Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1520 - Unusual Sequela: Candida-Infected Pseudocyst Treated With Lumen Opposing Metal Stent in Recurrent Pancreatitis
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- JR
Jayasree Ravilla, MD
Monmouth Medical Center/RWJBH
Long Branch, NJ
Presenting Author(s)
Jayasree Ravilla, MD1, Mahrukh Khan, MD1, Siva Naga Srinivas Yarrarapu, MD1, Medha Ghose, MD2, Sobaan Taj, MD3, Andrew Kruger, DO2
1Monmouth Medical Center/RWJBH, Long Branch, NJ; 2Monmouth Medical Center, Long Branch, NJ; 3Hackensack Meridian Jersey Shore University Medical Center, Neptune, NJ
Introduction: Pancreatic pseudocyst which is usually associated with chronic pancreatitis and rarely with acute pancreatitis is an encapsulated collection of fluid with or without necrotic tissue near pancreas. We present a case of pancreatic pseudocyst with infected candida Albicans necrotic mass that is associated with recurrent acute pancreatitis.
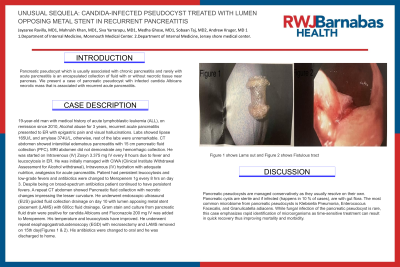
Case Description/Methods: 19-year-old man with medical history of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), on remission since 2010, Alcohol abuse for 3 years, recurrent acute pancreatitis presented to ER with epigastric pain and visual hallucinations. Labs showed lipase 165U/L and amylase 374U/L, otherwise, rest of the labs were unremarkable. CT abdomen showed interstitial edematous pancreatitis with 15 cm pancreatic fluid collection (PFC). MRI abdomen did not demonstrate any hemorrhagic collection. He was started on Intravenous (IV) Zosyn 3.375 mg IV every 8 hours due to fever and leucocytosis in ER. He was initially managed with CIWA (Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment for Alcohol withdrawal), Intravenous (IV) hydration with adequate nutrition, analgesics for acute pancreatitis. Patient had persistent leucocytosis and low-grade fevers and antibiotics were changed to Meropenem 1g every 8 hrs on day 3. Despite being on broad-spectrum antibiotics patient continued to have persistent fevers. A repeat CT abdomen showed Pancreatic fluid collection with necrotic changes impressing the lesser curvature. He underwent endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guided fluid collection drainage on day 10 with lumen apposing metal stent placement (LAMS) with 600cc fluid drainage. Gram stain and culture from pancreatic fluid drain were positive for candida Albicans and Fluconazole 200 mg IV was added to Meropenem. His temperature and leucocytosis have improved. He underwent repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) with necrosectomy and LAMS removed on 15th day(Figures 1 & 2). His antibiotics were changed to oral and he was discharged to home.
Discussion: Pancreatic pseudocysts are managed conservatively as they usually resolve on their own. Pancreatic cysts are sterile and if infected (happens in 10 % of cases), are with gut flora. The most common microbiome from pancreatic pseudocysts is Klebsiella Pneumonia, Enterococcus Facecalis, and Granulicatella adiacens. While fungal infection of the pancreatic pseudocyst is rare, this case emphasizes rapid identification of microorganisms as time-sensitive treatment can result in quick recovery thus improving mortality and morbidity.

Disclosures:
Jayasree Ravilla, MD1, Mahrukh Khan, MD1, Siva Naga Srinivas Yarrarapu, MD1, Medha Ghose, MD2, Sobaan Taj, MD3, Andrew Kruger, DO2. P1520 - Unusual Sequela: Candida-Infected Pseudocyst Treated With Lumen Opposing Metal Stent in Recurrent Pancreatitis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Monmouth Medical Center/RWJBH, Long Branch, NJ; 2Monmouth Medical Center, Long Branch, NJ; 3Hackensack Meridian Jersey Shore University Medical Center, Neptune, NJ
Introduction: Pancreatic pseudocyst which is usually associated with chronic pancreatitis and rarely with acute pancreatitis is an encapsulated collection of fluid with or without necrotic tissue near pancreas. We present a case of pancreatic pseudocyst with infected candida Albicans necrotic mass that is associated with recurrent acute pancreatitis.
Case Description/Methods: 19-year-old man with medical history of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), on remission since 2010, Alcohol abuse for 3 years, recurrent acute pancreatitis presented to ER with epigastric pain and visual hallucinations. Labs showed lipase 165U/L and amylase 374U/L, otherwise, rest of the labs were unremarkable. CT abdomen showed interstitial edematous pancreatitis with 15 cm pancreatic fluid collection (PFC). MRI abdomen did not demonstrate any hemorrhagic collection. He was started on Intravenous (IV) Zosyn 3.375 mg IV every 8 hours due to fever and leucocytosis in ER. He was initially managed with CIWA (Clinical Institute Withdrawal Assessment for Alcohol withdrawal), Intravenous (IV) hydration with adequate nutrition, analgesics for acute pancreatitis. Patient had persistent leucocytosis and low-grade fevers and antibiotics were changed to Meropenem 1g every 8 hrs on day 3. Despite being on broad-spectrum antibiotics patient continued to have persistent fevers. A repeat CT abdomen showed Pancreatic fluid collection with necrotic changes impressing the lesser curvature. He underwent endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) guided fluid collection drainage on day 10 with lumen apposing metal stent placement (LAMS) with 600cc fluid drainage. Gram stain and culture from pancreatic fluid drain were positive for candida Albicans and Fluconazole 200 mg IV was added to Meropenem. His temperature and leucocytosis have improved. He underwent repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) with necrosectomy and LAMS removed on 15th day(Figures 1 & 2). His antibiotics were changed to oral and he was discharged to home.
Discussion: Pancreatic pseudocysts are managed conservatively as they usually resolve on their own. Pancreatic cysts are sterile and if infected (happens in 10 % of cases), are with gut flora. The most common microbiome from pancreatic pseudocysts is Klebsiella Pneumonia, Enterococcus Facecalis, and Granulicatella adiacens. While fungal infection of the pancreatic pseudocyst is rare, this case emphasizes rapid identification of microorganisms as time-sensitive treatment can result in quick recovery thus improving mortality and morbidity.

Figure: Figure 1 shows Lams out and Figure 2 shows Fistulous tract
Disclosures:
Jayasree Ravilla indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Mahrukh Khan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Siva Naga Srinivas Yarrarapu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Medha Ghose indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sobaan Taj indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Kruger indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jayasree Ravilla, MD1, Mahrukh Khan, MD1, Siva Naga Srinivas Yarrarapu, MD1, Medha Ghose, MD2, Sobaan Taj, MD3, Andrew Kruger, DO2. P1520 - Unusual Sequela: Candida-Infected Pseudocyst Treated With Lumen Opposing Metal Stent in Recurrent Pancreatitis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
