Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P3236 - Non-Endoscopic Detection of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- AC
Amitabh Chak, MD, MS
University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center
UNIVERSITY HEIGHTS, OH
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Helen Moinova, PhD1, Suman Verma, PhD2, John Dumot, DO3, Ashley Faulx, MD3, Prasad Iyer, MD4, Marcia Canto, MD5, Jean Wang, MD6, Nicholas Shaheen, MD7, Prashanthi Thota, MD8, Lishan Aklog, MD2, Joseph Willis, MD3, Sanford Markowitz, MD, PhD1, Amitabh Chak, MD, MS3
1Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH; 2LucidDx, New York, NY; 3University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, Cleveland, OH; 4Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 5Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD; 6Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO; 7University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC; 8Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
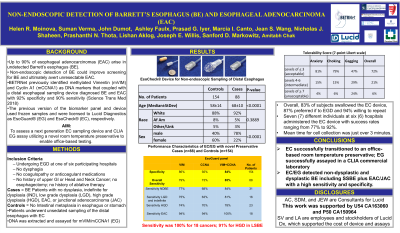
Introduction: We previously reported an encapsulated balloon (EsoCheckTM, EC), which selectively samples the distal esophagus, coupled with a two methylated DNA biomarker panel (EsoGuardTM, EG), detected Barrett’s esophagus (BE) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), with a sensitivity and specificity of 90.3% and 91.7%, respectively. Aim was to assess a next generation EC sampling device and EG assay utilizing a room temperature sample preservative to enable office-based testing.
Methods: Cases with nondysplastic (ND) and dysplastic (indefinite=IND, low grade dysplasia = LGD, high grade dysplasia = HGD) BE, EAC, junctional adenocarcinoma (JAC) and controls with no intestinal metaplasia (IM) were included. Nurses or physician assistants at six institutions were trained in EC administration, delivered the encapsulated balloon per orally and inflated it in the stomach. The inflated balloon was pulled back to sample 5 cm of the distal esophagus, then deflated and retracted into the EC capsule to prevent sample contamination from proximal esophagus. Nextgen EG sequencing assays performed on bisulfite-treated DNA extracted from EC samples determined levels of methylated Vimentin (mVIM) and methylated Cyclin A1 (mCCNA1) in batches in a CLIA-certified laboratory, blinded to patients’ phenotypes.
Results: A total of 242 evaluable patients – 88 cases (median age 68 years, 78% men, 92% white) and 154 controls (median age 58 years, 40% men, 88% white) – underwent adequate EC sampling. Mean time for EC sampling was just over 3 minutes. The cases included 31 NDBE, 17 IND/LGD, 22 HGD, and 18 EAC/JAC. Thirty-seven (53%) of the non-dysplastic and dysplastic BE cases were SSBE (< 3 cm). Overall sensitivity for detecting all cases was 85% (95% CI= 0.76-0.91) and specificity was 84% (95% CI=0.77-0.89). Sensitivity for SSBE was 76% (n=37). The EC/EG test detected 100% of cancers.
Discussion: When performed by trained personnel the next-generation EC/EG technology incorporating a room temperature sample collection preservative and CLIA certified laboratory detects non-dysplastic BE, dysplastic BE, and cancer with high sensitivity and specificity, replicating the prior pilot study. Future applications utilizing office based EC/EG screening of broader populations at risk for developing cancer are proposed.
Disclosures:
Helen Moinova, PhD1, Suman Verma, PhD2, John Dumot, DO3, Ashley Faulx, MD3, Prasad Iyer, MD4, Marcia Canto, MD5, Jean Wang, MD6, Nicholas Shaheen, MD7, Prashanthi Thota, MD8, Lishan Aklog, MD2, Joseph Willis, MD3, Sanford Markowitz, MD, PhD1, Amitabh Chak, MD, MS3. P3236 - Non-Endoscopic Detection of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Helen Moinova, PhD1, Suman Verma, PhD2, John Dumot, DO3, Ashley Faulx, MD3, Prasad Iyer, MD4, Marcia Canto, MD5, Jean Wang, MD6, Nicholas Shaheen, MD7, Prashanthi Thota, MD8, Lishan Aklog, MD2, Joseph Willis, MD3, Sanford Markowitz, MD, PhD1, Amitabh Chak, MD, MS3
1Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH; 2LucidDx, New York, NY; 3University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, Cleveland, OH; 4Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN; 5Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD; 6Washington University in St. Louis, St. Louis, MO; 7University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC; 8Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: We previously reported an encapsulated balloon (EsoCheckTM, EC), which selectively samples the distal esophagus, coupled with a two methylated DNA biomarker panel (EsoGuardTM, EG), detected Barrett’s esophagus (BE) and esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC), with a sensitivity and specificity of 90.3% and 91.7%, respectively. Aim was to assess a next generation EC sampling device and EG assay utilizing a room temperature sample preservative to enable office-based testing.
Methods: Cases with nondysplastic (ND) and dysplastic (indefinite=IND, low grade dysplasia = LGD, high grade dysplasia = HGD) BE, EAC, junctional adenocarcinoma (JAC) and controls with no intestinal metaplasia (IM) were included. Nurses or physician assistants at six institutions were trained in EC administration, delivered the encapsulated balloon per orally and inflated it in the stomach. The inflated balloon was pulled back to sample 5 cm of the distal esophagus, then deflated and retracted into the EC capsule to prevent sample contamination from proximal esophagus. Nextgen EG sequencing assays performed on bisulfite-treated DNA extracted from EC samples determined levels of methylated Vimentin (mVIM) and methylated Cyclin A1 (mCCNA1) in batches in a CLIA-certified laboratory, blinded to patients’ phenotypes.
Results: A total of 242 evaluable patients – 88 cases (median age 68 years, 78% men, 92% white) and 154 controls (median age 58 years, 40% men, 88% white) – underwent adequate EC sampling. Mean time for EC sampling was just over 3 minutes. The cases included 31 NDBE, 17 IND/LGD, 22 HGD, and 18 EAC/JAC. Thirty-seven (53%) of the non-dysplastic and dysplastic BE cases were SSBE (< 3 cm). Overall sensitivity for detecting all cases was 85% (95% CI= 0.76-0.91) and specificity was 84% (95% CI=0.77-0.89). Sensitivity for SSBE was 76% (n=37). The EC/EG test detected 100% of cancers.
Discussion: When performed by trained personnel the next-generation EC/EG technology incorporating a room temperature sample collection preservative and CLIA certified laboratory detects non-dysplastic BE, dysplastic BE, and cancer with high sensitivity and specificity, replicating the prior pilot study. Future applications utilizing office based EC/EG screening of broader populations at risk for developing cancer are proposed.
Disclosures:
Helen Moinova: LucidDx – Consultant.
Suman Verma: LucidDx – Employee.
John Dumot indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ashley Faulx indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Prasad Iyer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Marcia Canto indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jean Wang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nicholas Shaheen: LucidDx – Advisor or Review Panel Member.
Prashanthi Thota indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Lishan Aklog: LucidDx – Owner/Ownership Interest.
Joseph Willis: LucidDx – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Grant/Research Support, Intellectual Property/Patents, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Sanford Markowitz: Amgen – Consultant, Intellectual Property/Patents, Royalties. LucidDx – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Intellectual Property/Patents, Royalties, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Amitabh Chak: LucidDx – Advisor or Review Panel Member, Consultant, Grant/Research Support, Intellectual Property/Patents, Owner/Ownership Interest, Royalties, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Helen Moinova, PhD1, Suman Verma, PhD2, John Dumot, DO3, Ashley Faulx, MD3, Prasad Iyer, MD4, Marcia Canto, MD5, Jean Wang, MD6, Nicholas Shaheen, MD7, Prashanthi Thota, MD8, Lishan Aklog, MD2, Joseph Willis, MD3, Sanford Markowitz, MD, PhD1, Amitabh Chak, MD, MS3. P3236 - Non-Endoscopic Detection of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

