Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Small Intestine
P4101 - Targeted Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Dysregulated Intestinal Barrier in Necrotizing Enterocolitis Using ROS-responsive Quercetin Composite Hydrogel
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Hao Chen, PhD
Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital
Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Presenting Author(s)
Hao Chen, PhD1, Zewei Zhuo, MS2, Kehang Guo, MS3, Qi Yang, BS2, Weihong Sha, PhD1
1Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 2Guangdong Provincial people's Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 3The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
Introduction: Quercetin has demonstrated protective effects against Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. However, its efficacy is limited by poor solubility and low bioavailability. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop an orally targeted delivery system that can enhance the clinical translation of quercetin in NEC.
Methods: In this study, we developed a novel ROS-responsive composite hydrogel for synergistic delivery of quercetin, composed of mPEG-b-PMSPEP, sodium alginate, and calcium chloride. We employed an in vivo imaging system to assess the targeted efficacy of R-NPQuercetin in inflamed intestinal tissue. The effects of R-NPQuercetin on oxidative stress, inflammation, proliferation, apoptosis, and intestinal mucosal barrier function were evaluated both in vitro and in vivo.
Results: We observed that R-NPQuercetin, encapsulated with an alginic acid hydrogel, selectively degraded in response to high levels of ROS and accumulated in inflamed intestinal tissue (approximately 3.46-fold higher than free quercetin). R-NPQuercetin effectively scavenged excessive ROS, reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α), and upregulated anti-inflammatory factors (IL-10). Furthermore, we discovered that R-NPQuercetin promoted cell proliferation, inhibited apoptosis, and modulated intestinal mucosal barrier function in experimental NEC.
Discussion: Our study achieved the orally targeted delivery of quercetin by utilizing a ROS-responsive composite hydrogel, enabling precise treatment of NEC through the modulation of oxidative stress and the dysregulated intestinal barrier. The findings of this study demonstrate that the combination of the ROS-responsive composite hydrogel and quercetin holds great promise as a therapeutic strategy for repairing NEC.

Disclosures:
Hao Chen, PhD1, Zewei Zhuo, MS2, Kehang Guo, MS3, Qi Yang, BS2, Weihong Sha, PhD1. P4101 - Targeted Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Dysregulated Intestinal Barrier in Necrotizing Enterocolitis Using ROS-responsive Quercetin Composite Hydrogel, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 2Guangdong Provincial people's Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China; 3The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China
Introduction: Quercetin has demonstrated protective effects against Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. However, its efficacy is limited by poor solubility and low bioavailability. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop an orally targeted delivery system that can enhance the clinical translation of quercetin in NEC.
Methods: In this study, we developed a novel ROS-responsive composite hydrogel for synergistic delivery of quercetin, composed of mPEG-b-PMSPEP, sodium alginate, and calcium chloride. We employed an in vivo imaging system to assess the targeted efficacy of R-NPQuercetin in inflamed intestinal tissue. The effects of R-NPQuercetin on oxidative stress, inflammation, proliferation, apoptosis, and intestinal mucosal barrier function were evaluated both in vitro and in vivo.
Results: We observed that R-NPQuercetin, encapsulated with an alginic acid hydrogel, selectively degraded in response to high levels of ROS and accumulated in inflamed intestinal tissue (approximately 3.46-fold higher than free quercetin). R-NPQuercetin effectively scavenged excessive ROS, reduced pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α), and upregulated anti-inflammatory factors (IL-10). Furthermore, we discovered that R-NPQuercetin promoted cell proliferation, inhibited apoptosis, and modulated intestinal mucosal barrier function in experimental NEC.
Discussion: Our study achieved the orally targeted delivery of quercetin by utilizing a ROS-responsive composite hydrogel, enabling precise treatment of NEC through the modulation of oxidative stress and the dysregulated intestinal barrier. The findings of this study demonstrate that the combination of the ROS-responsive composite hydrogel and quercetin holds great promise as a therapeutic strategy for repairing NEC.

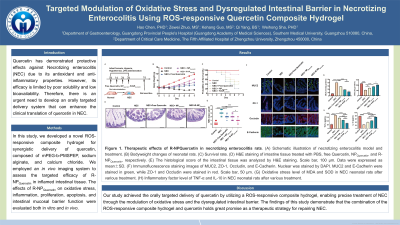
Figure: Figure 1. Therapeutic effects of R-NPQuercetin in necrotizing enterocolitis rats. (A) Schematic illustration of necrotizing enterocolitis model and treatment. (B) Bodyweight changes of neonatal rats. (C) Survival rate. (D) H&E staining of intestine tissue treated with PBS, free Quercetin, NPQuercetin, and R-NPQuercetin, respectively. (E) The histological score of the intestinal tissue was analyzed by H&E staining. Scale bar, 100 μm. Data were expressed as mean±SD. (F) Immunofluorescence staining images of MUC2, ZO-1, Occludin, and E-Cadherin. Nuclear was stained by DAPI. MUC2 and E-Cadherin were stained in green, while ZO-1 and Occludin were stained in red. Scale bar, 50 μm. (G)
Oxidative stress level of MDA and SOD in NEC neonatal rats after various treatment. (H) Inflammatory factor level of TNF-α and IL-10 in NEC neonatal rats after various treatment.
Oxidative stress level of MDA and SOD in NEC neonatal rats after various treatment. (H) Inflammatory factor level of TNF-α and IL-10 in NEC neonatal rats after various treatment.
Disclosures:
Hao Chen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zewei Zhuo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Kehang Guo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Qi Yang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Weihong Sha indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hao Chen, PhD1, Zewei Zhuo, MS2, Kehang Guo, MS3, Qi Yang, BS2, Weihong Sha, PhD1. P4101 - Targeted Modulation of Oxidative Stress and Dysregulated Intestinal Barrier in Necrotizing Enterocolitis Using ROS-responsive Quercetin Composite Hydrogel, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
