Tuesday Poster Session
Category: Esophagus
P3345 - It's Not Always in the Skin: Diagnosing Systemic Sclerosis Sine Scleroderma in a Patient With a Large Hiatal Hernia
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- XL
Xue Jing Li, MD
University of Arizona College of Medicine
Phoenix, AZ
Presenting Author(s)
Award: Presidential Poster Award
Xue Jing Li, MD1, Mahmoud Bayoumi, MD, MPH2, Rakesh Nanda, MD, FACG3
1University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 2University of Tennessee College of Medicine, Knoxville, TN; 3Phoenix VA Medical Center, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Systemic sclerosis is a generalized disease of collagen affecting many organs. The main feature is progressive skin fibrosis, but the esophagus is frequently involved. Here, we present a patient diagnosed with sine scleroderma after extensive workup, including high-resolution manometry (HRM), endoscopic functional luminal imaging probe (EndoFLIP), and esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD). Although esophageal HRM is the gold standard, the diagnosis was delayed due to the patient’s large hiatal hernia.
Case Description/Methods: A 57-years-old female with schizoaffective disorder, chronic iron deficiency anemia, gastroparesis, and recurrent aspiration pneumonia presented for dysphagia and nocturnal reflux despite using proton-pump inhibitors. Prior CT chest noted lung nodule, ground-glass opacities, and a patulous esophagus. Index EGD noted a 6cm hiatal hernia, dilated esophagus with debris but no structural obstruction, confirmed by endoscopic ultrasound. The barium esophagogram showed a moderate-large sliding hiatal hernia. Patient was referred to surgery but was lost to follow-up.
She returned 3 years later with similar complaints. A repeat EGD showed LA Grade D esophagitis, confluent ulcerations involving most of the esophagus with a stricture at 21cm. Biopsies showed esophagitis without infectious etiology. She then underwent HRM showing ten failed swallows with absent contractility and adequate lower esophageal sphincter relaxation.
Given the inconclusive finding, she was ultimately referred for EndoFLIP. The latter showed absent contractility, a stricture within the proximal esophagus, patent lower esophagus. Despite the lack of sclerodactyly or Raynaud, a scleroderma workup was initiated and was notable for >1:1280 anti-centromere and positive antinuclear antibodies. Based on autoimmune markers and HRM/EndoFLIP results, she was presumed to have sine scleroderma. Given the constellation of symptoms, she underwent laparoscopic repair of the paraesophageal hernia with the angle of His fundoplasty and pyloroplasty with symptom improvements.
Discussion: Currently, esophageal function can be assessed by HRM and functional luminal imaging probe which enhance our ability to detect motility dysfunction. As demonstrated in our case, scleroderma esophagus should be considered in any patient with esophageal aperistalsis and other organ involvement (i.e lung or kidney), as they can still have sclerosis sine scleroderma, a rare subset characterized by the total or partial absence of cutaneous manifestations.

Disclosures:
Xue Jing Li, MD1, Mahmoud Bayoumi, MD, MPH2, Rakesh Nanda, MD, FACG3. P3345 - It's Not Always in the Skin: Diagnosing Systemic Sclerosis Sine Scleroderma in a Patient With a Large Hiatal Hernia, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Xue Jing Li, MD1, Mahmoud Bayoumi, MD, MPH2, Rakesh Nanda, MD, FACG3
1University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ; 2University of Tennessee College of Medicine, Knoxville, TN; 3Phoenix VA Medical Center, Phoenix, AZ
Introduction: Systemic sclerosis is a generalized disease of collagen affecting many organs. The main feature is progressive skin fibrosis, but the esophagus is frequently involved. Here, we present a patient diagnosed with sine scleroderma after extensive workup, including high-resolution manometry (HRM), endoscopic functional luminal imaging probe (EndoFLIP), and esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD). Although esophageal HRM is the gold standard, the diagnosis was delayed due to the patient’s large hiatal hernia.
Case Description/Methods: A 57-years-old female with schizoaffective disorder, chronic iron deficiency anemia, gastroparesis, and recurrent aspiration pneumonia presented for dysphagia and nocturnal reflux despite using proton-pump inhibitors. Prior CT chest noted lung nodule, ground-glass opacities, and a patulous esophagus. Index EGD noted a 6cm hiatal hernia, dilated esophagus with debris but no structural obstruction, confirmed by endoscopic ultrasound. The barium esophagogram showed a moderate-large sliding hiatal hernia. Patient was referred to surgery but was lost to follow-up.
She returned 3 years later with similar complaints. A repeat EGD showed LA Grade D esophagitis, confluent ulcerations involving most of the esophagus with a stricture at 21cm. Biopsies showed esophagitis without infectious etiology. She then underwent HRM showing ten failed swallows with absent contractility and adequate lower esophageal sphincter relaxation.
Given the inconclusive finding, she was ultimately referred for EndoFLIP. The latter showed absent contractility, a stricture within the proximal esophagus, patent lower esophagus. Despite the lack of sclerodactyly or Raynaud, a scleroderma workup was initiated and was notable for >1:1280 anti-centromere and positive antinuclear antibodies. Based on autoimmune markers and HRM/EndoFLIP results, she was presumed to have sine scleroderma. Given the constellation of symptoms, she underwent laparoscopic repair of the paraesophageal hernia with the angle of His fundoplasty and pyloroplasty with symptom improvements.
Discussion: Currently, esophageal function can be assessed by HRM and functional luminal imaging probe which enhance our ability to detect motility dysfunction. As demonstrated in our case, scleroderma esophagus should be considered in any patient with esophageal aperistalsis and other organ involvement (i.e lung or kidney), as they can still have sclerosis sine scleroderma, a rare subset characterized by the total or partial absence of cutaneous manifestations.

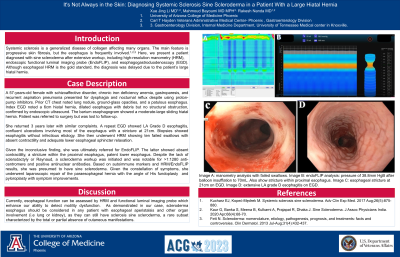
Figure: Image A: manometry analysis with failed swallows.
Image B: endoFLIP analysis: pressure of 38.8mm HgB after balloon insufflation to 70mL. Also show stricture within proximal esophagus.
Image C: esophageal stricture at 21cm on EGD.
Image D: extensive LA grade D esophagitis on EGD.
Image B: endoFLIP analysis: pressure of 38.8mm HgB after balloon insufflation to 70mL. Also show stricture within proximal esophagus.
Image C: esophageal stricture at 21cm on EGD.
Image D: extensive LA grade D esophagitis on EGD.
Disclosures:
Xue Jing Li indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahmoud Bayoumi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rakesh Nanda indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Xue Jing Li, MD1, Mahmoud Bayoumi, MD, MPH2, Rakesh Nanda, MD, FACG3. P3345 - It's Not Always in the Skin: Diagnosing Systemic Sclerosis Sine Scleroderma in a Patient With a Large Hiatal Hernia, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.

