Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P3250 - Trends in the Adoption of Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy Compared to Heller Myotomy in the United States
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Shefali Amin, DO, MSEd
Reading Hospital
Reading, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Ameya Deshmukh, DO1, Parth Desai, DO2, Zidong Zhang, PhD3, Shefali Amin, DO, MSEd4, Madhusudhan R.. Sanaka, MD5, Antonio Cheesman, MD1
1Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO; 2Tower Health-Reading Hospital, Reading, PA; 3Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO; 4Reading Hospital, Reading, PA; 5Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) is a minimally invasive technique used for the management of achalasia. Previous studies have suggested high efficacy and similar procedure related outcomes and complications compared to Heller Myotomy (HM). Yet, little is known about the longitudinal trend of adopting POEM in the United States. We hypothesize that the proportion of patients with achalasia undergoing POEM versus HM will be higher as training and experience in POEM has accumulated over time. Hence, aim of this study was to assess the trends in the utilization of POEM over time in the United States.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study using the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Nationwide Inpatient Sample database of years 2017 and 2019. Patients who were hospitalized with primary discharge diagnosis of achalasia (identified using ICD-10 code K22.0) and treated with either HM (ICD-9-CM: 42.7; ICD-10-PCS: 0D840ZZ, 0D843ZZ, 0D844ZZ; CPT: 43279, 43330, 43331, S2079) or POEM (ICD-10-PCS: 0D847ZZ, 0D848ZZ) were analyzed. Primary outcomes were proportions of the included patients in the community hospitals of various hospital settings (rural, urban non-teaching, urban teaching) and by region (Northeast, Midwest, South, West and other states).
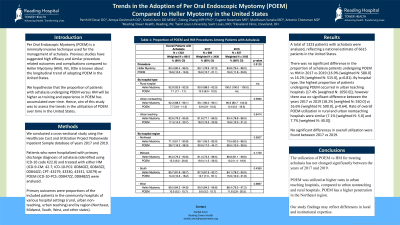
Results: A total of 1323 patients with achalasia were analyzed, reflecting a national estimate of 6615 patients in the United States. There was no significant difference in the proportion of achalasia patients undergoing POEM vs HM in 2017 vs 2019 (16.9% [weighted N: 580.0] vs 16.2% [weighted N: 515.0], p=0.81). By hospital type, the highest proportion of patients undergoing POEM occurred in urban teaching hospitals (17.4% [weighted N: 1050.0]), however there was no significant difference between the years 2017 vs 2019 (18.2% [weighted N: 550.0] vs 16.6% [weighted N: 500.0], p=0.64). Rate of overall POEM utilization in rural and urban nonteaching hospitals were similar (7.1% [weighted N: 5.0] and 7.7% [weighted N: 40.0]). No significant differences in overall utilization were found between 2017 vs 2019.
Discussion: The utilization of POEM vs HM for treating achalasia has not changed significantly between the years of 2017 and 2019. POEM was utilized at higher rates in urban teaching hospitals, compared to urban nonteaching and rural hospitals. POEM has a higher penetration in the Northeast region. Our study findings may reflect differences in local and institutional expertise.
Disclosures:
Ameya Deshmukh, DO1, Parth Desai, DO2, Zidong Zhang, PhD3, Shefali Amin, DO, MSEd4, Madhusudhan R.. Sanaka, MD5, Antonio Cheesman, MD1. P3250 - Trends in the Adoption of Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy Compared to Heller Myotomy in the United States, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Saint Louis University Hospital, St. Louis, MO; 2Tower Health-Reading Hospital, Reading, PA; 3Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO; 4Reading Hospital, Reading, PA; 5Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) is a minimally invasive technique used for the management of achalasia. Previous studies have suggested high efficacy and similar procedure related outcomes and complications compared to Heller Myotomy (HM). Yet, little is known about the longitudinal trend of adopting POEM in the United States. We hypothesize that the proportion of patients with achalasia undergoing POEM versus HM will be higher as training and experience in POEM has accumulated over time. Hence, aim of this study was to assess the trends in the utilization of POEM over time in the United States.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study using the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Nationwide Inpatient Sample database of years 2017 and 2019. Patients who were hospitalized with primary discharge diagnosis of achalasia (identified using ICD-10 code K22.0) and treated with either HM (ICD-9-CM: 42.7; ICD-10-PCS: 0D840ZZ, 0D843ZZ, 0D844ZZ; CPT: 43279, 43330, 43331, S2079) or POEM (ICD-10-PCS: 0D847ZZ, 0D848ZZ) were analyzed. Primary outcomes were proportions of the included patients in the community hospitals of various hospital settings (rural, urban non-teaching, urban teaching) and by region (Northeast, Midwest, South, West and other states).
Results: A total of 1323 patients with achalasia were analyzed, reflecting a national estimate of 6615 patients in the United States. There was no significant difference in the proportion of achalasia patients undergoing POEM vs HM in 2017 vs 2019 (16.9% [weighted N: 580.0] vs 16.2% [weighted N: 515.0], p=0.81). By hospital type, the highest proportion of patients undergoing POEM occurred in urban teaching hospitals (17.4% [weighted N: 1050.0]), however there was no significant difference between the years 2017 vs 2019 (18.2% [weighted N: 550.0] vs 16.6% [weighted N: 500.0], p=0.64). Rate of overall POEM utilization in rural and urban nonteaching hospitals were similar (7.1% [weighted N: 5.0] and 7.7% [weighted N: 40.0]). No significant differences in overall utilization were found between 2017 vs 2019.
Discussion: The utilization of POEM vs HM for treating achalasia has not changed significantly between the years of 2017 and 2019. POEM was utilized at higher rates in urban teaching hospitals, compared to urban nonteaching and rural hospitals. POEM has a higher penetration in the Northeast region. Our study findings may reflect differences in local and institutional expertise.
Disclosures:
Ameya Deshmukh indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Parth Desai indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zidong Zhang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Shefali Amin indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Madhusudhan Sanaka indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Antonio Cheesman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ameya Deshmukh, DO1, Parth Desai, DO2, Zidong Zhang, PhD3, Shefali Amin, DO, MSEd4, Madhusudhan R.. Sanaka, MD5, Antonio Cheesman, MD1. P3250 - Trends in the Adoption of Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy Compared to Heller Myotomy in the United States, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
