Monday Poster Session
Category: Colon
P1734 - Disseminated Colonic Histoplasmosis
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio
- ML
Muhddesa Lakhana, DO
Mount Sinai South Nassau
Valley Stream, NY
Presenting Author(s)
Nia Jagroop, MD1, Muhddesa Lakhana, DO2, Neal Shah, DO2, Pranay Srivastava, MD2
1Mount Sinai South Nassau, Franklin Square, NY; 2Mount Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, NY
Introduction: Histoplasma capsulatum is a dimorphic fungus endemic to the Midwestern and Southeastern United States as well as Central and South America. Immunocompromised patients are prone to developing disseminated disease. Symptoms typically manifest with findings of pneumonia prior to spread. We present a rare case of disseminated Histoplasmosis manifesting as a colonic lesion in a patient with interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Case Description/Methods: 56-year-old female with hx of ILD, B12 deficiency, chronic cough presenting with acute worsening cough for 2 weeks admitted for sepsis work up. Sputum Cx were positive for MRSA and broad spectrum antibiotics were initiated. CT chest showed chronic fibrosis and hilar lymphadenopathy. Hospital course complicated by progressively worsening severe anemia and dark stools. CT A/P this admission shows focal annular lesions proximal to mid transverse colon consistent with a colon carcinoma with mesenteric and retroperitoneal necrotic adenopathy. Course complicated by multiple episodes of bloody bowel movements post prep and upgrade to ICU. Colonoscopy showed hemorrhoids, multiple round ulcers in proximal, mid-transverse, and distal transverse colon, large 6cm friable excavated ulcerated lesion in proximal transverse colon ~70cm from anal verge. Slowly oozing. Biopsies were taken. The patient clinical status continued to deteriorate, and family elected for palliative approach. Biopsy results of colonic lesions showed Histoplasmosis confirmed with special stain Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain with newly stained Grocott methenamine-silver.
Discussion: H. Capsulatum rarely present in the Gastrointestinal (GI) tract and is typically a manifestation of disseminated disease in immunocompromised patients. Symptoms are nonspecific abdominal pain and intermittent, possibly bloody diarrhea. Most patients would have recent sick contacts, or travel from endemic areas; however, uniquely our patient had no such findings and instead presented with classic findings for colonic malignancy. GI manifestations of histoplasmosis is exceedingly rare. The likely risk factor that increased patients risk of exposure treatment of ILD with biologics. Treatment for disseminated histoplasmosis is amphotericin B however it is unclear if treatment would have provided any benefit because preliminary results came back after palliative approach was elected and confirmation studies returned after patients passing.

Disclosures:
Nia Jagroop, MD1, Muhddesa Lakhana, DO2, Neal Shah, DO2, Pranay Srivastava, MD2. P1734 - Disseminated Colonic Histoplasmosis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1Mount Sinai South Nassau, Franklin Square, NY; 2Mount Sinai South Nassau, Oceanside, NY
Introduction: Histoplasma capsulatum is a dimorphic fungus endemic to the Midwestern and Southeastern United States as well as Central and South America. Immunocompromised patients are prone to developing disseminated disease. Symptoms typically manifest with findings of pneumonia prior to spread. We present a rare case of disseminated Histoplasmosis manifesting as a colonic lesion in a patient with interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Case Description/Methods: 56-year-old female with hx of ILD, B12 deficiency, chronic cough presenting with acute worsening cough for 2 weeks admitted for sepsis work up. Sputum Cx were positive for MRSA and broad spectrum antibiotics were initiated. CT chest showed chronic fibrosis and hilar lymphadenopathy. Hospital course complicated by progressively worsening severe anemia and dark stools. CT A/P this admission shows focal annular lesions proximal to mid transverse colon consistent with a colon carcinoma with mesenteric and retroperitoneal necrotic adenopathy. Course complicated by multiple episodes of bloody bowel movements post prep and upgrade to ICU. Colonoscopy showed hemorrhoids, multiple round ulcers in proximal, mid-transverse, and distal transverse colon, large 6cm friable excavated ulcerated lesion in proximal transverse colon ~70cm from anal verge. Slowly oozing. Biopsies were taken. The patient clinical status continued to deteriorate, and family elected for palliative approach. Biopsy results of colonic lesions showed Histoplasmosis confirmed with special stain Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stain with newly stained Grocott methenamine-silver.
Discussion: H. Capsulatum rarely present in the Gastrointestinal (GI) tract and is typically a manifestation of disseminated disease in immunocompromised patients. Symptoms are nonspecific abdominal pain and intermittent, possibly bloody diarrhea. Most patients would have recent sick contacts, or travel from endemic areas; however, uniquely our patient had no such findings and instead presented with classic findings for colonic malignancy. GI manifestations of histoplasmosis is exceedingly rare. The likely risk factor that increased patients risk of exposure treatment of ILD with biologics. Treatment for disseminated histoplasmosis is amphotericin B however it is unclear if treatment would have provided any benefit because preliminary results came back after palliative approach was elected and confirmation studies returned after patients passing.

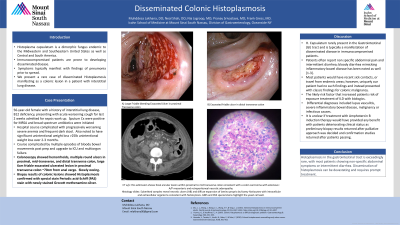
Figure: A Large Friable bleeding Excavated Ulcer in proximal tranverse colon
B Excavated friable ulcer in distal transverse colon
C and D Histology slides: Submitted samples reveal necrotic ulcers (AB) and diffuse expansion of lamina propria by foamy histiocytes with intracellular and extracellular organisms consistent with histiocytosis. GMS and PAS special stains highlight the yeast cell wall.
B Excavated friable ulcer in distal transverse colon
C and D Histology slides: Submitted samples reveal necrotic ulcers (AB) and diffuse expansion of lamina propria by foamy histiocytes with intracellular and extracellular organisms consistent with histiocytosis. GMS and PAS special stains highlight the yeast cell wall.
Disclosures:
Nia Jagroop indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Muhddesa Lakhana indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Neal Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Pranay Srivastava indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Nia Jagroop, MD1, Muhddesa Lakhana, DO2, Neal Shah, DO2, Pranay Srivastava, MD2. P1734 - Disseminated Colonic Histoplasmosis, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
