Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3102 - Mets Where You Least Expect Them
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- EL
Eliza Lewine, MD
NYU Long Island
Mineola, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Eliza Lewine, MD, Zinal Patel, MD, Jacqueline Forman, MD, Amar Manvar, MD, Iman Hanna, MD, Yousef Fazel, MD, Derek Gindi, MD
NYU Long Island, Mineola, NY
Introduction: Approximately 1% of colorectal cancers can be attributed to metastatic neoplasms originating from other primary sources typically the lung, ovary, breast, prostate, kidney or skin. These spread to the colon through peritoneal seeding or if distant through lymphatic or hematogenous systems. Metastasis to the colon from the thyroid is exceedingly rare.
Case Description/Methods: A 76-year-old male with a history of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) with pulmonary metastasis presented to the hospital with melena. Hemoglobin was 8 from a baseline of 13. He had no prior endoscopic work up. Treatment of his PTC consisted of remote total thyroidectomy, RAI and EBRT with recent initiation of Dabrafenib due to increased lung metastases.
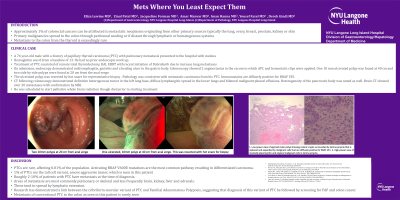
On admission, endoscopy demonstrated mild esophagitis, gastritis and a healing ulcer in the gastric body. Colonoscopy showed 2 angioectasias in the cecum to which APC and hemostatic clips were applied. One 10 mm ulcerated polyp was found at 40 cm and two side by side polyps were found at 20 cm from the anal verge. These polyps were Paris classification Isp with an irregular pit and vascular pattern under NBI examination. The ulcerated polyp at 40 cm was resected by hot snare for representative biopsy. Pathology is consistent with metastatic carcinoma from his PTC. Immunostains are diffusely positive for BRAF VE1.
CT following colonoscopy demonstrated definitive heterogenous tumor in the left lung base, diffuse lymphangitic spread in the lower lungs and bilateral malignant pleural effusions. Heterogeneity of the pancreatic body was noted as well. Brain CT showed over 20 metastases with confirmation by MRI. He is scheduled to start palliative whole brain radiation therapy.
Discussion: PTCs are rare, affecting roughly 0.01% of the population. Activating BRAF V600E mutations are the most common pathway resulting in differentiated carcinoma. 1% of PTCs are the tall cell variant, a more aggressive tumor, which is seen in this patient. Roughly 2-10% of patients with PTC have metastasis at the time of diagnosis. Areas of metastasis are most commonly pulmonary or skeletal and less frequently brain, kidney, liver and adrenals. These tend to spread by lymphatic extension. Research has demonstrated a link between the cribriform-morular variant of PTC and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis, suggesting that a diagnosis of this variant of PTC be followed by screening for FAP and colon cancer. However, metastasis of conventional PTC to the colon, as seen in this patient, is rarely seen.

Disclosures:
Eliza Lewine, MD, Zinal Patel, MD, Jacqueline Forman, MD, Amar Manvar, MD, Iman Hanna, MD, Yousef Fazel, MD, Derek Gindi, MD. P3102 - Mets Where You Least Expect Them, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
NYU Long Island, Mineola, NY
Introduction: Approximately 1% of colorectal cancers can be attributed to metastatic neoplasms originating from other primary sources typically the lung, ovary, breast, prostate, kidney or skin. These spread to the colon through peritoneal seeding or if distant through lymphatic or hematogenous systems. Metastasis to the colon from the thyroid is exceedingly rare.
Case Description/Methods: A 76-year-old male with a history of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) with pulmonary metastasis presented to the hospital with melena. Hemoglobin was 8 from a baseline of 13. He had no prior endoscopic work up. Treatment of his PTC consisted of remote total thyroidectomy, RAI and EBRT with recent initiation of Dabrafenib due to increased lung metastases.
On admission, endoscopy demonstrated mild esophagitis, gastritis and a healing ulcer in the gastric body. Colonoscopy showed 2 angioectasias in the cecum to which APC and hemostatic clips were applied. One 10 mm ulcerated polyp was found at 40 cm and two side by side polyps were found at 20 cm from the anal verge. These polyps were Paris classification Isp with an irregular pit and vascular pattern under NBI examination. The ulcerated polyp at 40 cm was resected by hot snare for representative biopsy. Pathology is consistent with metastatic carcinoma from his PTC. Immunostains are diffusely positive for BRAF VE1.
CT following colonoscopy demonstrated definitive heterogenous tumor in the left lung base, diffuse lymphangitic spread in the lower lungs and bilateral malignant pleural effusions. Heterogeneity of the pancreatic body was noted as well. Brain CT showed over 20 metastases with confirmation by MRI. He is scheduled to start palliative whole brain radiation therapy.
Discussion: PTCs are rare, affecting roughly 0.01% of the population. Activating BRAF V600E mutations are the most common pathway resulting in differentiated carcinoma. 1% of PTCs are the tall cell variant, a more aggressive tumor, which is seen in this patient. Roughly 2-10% of patients with PTC have metastasis at the time of diagnosis. Areas of metastasis are most commonly pulmonary or skeletal and less frequently brain, kidney, liver and adrenals. These tend to spread by lymphatic extension. Research has demonstrated a link between the cribriform-morular variant of PTC and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis, suggesting that a diagnosis of this variant of PTC be followed by screening for FAP and colon cancer. However, metastasis of conventional PTC to the colon, as seen in this patient, is rarely seen.

Figure: Pathology and Endoscopic Findings
Disclosures:
Eliza Lewine indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zinal Patel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jacqueline Forman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amar Manvar indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Iman Hanna indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yousef Fazel indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Derek Gindi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Eliza Lewine, MD, Zinal Patel, MD, Jacqueline Forman, MD, Amar Manvar, MD, Iman Hanna, MD, Yousef Fazel, MD, Derek Gindi, MD. P3102 - Mets Where You Least Expect Them, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
