Tuesday Poster Session
Category: IBD
P3642 - Clinical Characteristics of Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Retrospective Multi-Network Cohort Study
Tuesday, October 24, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:00 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Joseph Sleiman, MD
UPMC Presbyterian
Pittsburgh, PA
Presenting Author(s)
Joseph Sleiman, MD1, Vibhu Chittajallu, MD2, Jaime A. Perez, PhD3, Jeffrey M. Dueker, MD, MPH4, Miguel Regueiro, MD5, Emad Mansoor, MD2
1UPMC Presbyterian, Pittsburgh, PA; 2Case Western Reserve University / University Hospitals, Cleveland, OH; 3University Hospitals Clinical Research Center, Cleveland, OH; 4UPMC, Pittsburgh, PA; 5Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Recent literature suggests that hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) may manifest as a cutaneous extra-intestinal manifestation (EIM) in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We sought to assess the demographics and clinical characteristics of HS in IBD and compare them to those without HS.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using TriNetX (Cambridge, MA), a multi-institutional database of >80 US healthcare systems from 2006 to 2023. We identified all patients with a diagnosis of IBD, as well as those with or without a diagnosis of HS utilizing ICD-10-CM coding. Patients were included in the case group only if HS was diagnosed after IBD. The primary outcome was differences in demographics, medication use, and other EIMs among the cohorts.
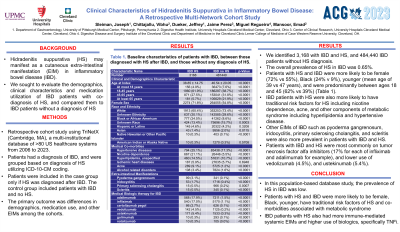
Results: We identified 3,168 with IBD and HS, and 484,440 IBD patients without HS diagnosis (Table 1). The overall prevalence of HS in IBD was 0.65%. Compared to patients with IBD and no HS, patients with HS and IBD were more likely to be female (72% vs 55%), Black (24% v 9%), younger (mean age of 39 vs 47 years), and were predominantly between ages 18 and 45 (62% vs 39%) (Table 1). IBD patients with HS were also more likely to have traditional risk factors for HS including nicotine dependence, acne, and other components of metabolic syndrome including hyperlipidemia and hypertensive disease. Other EIMs of IBD such as pyoderma gangrenosum, iridocyclitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and scleritis were also more prevalent in patients with IBD and HS. In terms of utilization of biologics therapy, patients with IBD and HS were most commonly on tumor necrosis factor alfa inhibitors (about 17% for each of infliximab and adalimumab for example), and lower use of vedolizumab (4.5%), and ustekinumab (5.4%).
Discussion: In this population-based database study, the prevalence of HS in IBD was low. Patients with HS and IBD were more likely to be female, Black, metabolic disease, and younger. IBD patients with HS also had more immune-mediated systemic EIMs and higher use of biologics, specifically TNFi.
Disclosures:
Joseph Sleiman, MD1, Vibhu Chittajallu, MD2, Jaime A. Perez, PhD3, Jeffrey M. Dueker, MD, MPH4, Miguel Regueiro, MD5, Emad Mansoor, MD2. P3642 - Clinical Characteristics of Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Retrospective Multi-Network Cohort Study, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1UPMC Presbyterian, Pittsburgh, PA; 2Case Western Reserve University / University Hospitals, Cleveland, OH; 3University Hospitals Clinical Research Center, Cleveland, OH; 4UPMC, Pittsburgh, PA; 5Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH
Introduction: Recent literature suggests that hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) may manifest as a cutaneous extra-intestinal manifestation (EIM) in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We sought to assess the demographics and clinical characteristics of HS in IBD and compare them to those without HS.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study using TriNetX (Cambridge, MA), a multi-institutional database of >80 US healthcare systems from 2006 to 2023. We identified all patients with a diagnosis of IBD, as well as those with or without a diagnosis of HS utilizing ICD-10-CM coding. Patients were included in the case group only if HS was diagnosed after IBD. The primary outcome was differences in demographics, medication use, and other EIMs among the cohorts.
Results: We identified 3,168 with IBD and HS, and 484,440 IBD patients without HS diagnosis (Table 1). The overall prevalence of HS in IBD was 0.65%. Compared to patients with IBD and no HS, patients with HS and IBD were more likely to be female (72% vs 55%), Black (24% v 9%), younger (mean age of 39 vs 47 years), and were predominantly between ages 18 and 45 (62% vs 39%) (Table 1). IBD patients with HS were also more likely to have traditional risk factors for HS including nicotine dependence, acne, and other components of metabolic syndrome including hyperlipidemia and hypertensive disease. Other EIMs of IBD such as pyoderma gangrenosum, iridocyclitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, and scleritis were also more prevalent in patients with IBD and HS. In terms of utilization of biologics therapy, patients with IBD and HS were most commonly on tumor necrosis factor alfa inhibitors (about 17% for each of infliximab and adalimumab for example), and lower use of vedolizumab (4.5%), and ustekinumab (5.4%).
Discussion: In this population-based database study, the prevalence of HS in IBD was low. Patients with HS and IBD were more likely to be female, Black, metabolic disease, and younger. IBD patients with HS also had more immune-mediated systemic EIMs and higher use of biologics, specifically TNFi.
Disclosures:
Joseph Sleiman indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Vibhu Chittajallu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jaime Perez indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jeffrey Dueker indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Miguel Regueiro: AbbVie – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Alfasigma – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Allergan – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Amgen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Bristol Myers Squibb – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Celgene – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Eli Lilly – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Genentech – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Gilead Sciences – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Janssen – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Miraca Labs – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Pfizer Inc – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Prometheus – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Salix – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Seres – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. Takeda – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Target RWE – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant. UCB – Advisory Committee/Board Member, Consultant, Unrestricted educational grants. Wolters Kluwer Health – Royalties.
Emad Mansoor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Joseph Sleiman, MD1, Vibhu Chittajallu, MD2, Jaime A. Perez, PhD3, Jeffrey M. Dueker, MD, MPH4, Miguel Regueiro, MD5, Emad Mansoor, MD2. P3642 - Clinical Characteristics of Hidradenitis Suppurativa in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Retrospective Multi-Network Cohort Study, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
