Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P3307 - Missing Tracheoesophageal Prosthesis: An Interesting Case of Esophageal Foreign Body
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- AD
Akshay Duddu, MD
Greater Baltimore Medical Center
Towson, MD
Presenting Author(s)
Akshay Duddu, MD, Jayashrei Sairam, MD, Ayesha Khan, MD, Fazl Rahim Wazeen, MD, Zilla Hussain, MD
Greater Baltimore Medical Center, Towson, MD
Introduction: Tracheoesophageal voice prosthesis (TEP) is considered the gold standard for voice restoration after a total laryngectomy. We report an interesting case of a dislodged TEP presenting as an esophageal foreign body on imaging where removal was complicated by a proximal esophageal radiation stricture.
Case Description/Methods: A thin 79 year old man with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of larynx status post total laryngectomy with TEP placement, and chemoradiation was sent to the emergency department (ED) by his speech therapist after noting dislodgement of his TEP earlier that day. A temporary TEP was placed before ED referral to prevent aspiration via the preformed TE fistula. Patient reported gradual unintentional weight loss due to worsening dysphagia. A CT abdomen pelvis revealed a radiopaque foreign body in the gastroesophageal (GE) junction. The patient was acutely asymptomatic and repeat imaging showed persistent prosthesis at the level of the GE junction. An EGD was performed which initially revealed note of a severe 4 mm radiation stricture in the proximal esophagus. The stricture was traversed after downsizing the scope (XP scope) and gradually dilated to 8 mm with mucosal disruption. A small hiatal hernia with moderate Schatzki's ring was seen where TEP was noted to be lodged. Given the size of the proximal stricture, mucosal disruption noted post-dilation, and limited maneuvering ability of the XP scope, the foreign body was gently advanced to the gastric body which subsequently passed. Patient underwent repeat gradual dilations of his severe radiation stricture with savory dilations to 16 mm and balloon dilation of his Schatzki's ring.
Discussion: Dislodgement of a TEP into the trachea is commonly encountered, leading to aspiration. There is very limited data available on the dislodgement of TEP into the esophagus as it is not a well-known complication. It is pertinent for endoscopists to be aware that TEP which is widely used for voice restoration among laryngectomized patients can present as an esophageal foreign body. Our case also highlights the challenges encountered while managing an esophageal foreign body in the setting of a stricture.

Disclosures:
Akshay Duddu, MD, Jayashrei Sairam, MD, Ayesha Khan, MD, Fazl Rahim Wazeen, MD, Zilla Hussain, MD. P3307 - Missing Tracheoesophageal Prosthesis: An Interesting Case of Esophageal Foreign Body, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Greater Baltimore Medical Center, Towson, MD
Introduction: Tracheoesophageal voice prosthesis (TEP) is considered the gold standard for voice restoration after a total laryngectomy. We report an interesting case of a dislodged TEP presenting as an esophageal foreign body on imaging where removal was complicated by a proximal esophageal radiation stricture.
Case Description/Methods: A thin 79 year old man with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of larynx status post total laryngectomy with TEP placement, and chemoradiation was sent to the emergency department (ED) by his speech therapist after noting dislodgement of his TEP earlier that day. A temporary TEP was placed before ED referral to prevent aspiration via the preformed TE fistula. Patient reported gradual unintentional weight loss due to worsening dysphagia. A CT abdomen pelvis revealed a radiopaque foreign body in the gastroesophageal (GE) junction. The patient was acutely asymptomatic and repeat imaging showed persistent prosthesis at the level of the GE junction. An EGD was performed which initially revealed note of a severe 4 mm radiation stricture in the proximal esophagus. The stricture was traversed after downsizing the scope (XP scope) and gradually dilated to 8 mm with mucosal disruption. A small hiatal hernia with moderate Schatzki's ring was seen where TEP was noted to be lodged. Given the size of the proximal stricture, mucosal disruption noted post-dilation, and limited maneuvering ability of the XP scope, the foreign body was gently advanced to the gastric body which subsequently passed. Patient underwent repeat gradual dilations of his severe radiation stricture with savory dilations to 16 mm and balloon dilation of his Schatzki's ring.
Discussion: Dislodgement of a TEP into the trachea is commonly encountered, leading to aspiration. There is very limited data available on the dislodgement of TEP into the esophagus as it is not a well-known complication. It is pertinent for endoscopists to be aware that TEP which is widely used for voice restoration among laryngectomized patients can present as an esophageal foreign body. Our case also highlights the challenges encountered while managing an esophageal foreign body in the setting of a stricture.

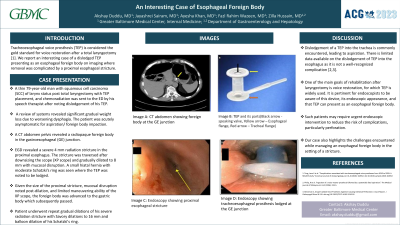
Figure: Image A: Computed tomography showing foreign body at the gastroesophageal junction (Yellow arrow); Image B: Tracheoesophageal prosthesis and its parts (Black arrow pointing to unidirectional speaking valve, yellow arrow pointing to esophageal flange, and red arrow pointing to tracheal flange); Image C: Upper GI endoscopy showing proximal esophageal stricture (Yellow arrow); Image D: Upper GI endoscopy showing tracheoesophageal prosthesis lodged at the GE junction
Disclosures:
Akshay Duddu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jayashrei Sairam indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayesha Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Fazl Rahim Wazeen indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Zilla Hussain indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Akshay Duddu, MD, Jayashrei Sairam, MD, Ayesha Khan, MD, Fazl Rahim Wazeen, MD, Zilla Hussain, MD. P3307 - Missing Tracheoesophageal Prosthesis: An Interesting Case of Esophageal Foreign Body, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

