Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P1621 - Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Colorectal Cancer Patients With COVID-19
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall

Sania Saleem, MD
John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County
Chicago, IL
Presenting Author(s)
Ayobami Olafimihan, MD1, Sania Saleem, MD1, Chidiebele Omaliko, MD2, Oluwanifemi Balogun, MD3, Oghenefejiro Ogwor, MD4, Olawale Adediran, MBBS5, Praise Fawehinmi, BSc6, Hemant Mutneja, MD1
1John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 2One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3Albert Einstein Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA; 4St. Peters University Hospital, New Brunswick, NJ; 5University College Hospital, Ibadan, Oyo, Nigeria; 6Southern Illinois University, Edwardsville, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Acute kidney injury (AKI) leads to worse outcomes in hospitalized patients, more so in patients with malignancies. Due to multiple factors, patients with malignancy are more susceptible to infection with COVID-19 Infection. Considering the higher incidence of AKI in patients with COVID-19, we aimed to analyze the impact of AKI on inpatient outcomes of colorectal cancer patients who had COVID-19 infection.
Methods: Retrospective cohort analyses were conducted using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS), 2020. Multivariate logistic regression was used to identify the predictors and examine the effect of AKI among CRC patients hospitalized for COVID-19.
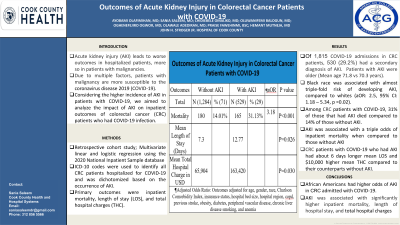
Results: A total of 1,815 CRC patients with COVID-19 infections were identified. Of these, 530 (29.2%) had a secondary diagnosis of AKI. Hospitalizations with AKI had higher mean age (71.8 vs. 70.3 years). Black race was associated with almost triple-fold risk of developing AKI, compared to whites (adjusted odds ratio (AOR): 2.5, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.18 – 5.34, p =0.02).
Amidst CRC patients with COVID-19, 31% of those that had AKI died in comparison to 14% of those without AKI. On multivariate analysis, AKI was associated with a three-fold higher risk of inpatient mortality when compared to those without AKI (AOR: 3.18, 95% CI: 1.69-6.00, p< 0.01). AKI was associated with increased mean length of hospital stay (LOS) compared to those without AKI (12.8 vs. 7.3 days, 95% CI: 0.61 - 9.78, p = 0.03). CRC patients with COVID-19 who had AKI had $10,000 higher mean total hospital charges compared to their counterparts without AKI ($163,420 vs $65,904, 95% CI: 10,100 - 195,783, p = 0.03).
Discussion: In CRC patients admitted for COVID-19 infection, 29% had AKI. African American race had higher odds of AKI in CRC with COVID-19. AKI was associated with significantly higher inpatient mortality, LOS, and total hospital charges.
Disclosures:
Ayobami Olafimihan, MD1, Sania Saleem, MD1, Chidiebele Omaliko, MD2, Oluwanifemi Balogun, MD3, Oghenefejiro Ogwor, MD4, Olawale Adediran, MBBS5, Praise Fawehinmi, BSc6, Hemant Mutneja, MD1. P1621 - Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Colorectal Cancer Patients With COVID-19, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1John H. Stroger, Jr. Hospital of Cook County, Chicago, IL; 2One Brooklyn Health-Brookdale University Hospital Medical Center, Brooklyn, NY; 3Albert Einstein Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA; 4St. Peters University Hospital, New Brunswick, NJ; 5University College Hospital, Ibadan, Oyo, Nigeria; 6Southern Illinois University, Edwardsville, Chicago, IL
Introduction: Acute kidney injury (AKI) leads to worse outcomes in hospitalized patients, more so in patients with malignancies. Due to multiple factors, patients with malignancy are more susceptible to infection with COVID-19 Infection. Considering the higher incidence of AKI in patients with COVID-19, we aimed to analyze the impact of AKI on inpatient outcomes of colorectal cancer patients who had COVID-19 infection.
Methods: Retrospective cohort analyses were conducted using the National Inpatient Sample (NIS), 2020. Multivariate logistic regression was used to identify the predictors and examine the effect of AKI among CRC patients hospitalized for COVID-19.
Results: A total of 1,815 CRC patients with COVID-19 infections were identified. Of these, 530 (29.2%) had a secondary diagnosis of AKI. Hospitalizations with AKI had higher mean age (71.8 vs. 70.3 years). Black race was associated with almost triple-fold risk of developing AKI, compared to whites (adjusted odds ratio (AOR): 2.5, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.18 – 5.34, p =0.02).
Amidst CRC patients with COVID-19, 31% of those that had AKI died in comparison to 14% of those without AKI. On multivariate analysis, AKI was associated with a three-fold higher risk of inpatient mortality when compared to those without AKI (AOR: 3.18, 95% CI: 1.69-6.00, p< 0.01). AKI was associated with increased mean length of hospital stay (LOS) compared to those without AKI (12.8 vs. 7.3 days, 95% CI: 0.61 - 9.78, p = 0.03). CRC patients with COVID-19 who had AKI had $10,000 higher mean total hospital charges compared to their counterparts without AKI ($163,420 vs $65,904, 95% CI: 10,100 - 195,783, p = 0.03).
Discussion: In CRC patients admitted for COVID-19 infection, 29% had AKI. African American race had higher odds of AKI in CRC with COVID-19. AKI was associated with significantly higher inpatient mortality, LOS, and total hospital charges.
Disclosures:
Ayobami Olafimihan indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Sania Saleem indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Chidiebele Omaliko indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Oluwanifemi Balogun indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Oghenefejiro Ogwor indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Olawale Adediran indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Praise Fawehinmi indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Hemant Mutneja indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ayobami Olafimihan, MD1, Sania Saleem, MD1, Chidiebele Omaliko, MD2, Oluwanifemi Balogun, MD3, Oghenefejiro Ogwor, MD4, Olawale Adediran, MBBS5, Praise Fawehinmi, BSc6, Hemant Mutneja, MD1. P1621 - Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Colorectal Cancer Patients With COVID-19, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
