Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P3256 - Utility of the Esophageal Screen During Modified Barium Swallow Study to Identify Esophageal Transit Abnormalities
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Chloe K. Tom, MD
Keck School of Medicine of USC
Los Angeles, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Chloe K. Tom, MD1, Brenda Capobres Villegas, EdD, MS, CCC-SLP2, Tapas Tejura, MD1, Ibrahim Abboud, BS3, Sonia Sharma, MD1, Yan Jiang, MD1, Edy Soffer, MD, FACG1, Anisa Shaker, MD1
1Keck School of Medicine of USC, Los Angeles, CA; 2University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA; 3Keck School of Medicine of USC and University of California, Riverside School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: As part of dysphagia evaluation, a modified barium swallow study (MBSS) that includes limited fluoroscopic esophageal assessment may be obtained and a speech language pathologist (SLP) comments on esophageal clearance. Correlation between SLP and radiologist interpretations of clearance on MBSS and with barium esophagram (BE) findings, the gold standard of radiographic esophageal imaging is not clear. Our goals were to 1. determine the frequency which normal esophageal clearance (NEC) vs reduced esophageal clearance (REC) was noted on MBSS by a SLP and correlation with radiology interpretation of the same study; and 2. compare BE findings in NEC vs REC groups.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed MBSS conducted by a single SLP from January 2021 to March 2023. Patient demographics were collected and SLP impression was recorded as NEC or REC when an esophageal sweep was conducted with a 5 mL bolus of Varibar pudding in the anterior posterior upright view. A single radiologist blinded to results reviewed the MBSS images and recorded transit of barium, muffin, and/or tablet when BE was available.
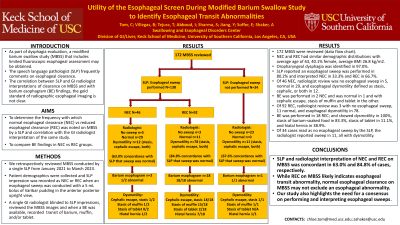
Results: One hundred and seventy-two MBSS were reviewed (Data flow chart). NEC and REC had similar demographic distributions with an average age of 63 years, 40.1% of cases were female, and average BMI was 26.8 kg/m2. Oropharyngeal dysphagia was identified in 97.0%. The SLP reported an esophageal sweep was performed in 80.2% of cases and interpreted NEC in 33.3% and REC in 66.7%. Of 46 NEC, radiologist review was no esophageal sweep in 5, normal in 29, and esophageal dysmotility defined as stasis, cephalic, or both in 12. BE was performed in 2 NEC and was normal in 1 and with cephalic escape, stasis of muffin and tablet in the other. Of 92 REC, radiologist review was 3 with no esophageal sweep, 11 normal, and esophageal dysmotility in 78. BE was performed in 18 REC; and showed dysmotility in 100%, stasis of barium-soaked food in 83.3%, stasis of tablet in 11.1%, and hiatal hernia in 38.9%. Of 34 cases read as no esophageal sweep by the SLP, the radiologist reported sweep in 11, all with dysmotility.
Discussion: SLP and radiologist interpretation of NEC and REC on MBSS was concordant in 63.0% and 84.8% of cases, respectively. While REC on MBSS likely indicates esophageal transit abnormality, normal esophageal clearance on MBSS may not exclude an esophageal abnormality. Our study also highlights the need for a consensus on performing and interpreting esophageal sweeps.

Disclosures:
Chloe K. Tom, MD1, Brenda Capobres Villegas, EdD, MS, CCC-SLP2, Tapas Tejura, MD1, Ibrahim Abboud, BS3, Sonia Sharma, MD1, Yan Jiang, MD1, Edy Soffer, MD, FACG1, Anisa Shaker, MD1. P3256 - Utility of the Esophageal Screen During Modified Barium Swallow Study to Identify Esophageal Transit Abnormalities, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Keck School of Medicine of USC, Los Angeles, CA; 2University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA; 3Keck School of Medicine of USC and University of California, Riverside School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: As part of dysphagia evaluation, a modified barium swallow study (MBSS) that includes limited fluoroscopic esophageal assessment may be obtained and a speech language pathologist (SLP) comments on esophageal clearance. Correlation between SLP and radiologist interpretations of clearance on MBSS and with barium esophagram (BE) findings, the gold standard of radiographic esophageal imaging is not clear. Our goals were to 1. determine the frequency which normal esophageal clearance (NEC) vs reduced esophageal clearance (REC) was noted on MBSS by a SLP and correlation with radiology interpretation of the same study; and 2. compare BE findings in NEC vs REC groups.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed MBSS conducted by a single SLP from January 2021 to March 2023. Patient demographics were collected and SLP impression was recorded as NEC or REC when an esophageal sweep was conducted with a 5 mL bolus of Varibar pudding in the anterior posterior upright view. A single radiologist blinded to results reviewed the MBSS images and recorded transit of barium, muffin, and/or tablet when BE was available.
Results: One hundred and seventy-two MBSS were reviewed (Data flow chart). NEC and REC had similar demographic distributions with an average age of 63 years, 40.1% of cases were female, and average BMI was 26.8 kg/m2. Oropharyngeal dysphagia was identified in 97.0%. The SLP reported an esophageal sweep was performed in 80.2% of cases and interpreted NEC in 33.3% and REC in 66.7%. Of 46 NEC, radiologist review was no esophageal sweep in 5, normal in 29, and esophageal dysmotility defined as stasis, cephalic, or both in 12. BE was performed in 2 NEC and was normal in 1 and with cephalic escape, stasis of muffin and tablet in the other. Of 92 REC, radiologist review was 3 with no esophageal sweep, 11 normal, and esophageal dysmotility in 78. BE was performed in 18 REC; and showed dysmotility in 100%, stasis of barium-soaked food in 83.3%, stasis of tablet in 11.1%, and hiatal hernia in 38.9%. Of 34 cases read as no esophageal sweep by the SLP, the radiologist reported sweep in 11, all with dysmotility.
Discussion: SLP and radiologist interpretation of NEC and REC on MBSS was concordant in 63.0% and 84.8% of cases, respectively. While REC on MBSS likely indicates esophageal transit abnormality, normal esophageal clearance on MBSS may not exclude an esophageal abnormality. Our study also highlights the need for a consensus on performing and interpreting esophageal sweeps.

Figure: Data flow chart.
MBSS: modified barium swallow study; SLP: speech language pathologist; NEC: normal esophageal clearance; REC: reduced esophageal clearance
MBSS: modified barium swallow study; SLP: speech language pathologist; NEC: normal esophageal clearance; REC: reduced esophageal clearance
Disclosures:
Chloe Tom indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Brenda Capobres Villegas indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Tapas Tejura indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ibrahim Abboud indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sonia Sharma indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yan Jiang indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Edy Soffer indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Anisa Shaker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chloe K. Tom, MD1, Brenda Capobres Villegas, EdD, MS, CCC-SLP2, Tapas Tejura, MD1, Ibrahim Abboud, BS3, Sonia Sharma, MD1, Yan Jiang, MD1, Edy Soffer, MD, FACG1, Anisa Shaker, MD1. P3256 - Utility of the Esophageal Screen During Modified Barium Swallow Study to Identify Esophageal Transit Abnormalities, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
