Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1529 - Cholangioscopy of IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangitis as Cholangiocarcinoma Mimic
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- MS
Michael Sikes, DO
Naval Medical Center
San Diego, CA
Presenting Author(s)
Michael Sikes, DO, Scott Liu, MD
Naval Medical Center, San Diego, CA
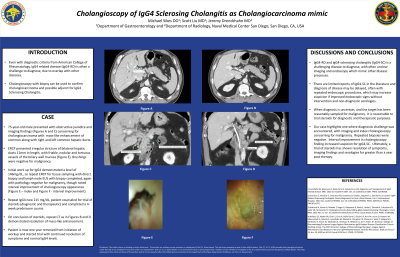
Introduction: As a disease process first described in 2003, IgG4 related disease (IgG4-RD) and IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis is often difficult to diagnose. The American College of Rheumatology and European League Against Rheumatism developed a set of criteria for diagnosis of IgG4-RD, unique to location of pathology. Our patient met some of these criteria, though there was overlap with other diagnoses such as primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Cholangioscopy and targeted intra-ductal biopsies is a relatively new in endoscopy and improves CCA yield. If CCA is not confirmed on biopsies, then IgG4-RD should be considered. With emerging data and groups working towards consensus diagnostic definitions, this case report highlights challenges encountered given the similarities with other disease entities.
Case Description/Methods: We present a case of a 75-year-old male evaluated for obstructive jaundice with imaging findings concerning for likely CCA with mass-like enhancement of proximal left and right hepatic ducts extending to common hepatic duct. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) demonstrated irregular stricture to bilateral hepatic ducts measuring 11mm in length. Despite concerning cholangioscopy findings of friable, nodular, and tortuous dilated vessels of the biliary wall mucosa, along with imaging findings, biopsies and brushings were negative for malignancy. A concurrent work up for IgG4-RD showed an IgG4 level of 146mg/dL. ERCP was repeated with direct ductal biopsy and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) biopsy of adjacent lymph node, again negative for malignancy. Repeat cholangioscopy demonstrated improvement in ductal stricture and mucosal wall and IgG4 increased to 215. Patient was counseled and subsequently trialed on prednisone for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Follow up imaging demonstrated near complete resolution of mass like enhancement, 4 weeks after completion of steroid taper, favoring IgG4-SC over malignancy. Now greater than 1 year from initiation of work up, patient remains asymptomatic with normal IgG4 level and intrahepatic bile ducts on CT.
Discussion: Our case highlights difficulty diagnosing IgG4-SC. Our patient had extensive malignancy workups that were negative. Ultimately serologies and steroids trial initiated for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes confirmed the diagnosis. Cholangioscopy for IgG-RD in the literature is very limited. Repeated cholangioscopy with improving findings not on steroids may increase suspicion for IgG-RD.
Disclosures:
Michael Sikes, DO, Scott Liu, MD. P1529 - Cholangioscopy of IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangitis as Cholangiocarcinoma Mimic, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Naval Medical Center, San Diego, CA
Introduction: As a disease process first described in 2003, IgG4 related disease (IgG4-RD) and IgG4 sclerosing cholangitis is often difficult to diagnose. The American College of Rheumatology and European League Against Rheumatism developed a set of criteria for diagnosis of IgG4-RD, unique to location of pathology. Our patient met some of these criteria, though there was overlap with other diagnoses such as primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and cholangiocarcinoma (CCA). Cholangioscopy and targeted intra-ductal biopsies is a relatively new in endoscopy and improves CCA yield. If CCA is not confirmed on biopsies, then IgG4-RD should be considered. With emerging data and groups working towards consensus diagnostic definitions, this case report highlights challenges encountered given the similarities with other disease entities.
Case Description/Methods: We present a case of a 75-year-old male evaluated for obstructive jaundice with imaging findings concerning for likely CCA with mass-like enhancement of proximal left and right hepatic ducts extending to common hepatic duct. Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) demonstrated irregular stricture to bilateral hepatic ducts measuring 11mm in length. Despite concerning cholangioscopy findings of friable, nodular, and tortuous dilated vessels of the biliary wall mucosa, along with imaging findings, biopsies and brushings were negative for malignancy. A concurrent work up for IgG4-RD showed an IgG4 level of 146mg/dL. ERCP was repeated with direct ductal biopsy and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) biopsy of adjacent lymph node, again negative for malignancy. Repeat cholangioscopy demonstrated improvement in ductal stricture and mucosal wall and IgG4 increased to 215. Patient was counseled and subsequently trialed on prednisone for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Follow up imaging demonstrated near complete resolution of mass like enhancement, 4 weeks after completion of steroid taper, favoring IgG4-SC over malignancy. Now greater than 1 year from initiation of work up, patient remains asymptomatic with normal IgG4 level and intrahepatic bile ducts on CT.
Discussion: Our case highlights difficulty diagnosing IgG4-SC. Our patient had extensive malignancy workups that were negative. Ultimately serologies and steroids trial initiated for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes confirmed the diagnosis. Cholangioscopy for IgG-RD in the literature is very limited. Repeated cholangioscopy with improving findings not on steroids may increase suspicion for IgG-RD.
Disclosures:
Michael Sikes indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Scott Liu indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Michael Sikes, DO, Scott Liu, MD. P1529 - Cholangioscopy of IgG4 Sclerosing Cholangitis as Cholangiocarcinoma Mimic, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
