Monday Poster Session
Category: Biliary/Pancreas
P1539 - Swift Intervention for Acalculous Cholecystitis: Mitigating Mortality in Hospitalized and Critically Ill Patients
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Gretchen Rios, MD
University of Puerto Rico
San Juan, Dominican Republic
Presenting Author(s)
Gretchen Rios, MD1, Nicole Rassi-Stella, MD1, Adrian Chico, MD2, Paola Laracuente-Román, MD3
1University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, Puerto Rico; 2VA Caribbean Healthcare System, San Juan, Puerto Rico; 3University of Puerto Rico, Medical Sciences Campus, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Introduction: Prompt recognition and treatment of acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) are vital in reducing mortality rates among hospitalized and critically ill individuals. This condition, although rare, can lead to life-threatening complications such as gallbladder necrosis and perforation if left untreated.
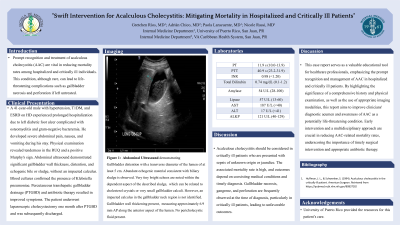
Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old male with hypertension, T1DM, and ESRD on HD experienced prolonged hospitalization due to left diabetic foot ulcer complicated with osteomyelitis and gram-negative bacteremia. He developed severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting during his stay. Physical examination revealed tenderness in the RUQ and a positive Murphy's sign. Abdominal ultrasound demonstrated significant gallbladder wall thickness, distention, and echogenic bile or sludge, without an impacted calculus. Blood cultures confirmed the presence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage (PTGBD) and antibiotic therapy resulted in improved symptoms. The patient underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy one month after PTGBD and was subsequently discharged.
Discussion: Acalculous cholecystitis should be considered in critically ill patients who are presented with sepsis of unknown origin or jaundice. The associated mortality rate is high, and outcomes depend on coexisting medical conditions and timely diagnosis. Gallbladder necrosis, gangrene, and perforation are frequently observed at the time of diagnosis, particularly in critically ill patients, leading to unfavorable outcomes. This case report serves as a valuable educational tool for healthcare professionals, emphasizing the prompt recognition and management of AAC in hospitalized and critically ill patients. By highlighting the significance of a comprehensive history and physical examination, as well as the use of appropriate imaging modalities, this report aims to improve clinicians' diagnostic acumen and awareness of AAC as a potentially life-threatening condition. Early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach are crucial in reducing AAC-related mortality rates, underscoring the importance of timely surgical intervention and appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Disclosures:
Gretchen Rios, MD1, Nicole Rassi-Stella, MD1, Adrian Chico, MD2, Paola Laracuente-Román, MD3. P1539 - Swift Intervention for Acalculous Cholecystitis: Mitigating Mortality in Hospitalized and Critically Ill Patients, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, Puerto Rico; 2VA Caribbean Healthcare System, San Juan, Puerto Rico; 3University of Puerto Rico, Medical Sciences Campus, San Juan, Puerto Rico
Introduction: Prompt recognition and treatment of acalculous cholecystitis (AAC) are vital in reducing mortality rates among hospitalized and critically ill individuals. This condition, although rare, can lead to life-threatening complications such as gallbladder necrosis and perforation if left untreated.
Case Description/Methods: A 41-year-old male with hypertension, T1DM, and ESRD on HD experienced prolonged hospitalization due to left diabetic foot ulcer complicated with osteomyelitis and gram-negative bacteremia. He developed severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting during his stay. Physical examination revealed tenderness in the RUQ and a positive Murphy's sign. Abdominal ultrasound demonstrated significant gallbladder wall thickness, distention, and echogenic bile or sludge, without an impacted calculus. Blood cultures confirmed the presence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage (PTGBD) and antibiotic therapy resulted in improved symptoms. The patient underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy one month after PTGBD and was subsequently discharged.
Discussion: Acalculous cholecystitis should be considered in critically ill patients who are presented with sepsis of unknown origin or jaundice. The associated mortality rate is high, and outcomes depend on coexisting medical conditions and timely diagnosis. Gallbladder necrosis, gangrene, and perforation are frequently observed at the time of diagnosis, particularly in critically ill patients, leading to unfavorable outcomes. This case report serves as a valuable educational tool for healthcare professionals, emphasizing the prompt recognition and management of AAC in hospitalized and critically ill patients. By highlighting the significance of a comprehensive history and physical examination, as well as the use of appropriate imaging modalities, this report aims to improve clinicians' diagnostic acumen and awareness of AAC as a potentially life-threatening condition. Early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach are crucial in reducing AAC-related mortality rates, underscoring the importance of timely surgical intervention and appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Disclosures:
Gretchen Rios indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nicole Rassi-Stella indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Adrian Chico indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Paola Laracuente-Román indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Gretchen Rios, MD1, Nicole Rassi-Stella, MD1, Adrian Chico, MD2, Paola Laracuente-Román, MD3. P1539 - Swift Intervention for Acalculous Cholecystitis: Mitigating Mortality in Hospitalized and Critically Ill Patients, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
