Tuesday Poster Session
Category: GI Bleeding
P3474 - A Rare Cause of GI Bleeding in Adults: Meckel’s Diverticulum
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- VB
Vaishnavi Boppana, MD
University of New Mexico
Albuquerque, New Mexico
Presenting Author(s)
Vaishnavi Boppana, MD1, Swathi Paleti, MD2
1University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM; 2University of New Mexio, Albuquerque, NM
Introduction: Meckel’s diverticulum (MD), a commonest congenital gastrointestinal malformation is typically asymptomatic in adults. However, diagnosis of symptomatic adults requires a high index of clinical suspicion.
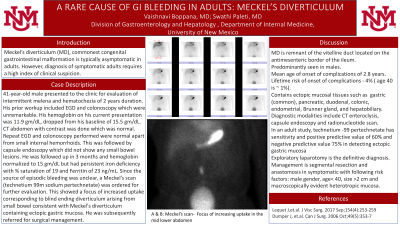
Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old male presented to the clinic for evaluation of intermittent melena and hematochezia of 2 years duration. His prior workup included an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy which were unremarkable. His hemoglobin on his current presentation was 11.9 gm/dL, which was a drop from his baseline of 15.5 gm/dL. A computed tomography abdomen was done which was normal. A repeat EGD and colonoscopy were performed which were normal apart from small internal hemorrhoids. This was followed by a capsule endoscopy which did not show any small bowel lesions. He was followed up in 3 months and his hemoglobin normalized to 15 gm/dL but had persistent iron deficiency with % saturation of 19 and Ferritin of 23 ng/mL. Since the source of episodic bleeding was unclear, a Meckel’s scan (technetium 99m sodium pertechnetate) was ordered for further evaluation. This showed a focus of increased uptake corresponding to blind ending diverticulum arising from small bowel consistent with Meckel's diverticulum containing ectopic gastric mucosa. He was subsequently referred for surgical management.
Discussion: MD a remnant of the vitelline duct is located on the antimesenteric border of the ileum and is predominantly seen in males with a mean age of onset of complications of 2.8 years. MD can develop ectopic mucosal tissues such as gastric (common), pancreatic, duodenal, colonic, endometrial, Brunner gland, and hepatobiliary. Overall lifetime risk of onset of complications is 4% , decreasing with age and the probability near age 40 is ~ 1%. Diagnostic modalities that can be used include CT enteroclysis, capsule endoscopy and radionucleotide scan. In an adult study, the sensitivity and positive predictive value is 60% and negative predictive value is 75% of technetium -99 pertechnetate in detecting ectopic gastric mucosa. Exploratory laparotomy is the definitive diagnosis. Management of MD is segmental resection-anastomosis and should be considered in those who are symptomatic with following risk factors: male gender, age< 40, size >2 cm and macroscopically evident heterotropic mucosa.
Disclosures:
Vaishnavi Boppana, MD1, Swathi Paleti, MD2. P3474 - A Rare Cause of GI Bleeding in Adults: Meckel’s Diverticulum, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM; 2University of New Mexio, Albuquerque, NM
Introduction: Meckel’s diverticulum (MD), a commonest congenital gastrointestinal malformation is typically asymptomatic in adults. However, diagnosis of symptomatic adults requires a high index of clinical suspicion.
Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old male presented to the clinic for evaluation of intermittent melena and hematochezia of 2 years duration. His prior workup included an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy which were unremarkable. His hemoglobin on his current presentation was 11.9 gm/dL, which was a drop from his baseline of 15.5 gm/dL. A computed tomography abdomen was done which was normal. A repeat EGD and colonoscopy were performed which were normal apart from small internal hemorrhoids. This was followed by a capsule endoscopy which did not show any small bowel lesions. He was followed up in 3 months and his hemoglobin normalized to 15 gm/dL but had persistent iron deficiency with % saturation of 19 and Ferritin of 23 ng/mL. Since the source of episodic bleeding was unclear, a Meckel’s scan (technetium 99m sodium pertechnetate) was ordered for further evaluation. This showed a focus of increased uptake corresponding to blind ending diverticulum arising from small bowel consistent with Meckel's diverticulum containing ectopic gastric mucosa. He was subsequently referred for surgical management.
Discussion: MD a remnant of the vitelline duct is located on the antimesenteric border of the ileum and is predominantly seen in males with a mean age of onset of complications of 2.8 years. MD can develop ectopic mucosal tissues such as gastric (common), pancreatic, duodenal, colonic, endometrial, Brunner gland, and hepatobiliary. Overall lifetime risk of onset of complications is 4% , decreasing with age and the probability near age 40 is ~ 1%. Diagnostic modalities that can be used include CT enteroclysis, capsule endoscopy and radionucleotide scan. In an adult study, the sensitivity and positive predictive value is 60% and negative predictive value is 75% of technetium -99 pertechnetate in detecting ectopic gastric mucosa. Exploratory laparotomy is the definitive diagnosis. Management of MD is segmental resection-anastomosis and should be considered in those who are symptomatic with following risk factors: male gender, age< 40, size >2 cm and macroscopically evident heterotropic mucosa.
Disclosures:
Vaishnavi Boppana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Swathi Paleti indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vaishnavi Boppana, MD1, Swathi Paleti, MD2. P3474 - A Rare Cause of GI Bleeding in Adults: Meckel’s Diverticulum, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
