rate of 90.4% (95% CI 84.26 – 96.54).
Discussion: Immune-mediated checkpoint inhibitor colitis is a potentially life-threatening adverse event from the therapy. While steroids are the initial treatment of choice for moderate-severe colitis, both infliximab and vedolizumab are effective treatments for ICI colitis. Further studies are needed to determine how long these drugs should be used to maintain long-term remission from checkpoint inhibitor colitis.

Figure: Forrest Plot for combined response (A), Infliximab response (B), and Vedolizumab response (C)
Disclosures:
Shaharyar Zuberi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kelsey Anderson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Porth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vikas Taneja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Feuerstein indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shaharyar Zuberi, MD1, Kelsey Anderson, MD1, Rachel Porth, MD1, Vikas Taneja, MD2, Joseph D. Feuerstein, MD1. P3046 - Efficacy of Infliximab and Vedolizumab in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Colitis: A Meta-Analysis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
