Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1463 - Change in Total Serum Bile Acids Correlates With Improvement in Itch in Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Receiving Linerixibat
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- PT
Philip J.F. Troke, PhD
GSK
London, England, United Kingdom
Presenting Author(s)
Eleni Karatza, 1, Fernando Carreño, 2, Sumanta Mukherjee, 2, Linda Casillas, 2, James Fettiplace, 3, Philip J.F. Troke, PhD3, Megan M. McLaughlin, 2, Brandon Swift, 4
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC; 2GSK, Collegeville, PA; 3GSK, London, England, United Kingdom; 4GSK, Durham, NC
Introduction: Cholestatic pruritus (itch) affects up to 80% of pts with PBC. Bile acids are an important pathophysiological mediator of cholestatic itch. Linerixibat, a selective small-molecule inhibitor of the ileal bile acid transporter, reduced circulating TSBA levels and improved itch in patients with PBC. Here, we analyse the linerixibat dose-TSBA relationship and explore the correlation between change in TSBA and change in itch.
Methods: Data from Phase 1/2 studies of healthy volunteers or pts with PBC were used to develop a population dose–pharmacodynamic (k-PD) model. Simulations were performed to explore the effect of linerixibat dose and regimen on daily TSBA profiles. Modelling was used post hoc to derive the area under the TSBA concentration-curve (AUC0-24) for pts in GLIMMER, a Phase 2b study of linerixibat in pts with PBC and itch (NCT02966834). AUC0-24 estimates were correlated with change in weekly itch score (previously mean worst daily itch) and monthly itch score (MIS) reported on a 0–10 numerical rating scale (NRS). In GLIMMER, 4 weeks single-blind placebo (PBO; baseline [BL]=Week 4) was followed by a 12-week treatment period with linerixibat or PBO (to Week 16), then 4 weeks single-blind PBO (to Week 20). Itch responders were defined as having a ≥2 point improvement in MIS at Week 16.
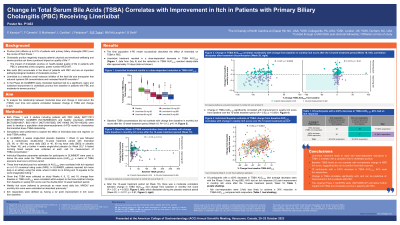
Results: The final population k-PD model successfully described the effect of linerixibat on TSBA in PBC. Linerixibat treatment resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in TSBA AUC0-24; the reduction in TSBA AUC0-24 was apparent after a single dose. BL TSBA concentrations did not correlate with change from BL in MIS at Week 16 (r=-0.13, p=0.14). At Week 16, there was a moderate correlation between change in TSBA AUC0-24 and change in MIS from BL (r=0.27, p=0.002), which dissipated during PBO washout (Week 20; r=0.011, p=0.91). Change in TSBA AUC0-24 significantly correlated with improvement in weekly itch score from BL over the 12-week treatment period (r=0.52, p< 0.0001). A ≥30% decrease in TSBA AUC0-24 was associated with 64% of participants having an itch response.
Discussion: Linerixibat treatment leads to rapid and dose-dependent reductions in TSBA. BL TSBA levels do not correlate with on-treatment change in NRS itch score, suggesting they do not predict linerixibat response. Change in TSBA over the 12-week treatment period correlates significantly with, and can be predictive of, improvement in itch in pts with PBC.
Encore: A modified version of this abstract was presented at EASL and UEGW 2023.
Disclosures:
Eleni Karatza, 1, Fernando Carreño, 2, Sumanta Mukherjee, 2, Linda Casillas, 2, James Fettiplace, 3, Philip J.F. Troke, PhD3, Megan M. McLaughlin, 2, Brandon Swift, 4. P1463 - Change in Total Serum Bile Acids Correlates With Improvement in Itch in Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Receiving Linerixibat, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC; 2GSK, Collegeville, PA; 3GSK, London, England, United Kingdom; 4GSK, Durham, NC
Introduction: Cholestatic pruritus (itch) affects up to 80% of pts with PBC. Bile acids are an important pathophysiological mediator of cholestatic itch. Linerixibat, a selective small-molecule inhibitor of the ileal bile acid transporter, reduced circulating TSBA levels and improved itch in patients with PBC. Here, we analyse the linerixibat dose-TSBA relationship and explore the correlation between change in TSBA and change in itch.
Methods: Data from Phase 1/2 studies of healthy volunteers or pts with PBC were used to develop a population dose–pharmacodynamic (k-PD) model. Simulations were performed to explore the effect of linerixibat dose and regimen on daily TSBA profiles. Modelling was used post hoc to derive the area under the TSBA concentration-curve (AUC0-24) for pts in GLIMMER, a Phase 2b study of linerixibat in pts with PBC and itch (NCT02966834). AUC0-24 estimates were correlated with change in weekly itch score (previously mean worst daily itch) and monthly itch score (MIS) reported on a 0–10 numerical rating scale (NRS). In GLIMMER, 4 weeks single-blind placebo (PBO; baseline [BL]=Week 4) was followed by a 12-week treatment period with linerixibat or PBO (to Week 16), then 4 weeks single-blind PBO (to Week 20). Itch responders were defined as having a ≥2 point improvement in MIS at Week 16.
Results: The final population k-PD model successfully described the effect of linerixibat on TSBA in PBC. Linerixibat treatment resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in TSBA AUC0-24; the reduction in TSBA AUC0-24 was apparent after a single dose. BL TSBA concentrations did not correlate with change from BL in MIS at Week 16 (r=-0.13, p=0.14). At Week 16, there was a moderate correlation between change in TSBA AUC0-24 and change in MIS from BL (r=0.27, p=0.002), which dissipated during PBO washout (Week 20; r=0.011, p=0.91). Change in TSBA AUC0-24 significantly correlated with improvement in weekly itch score from BL over the 12-week treatment period (r=0.52, p< 0.0001). A ≥30% decrease in TSBA AUC0-24 was associated with 64% of participants having an itch response.
Discussion: Linerixibat treatment leads to rapid and dose-dependent reductions in TSBA. BL TSBA levels do not correlate with on-treatment change in NRS itch score, suggesting they do not predict linerixibat response. Change in TSBA over the 12-week treatment period correlates significantly with, and can be predictive of, improvement in itch in pts with PBC.
Encore: A modified version of this abstract was presented at EASL and UEGW 2023.
Disclosures:
Eleni Karatza: GSK – Grant/Research Support. Janssen – Stock Options. Johnson & Johnson – Stock Options.
Fernando Carreño: GSK – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Sumanta Mukherjee: GSK – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Linda Casillas: GSK – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
James Fettiplace: GSK – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Philip J.F. Troke: GSK – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Megan McLaughlin: GSK – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Brandon Swift: GSK – Employee, Stock-publicly held company(excluding mutual/index funds).
Eleni Karatza, 1, Fernando Carreño, 2, Sumanta Mukherjee, 2, Linda Casillas, 2, James Fettiplace, 3, Philip J.F. Troke, PhD3, Megan M. McLaughlin, 2, Brandon Swift, 4. P1463 - Change in Total Serum Bile Acids Correlates With Improvement in Itch in Patients With Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Receiving Linerixibat, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
