Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P3109 - Medical Myopia: Dysfunctional Elimination Syndrome in Stricturing Crohn's Disease
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Chukwunonso B. Ezeani, MBBS
Baton Rouge General Hospital
Baton Rouge, LA
Presenting Author(s)
Chukwunonso B. Ezeani, MBBS1, Sullivan Heather, RN2, Randee Kidder, RN3, Ogochukwu Ugochukwu, MBBS4, Joseph Sleiman, MD5, Jonathon Chapman, MD1
1Baton Rouge General Hospital, Baton Rouge, LA; 2Baton Rouge Medical Center, Baton Rouge, LA; 3Baton Rouge General Medical Center, Baton Rouge, LA; 4University of Nigeria, Baton Rouge, LA; 5UPMC Presbyterian, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Crohn's disease, (CD), is an autoimmune disease characterized by a relapsing and remitting course leading to strictures in half of patients within 10 years of diagnosis. Symptomatic strictures may present with postprandial abdominal pain, bloating, nausea and vomiting. However, some patients may present with atypical extra-intestinal symptoms, and diagnosis may be missed or delayed due to medical myopia. We present a case of a 25-year-old lady with urinary symptoms as the presenting symptom for symptomatic stricturing CD.
Case Description/Methods: A 25-year-old female with 12-year history of CD presented with recurrent dysuria and lower abdominal pain that worsens with straining and improves with defecation over one year duration. She otherwise reports soft and well-formed stools, tenesmus, and low-back pain. Prior work-up with urinalysis and culture was unremarkable and therapies such as multiple antibiotic courses and flexible cystourethroscopy with urethral dilation yielded no clinical benefit.
She has a history of symptomatic inflammatory stenosis of the sigmoid colon, and obstructive hepatic flexure lesion leading to sigmoid and hepatic flexure resection with colo-colonic end to side anastomosis. Repeat colonoscopies revealed proximal peri- anastomotic stricture requiring yearly dilation and an ileocolonic stricture that required no dilation. Colonoscopy 3 months prior to presentation revealed severe stenosis around the anastomotic site which could not be bypassed.
Her physical exam revealed a soft and non-tender abdomen. Due to findings on her last colonoscopy, an MR enterography was performed and revealed mural thickening in the distal ileum adjacent to anastomotic site, along with colonic dilation resting on the urinary bladder. She underwent robotic ileocecectomy and anastomotic stricture resection with primary anastomosis. Intraoperatively, the dilated colon was resting freely on the bladder without fistula or abscess. At one month follow-up, she had resolution of her urinary symptoms and improvement in wellbeing.
Discussion: Urinary symptoms may often be a referring sign to urinary symptoms outside of the urinary tract and may lead to delay in diagnosis and appropriate management. MR enterography in this case, which was reviewed by multidisciplinary team, led to the diagnosis of dysfunctional elimination syndrome (DES) manifested by bladder spasms and overactivity. Gastroenterologists should consider DES a rare yet possible presentation for patients with stricturing or penetrating CD.

Disclosures:
Chukwunonso B. Ezeani, MBBS1, Sullivan Heather, RN2, Randee Kidder, RN3, Ogochukwu Ugochukwu, MBBS4, Joseph Sleiman, MD5, Jonathon Chapman, MD1. P3109 - Medical Myopia: Dysfunctional Elimination Syndrome in Stricturing Crohn's Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Baton Rouge General Hospital, Baton Rouge, LA; 2Baton Rouge Medical Center, Baton Rouge, LA; 3Baton Rouge General Medical Center, Baton Rouge, LA; 4University of Nigeria, Baton Rouge, LA; 5UPMC Presbyterian, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction: Crohn's disease, (CD), is an autoimmune disease characterized by a relapsing and remitting course leading to strictures in half of patients within 10 years of diagnosis. Symptomatic strictures may present with postprandial abdominal pain, bloating, nausea and vomiting. However, some patients may present with atypical extra-intestinal symptoms, and diagnosis may be missed or delayed due to medical myopia. We present a case of a 25-year-old lady with urinary symptoms as the presenting symptom for symptomatic stricturing CD.
Case Description/Methods: A 25-year-old female with 12-year history of CD presented with recurrent dysuria and lower abdominal pain that worsens with straining and improves with defecation over one year duration. She otherwise reports soft and well-formed stools, tenesmus, and low-back pain. Prior work-up with urinalysis and culture was unremarkable and therapies such as multiple antibiotic courses and flexible cystourethroscopy with urethral dilation yielded no clinical benefit.
She has a history of symptomatic inflammatory stenosis of the sigmoid colon, and obstructive hepatic flexure lesion leading to sigmoid and hepatic flexure resection with colo-colonic end to side anastomosis. Repeat colonoscopies revealed proximal peri- anastomotic stricture requiring yearly dilation and an ileocolonic stricture that required no dilation. Colonoscopy 3 months prior to presentation revealed severe stenosis around the anastomotic site which could not be bypassed.
Her physical exam revealed a soft and non-tender abdomen. Due to findings on her last colonoscopy, an MR enterography was performed and revealed mural thickening in the distal ileum adjacent to anastomotic site, along with colonic dilation resting on the urinary bladder. She underwent robotic ileocecectomy and anastomotic stricture resection with primary anastomosis. Intraoperatively, the dilated colon was resting freely on the bladder without fistula or abscess. At one month follow-up, she had resolution of her urinary symptoms and improvement in wellbeing.
Discussion: Urinary symptoms may often be a referring sign to urinary symptoms outside of the urinary tract and may lead to delay in diagnosis and appropriate management. MR enterography in this case, which was reviewed by multidisciplinary team, led to the diagnosis of dysfunctional elimination syndrome (DES) manifested by bladder spasms and overactivity. Gastroenterologists should consider DES a rare yet possible presentation for patients with stricturing or penetrating CD.

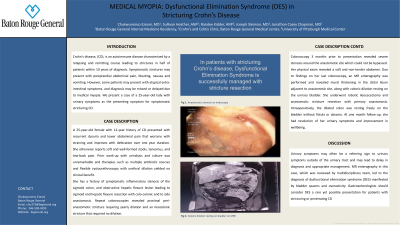
Figure: A. Intrinsic severe stenosis (1mm internal diameter) in proximal descending colon. B. Ileocecal stricture with mural thickening. C. Stricture around colo-colonic anastomosis. D. Distended bowel resting on the bladder wall
Disclosures:
Chukwunonso Ezeani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sullivan Heather indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Randee Kidder indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ogochukwu Ugochukwu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Sleiman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jonathon Chapman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chukwunonso B. Ezeani, MBBS1, Sullivan Heather, RN2, Randee Kidder, RN3, Ogochukwu Ugochukwu, MBBS4, Joseph Sleiman, MD5, Jonathon Chapman, MD1. P3109 - Medical Myopia: Dysfunctional Elimination Syndrome in Stricturing Crohn's Disease, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
