Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P1581 - Radiation Induces BRCA1 Expression in a Genetically Engineered Mouse Model of Colorectal Cancer
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- RN
Rafic Nabbout, MD
Duke University
Durham, North Carolina
Presenting Author(s)
Rafic Nabbout, MD, Chang-Lung Lee, PhD, Jatin Roper, MD
Duke University, Durham, NC
Introduction: The standard of care for stage 2-3 colorectal (CRC) cancer is neoadjuvant radiation. However, only 20% of patients obtain a complete pathologic response following neoadjuvant therapy, for unclear reasons. A major challenge in the field is understanding how patient factors, such as genetics, affect response to radiation therapy. Brca1 is a protein that is essential for the repair of double stranded DNA breaks, which are the most biologically significant lesions caused by radiation injury. Prior evidence suggests that normal intestinal stem cells resist radiation injury by activating Brca1 and preventing subsequent DNA damage. However, the effect of radiotherapy on Brca1 expression in the context of CRC is unknown.
Methods: We induced Apc-null tumors in the distal colons of Apcfl/flVillinCreERT2 and Apcfl/flBrca1fl/flVillinCreERT2 mice via colonoscopy-guided injection of 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Mice were either exposed to 12 GY whole body radiation or sham treatment, two weeks post-tumor induction. Colon tumors were harvested one hour post-treatment and the expression of Brca1 protein was assessed by immunohistochemistry of tissue histology sections (n=2).
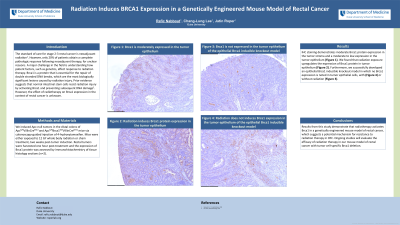
Results: IHC staining demonstrates moderate Brca1 protein expression in the tumor stroma and a moderate to low expression in the tumor epithelium (Figure 1). We found that radiation exposure upregulates the expression of Brca1 protein in tumor epithelium (Figure 2). Furthermore, we successfully developed an epithelial Brca1 inducible knockout model in which no Brca1 expression is noted in tumor epithelial cells, with (Figure 4) or without radiation (Figure 3).
Discussion: Results from this study demonstrate that radiotherapy activates Brca1 in a genetically engineered mouse model of CRC, which suggests a potential mechanism for resistance to radiation therapy in CRC. Ongoing studies will evaluate the efficacy of radiation therapy in our mouse model of CRC with tumor cell-specific Brca1 deletion.

Disclosures:
Rafic Nabbout, MD, Chang-Lung Lee, PhD, Jatin Roper, MD. P1581 - Radiation Induces BRCA1 Expression in a Genetically Engineered Mouse Model of Colorectal Cancer, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
Duke University, Durham, NC
Introduction: The standard of care for stage 2-3 colorectal (CRC) cancer is neoadjuvant radiation. However, only 20% of patients obtain a complete pathologic response following neoadjuvant therapy, for unclear reasons. A major challenge in the field is understanding how patient factors, such as genetics, affect response to radiation therapy. Brca1 is a protein that is essential for the repair of double stranded DNA breaks, which are the most biologically significant lesions caused by radiation injury. Prior evidence suggests that normal intestinal stem cells resist radiation injury by activating Brca1 and preventing subsequent DNA damage. However, the effect of radiotherapy on Brca1 expression in the context of CRC is unknown.
Methods: We induced Apc-null tumors in the distal colons of Apcfl/flVillinCreERT2 and Apcfl/flBrca1fl/flVillinCreERT2 mice via colonoscopy-guided injection of 4-hydroxytamoxifen. Mice were either exposed to 12 GY whole body radiation or sham treatment, two weeks post-tumor induction. Colon tumors were harvested one hour post-treatment and the expression of Brca1 protein was assessed by immunohistochemistry of tissue histology sections (n=2).
Results: IHC staining demonstrates moderate Brca1 protein expression in the tumor stroma and a moderate to low expression in the tumor epithelium (Figure 1). We found that radiation exposure upregulates the expression of Brca1 protein in tumor epithelium (Figure 2). Furthermore, we successfully developed an epithelial Brca1 inducible knockout model in which no Brca1 expression is noted in tumor epithelial cells, with (Figure 4) or without radiation (Figure 3).
Discussion: Results from this study demonstrate that radiotherapy activates Brca1 in a genetically engineered mouse model of CRC, which suggests a potential mechanism for resistance to radiation therapy in CRC. Ongoing studies will evaluate the efficacy of radiation therapy in our mouse model of CRC with tumor cell-specific Brca1 deletion.

Figure: Figure 1: IHC staining shows baseline Brca1 expression in APC deficient tumors.
Figure 2: IHC staining shows Brca1 expression in APC deficient tumors, one hour post-12 GY whole body radiation.
Figure 3: IHC staining shows baseline Brca1 expression in APC deficient tumors with epithelial Brca1 knockout.
Figure 4: IHC staining shows Brca1 expression in APC deficient tumors with epithelial Brca1 knockout, one hour post-12 GY whole body radiation.
Figure 2: IHC staining shows Brca1 expression in APC deficient tumors, one hour post-12 GY whole body radiation.
Figure 3: IHC staining shows baseline Brca1 expression in APC deficient tumors with epithelial Brca1 knockout.
Figure 4: IHC staining shows Brca1 expression in APC deficient tumors with epithelial Brca1 knockout, one hour post-12 GY whole body radiation.
Disclosures:
Rafic Nabbout indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chang-Lung Lee indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Jatin Roper indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rafic Nabbout, MD, Chang-Lung Lee, PhD, Jatin Roper, MD. P1581 - Radiation Induces BRCA1 Expression in a Genetically Engineered Mouse Model of Colorectal Cancer, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
