Tuesday Poster Session
Category: General Endoscopy
P3406 - Utilization of a Novel Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for Assessment and Categorization of Endoscope Instrument Channel Defects With Borescope Inspection
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
.jpg)
Sagar Shah, MD
UCLA
Los Angeles, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Sagar Shah, MD1, Michael Humason, 2, V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, MAS1
1UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 2BH2 Innovations, Inc., Newbury Park, CA
Introduction: The evaluation of endoscope instrument channels with borescopes is an area of significant interest given its relevance to infection control and endoscope functionality. Several studies have demonstrated that borescopes can effectively detect defects such as scratches, stains, crimps, fluid droplets and foreign objects. Current practices for endoscope inspection post-reprocessing lack standardization and inspection quality is highly dependent on technician experience, resulting in considerable interobserver variability. The application of artificial intelligence (AI) to aid in borescope image interpretation may facilitate the standardization of this process.
Methods: The working channels of endoscopes and bronchoscopes used at a single tertiary center between August 2022 and May 2023 were inspected with a video borescope (FIS-007 Flexible Inspection Scope, Healthmark Industries Co). Video recordings were manually reviewed by a single, expert reviewer. Results of the manual review served as the ground truth against which a novel AI algorithm (WatchDog Endo AI™, BH2 Innovations Inc.) was evaluated. The software identified the number of scratches, stains, crimps, droplets, and peeling. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were evaluated for each type of defect on a per-inspection basis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed to evaluate the accuracy of WatchDog across a variety of diagnostic thresholds.
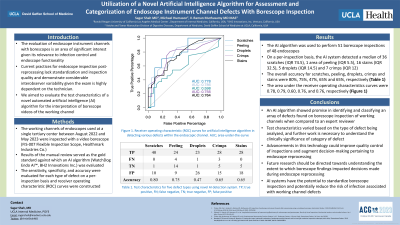
Results: The AI algorithm was used to perform 51 borescope inspections of 48 unique endoscopes. On a per-inspection basis, the AI system detected a median of 36 scratches (IQR 74.5), 1 area of peeling (IQR 5.5), 16 stains (IQR 32.5), 5 droplets (IQR 14.5) and 7 crimps (IQR 12). The overall accuracy for scratches, peeling, droplets, crimps and stains were 80%, 75%, 47%, 65% and 65%, respectively. (Table 1) The area under the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves were 0.78, 0.79, 0.60, 0.76, and 0.76, respectively. Figure 1 depicts the ROC curves for scratches, peeling, droplets, crimps and stains.
Discussion: An AI algorithm showed promise in identifying and classifying borescope findings when compared to an expert reviewer. Manual inspection of endoscope working channels with borescopes currently lacks standardization and is a time- and focus-intensive process. Future advancements in this technology could improve quality control of inspections and augment decision-making pertaining to endoscope reprocessing.

Disclosures:
Sagar Shah, MD1, Michael Humason, 2, V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, MAS1. P3406 - Utilization of a Novel Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for Assessment and Categorization of Endoscope Instrument Channel Defects With Borescope Inspection, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UCLA, Los Angeles, CA; 2BH2 Innovations, Inc., Newbury Park, CA
Introduction: The evaluation of endoscope instrument channels with borescopes is an area of significant interest given its relevance to infection control and endoscope functionality. Several studies have demonstrated that borescopes can effectively detect defects such as scratches, stains, crimps, fluid droplets and foreign objects. Current practices for endoscope inspection post-reprocessing lack standardization and inspection quality is highly dependent on technician experience, resulting in considerable interobserver variability. The application of artificial intelligence (AI) to aid in borescope image interpretation may facilitate the standardization of this process.
Methods: The working channels of endoscopes and bronchoscopes used at a single tertiary center between August 2022 and May 2023 were inspected with a video borescope (FIS-007 Flexible Inspection Scope, Healthmark Industries Co). Video recordings were manually reviewed by a single, expert reviewer. Results of the manual review served as the ground truth against which a novel AI algorithm (WatchDog Endo AI™, BH2 Innovations Inc.) was evaluated. The software identified the number of scratches, stains, crimps, droplets, and peeling. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were evaluated for each type of defect on a per-inspection basis. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed to evaluate the accuracy of WatchDog across a variety of diagnostic thresholds.
Results: The AI algorithm was used to perform 51 borescope inspections of 48 unique endoscopes. On a per-inspection basis, the AI system detected a median of 36 scratches (IQR 74.5), 1 area of peeling (IQR 5.5), 16 stains (IQR 32.5), 5 droplets (IQR 14.5) and 7 crimps (IQR 12). The overall accuracy for scratches, peeling, droplets, crimps and stains were 80%, 75%, 47%, 65% and 65%, respectively. (Table 1) The area under the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves were 0.78, 0.79, 0.60, 0.76, and 0.76, respectively. Figure 1 depicts the ROC curves for scratches, peeling, droplets, crimps and stains.
Discussion: An AI algorithm showed promise in identifying and classifying borescope findings when compared to an expert reviewer. Manual inspection of endoscope working channels with borescopes currently lacks standardization and is a time- and focus-intensive process. Future advancements in this technology could improve quality control of inspections and augment decision-making pertaining to endoscope reprocessing.

Figure: Figure 1. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for artificial intelligence algorithm in detecting various defects within the endoscopic channel. AUC; area under the curve
Disclosures:
Sagar Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Humason indicated no relevant financial relationships.
V. Raman Muthusamy: Boston Scientific – Consultant, Grant/Research Support. Capsovision – Stock Options. Endogastric Solutions – Advisory Committee/Board Member. Motus GI – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Sagar Shah, MD1, Michael Humason, 2, V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, MAS1. P3406 - Utilization of a Novel Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for Assessment and Categorization of Endoscope Instrument Channel Defects With Borescope Inspection, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
