Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3640 - Reversal of Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Drug Antibodies in Response to Drug Escalation and/or Immunomodulator Addition Is More Successful with Infliximab Than Adalimumab
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
.jpg)
Benjamin Gow-Lee, MD
University of Utah School of Medicine
Salt Lake City, UT
Presenting Author(s)
Benjamin Gow-Lee, MD, John F. Valentine, MD, Ann Flynn, MD, Jessica B. Johnson, MD, MS, Amir Kashani, MD, MPH
University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT
Introduction: Formation of antidrug antibodies (ADA) against anti-tumor necrosis factor α (TNF) drugs is a major cause of loss of response in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) treatment. Salvage strategies to continue the same anti-TNF drug after development of ADA include dose escalation, addition of an immunomodulator (IMM, e.g., methotrexate or azathioprine), or both (a dual strategy). IMM addition has been found to successfully reverse ADAs in small studies. This study compares the efficacy of these ADA reversal strategies when used in patients treated with infliximab versus adalimumab.
Methods: We reviewed the case records of our IBD patients who had developed ADAs to infliximab or adalimumab and were subsequently treated with different salvage strategies, including anti-TNF escalation (increase in either dose, frequency, or both), immunomodulator addition, or both. The primary outcome was ADA reversal (undetectable ADA). A secondary outcome was the change in anti-TNF drug level. Both the patient’s original anti-TNF drug and the salvage strategy used were then correlated to the primary and secondary outcomes.
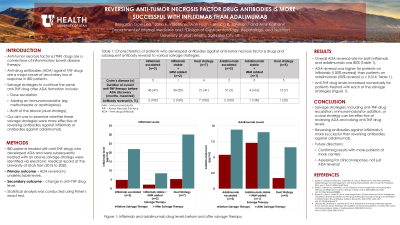
Results: 20 patients were identified. 15 patients had Crohn’s disease and 5 had ulcerative colitis. The median duration of anti-TNF therapy before ADA discovery was 10 months. At the time of ADA discovery, 12 patients were on infliximab; 3 patients underwent anti-TNF dose escalation, 2 had an IMM added, and 7 had both anti-TNF escalation and IMM addition. 8 patients were on adalimumab; 2 patients had anti-TNF therapy escalated, 1 had an IMM added, and 5 had a dual strategy. The overall ADA reversal rate was 80% (Table 1). Overall, antibody reversal was higher for patients on infliximab compared to adalimumab (100% vs 50%, respectively; p= 0.014). Sensitivity analysis comparing patients who received the dual strategy showed greater antibody reversal for patients on infliximab compared to adalimumab (100% versus 20%, p= 0.010). Anti-TNF drug levels increased significantly for patients treated with the dual salvage strategy and trended towards higher levels for patients treated with anti-TNF drug escalation or IMM addition alone.
Discussion: Salvage strategies including anti-TNF dose escalation, immunomodulator addition, or a dual strategy, are effective in ADA reversal. A dual strategy significantly increases anti-TNF drug level. Fewer patients on adalimumab had successful ADA reversal compared to patients on infliximab, suggesting ADA reversal is more successful with infliximab.

Disclosures:
Benjamin Gow-Lee, MD, John F. Valentine, MD, Ann Flynn, MD, Jessica B. Johnson, MD, MS, Amir Kashani, MD, MPH. P3640 - Reversal of Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Drug Antibodies in Response to Drug Escalation and/or Immunomodulator Addition Is More Successful with Infliximab Than Adalimumab, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT
Introduction: Formation of antidrug antibodies (ADA) against anti-tumor necrosis factor α (TNF) drugs is a major cause of loss of response in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) treatment. Salvage strategies to continue the same anti-TNF drug after development of ADA include dose escalation, addition of an immunomodulator (IMM, e.g., methotrexate or azathioprine), or both (a dual strategy). IMM addition has been found to successfully reverse ADAs in small studies. This study compares the efficacy of these ADA reversal strategies when used in patients treated with infliximab versus adalimumab.
Methods: We reviewed the case records of our IBD patients who had developed ADAs to infliximab or adalimumab and were subsequently treated with different salvage strategies, including anti-TNF escalation (increase in either dose, frequency, or both), immunomodulator addition, or both. The primary outcome was ADA reversal (undetectable ADA). A secondary outcome was the change in anti-TNF drug level. Both the patient’s original anti-TNF drug and the salvage strategy used were then correlated to the primary and secondary outcomes.
Results: 20 patients were identified. 15 patients had Crohn’s disease and 5 had ulcerative colitis. The median duration of anti-TNF therapy before ADA discovery was 10 months. At the time of ADA discovery, 12 patients were on infliximab; 3 patients underwent anti-TNF dose escalation, 2 had an IMM added, and 7 had both anti-TNF escalation and IMM addition. 8 patients were on adalimumab; 2 patients had anti-TNF therapy escalated, 1 had an IMM added, and 5 had a dual strategy. The overall ADA reversal rate was 80% (Table 1). Overall, antibody reversal was higher for patients on infliximab compared to adalimumab (100% vs 50%, respectively; p= 0.014). Sensitivity analysis comparing patients who received the dual strategy showed greater antibody reversal for patients on infliximab compared to adalimumab (100% versus 20%, p= 0.010). Anti-TNF drug levels increased significantly for patients treated with the dual salvage strategy and trended towards higher levels for patients treated with anti-TNF drug escalation or IMM addition alone.
Discussion: Salvage strategies including anti-TNF dose escalation, immunomodulator addition, or a dual strategy, are effective in ADA reversal. A dual strategy significantly increases anti-TNF drug level. Fewer patients on adalimumab had successful ADA reversal compared to patients on infliximab, suggesting ADA reversal is more successful with infliximab.

Figure: Figure 1: Drug levels of (A) infliximab and (B) adalimumab before and after salvage therapy by anti-TNF drug escalation, immunomodulator (IMM) addition, or a dual strategy of both anti-TNF drug escalation and IMM addition. Both infliximab and adalimumab levels increased significantly with the dual strategy and trended towards a significant increase with anti-TNF drug escalation or IMM addition.
Disclosures:
Benjamin Gow-Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
John Valentine: AbbVie – Grant/Research Support. Abivax – Grant/Research Support. Advanced Molecular Transport – Grant/Research Support. AstraZeneca – Grant/Research Support. Boehringer Ingelheim – Grant/Research Support. Bristol-Myers Squibb – Grant/Research Support. Pfizer – Grant/Research Support. Roche/Genentech – Grant/Research Support. Takeda – Grant/Research Support.
Ann Flynn indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jessica Johnson indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Amir Kashani indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Benjamin Gow-Lee, MD, John F. Valentine, MD, Ann Flynn, MD, Jessica B. Johnson, MD, MS, Amir Kashani, MD, MPH. P3640 - Reversal of Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Drug Antibodies in Response to Drug Escalation and/or Immunomodulator Addition Is More Successful with Infliximab Than Adalimumab, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
