Monday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P1753 - Analysis of mt-sDNA for Colorectal Cancer Screening
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
Has Audio

Ann Kopera, DO
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital
Washington, DC
Presenting Author(s)
Ann Kopera, DO, Stephanie M. Woo, MD, Priyanka Kanth, MD, MS
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the fourth most common cancer and second leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States. Based on data from 2022, an estimated 106,180 new cases of colon cancer and 44,850 new cases of rectal cancer will occur in the United States. The newest stool-based test available for CRC screening is mt-sDNA, which was FDA approved in 2014. This study sought to analyze demographics and determine completion rates and outcomes of ordered mt-sDNA screening tests.
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted which included patients who had a mt-sDNA test ordered at MedStar Georgetown University Hospital ambulatory clinics from 12/1/2019-2/28/2023. Patients were identified using the mt-sDNA order code in the electronic medical record. Patients ages 50-75 were included. The number of completed tests, results, referrals for colonoscopy, and biopsy results were analyzed. Demographic information was collected.
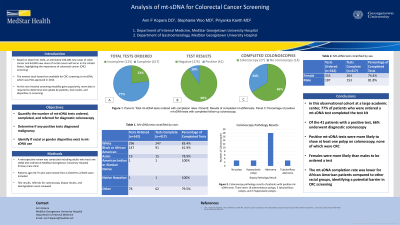
Results: There were 542 mt-sDNA tests ordered and 417 (77%) completed. There were 41 (10%) positive tests, and 27 (66%) went for diagnostic colonoscopy. Of colonoscopies performed, 18 had adenomatous polyps, 3 had tubulovillous polyps, 3 had hyperplastic polyps, and 3 were normal. No cancerous lesions were identified on pathology. The screening completion rate was 83.4% for white patients, 61.9% for African American patients, and 78.9% for Asian patients. There were 355 (65.5%) female patients and 187 (34.5%) male patients ordered a test in the cohort. Among females with an ordered test, 264 (74.4%) were completed. Among males with an ordered test, 153 (81.8%) were completed.
Discussion: In this observational cohort at clinics of a large academic center, more than 75% of mt-sDNA tests ordered for CRC screening at ambulatory clinics were completed. Two-thirds of patients with a positive screening test underwent diagnostic colonoscopy. Positive FIT-DNA tests were more likely to show at least one polyp on colonoscopy, none of which were CRC. Females were more likely than males to be ordered a test. The mt-sDNA completion rate was lower for African American patients compared to white patients, identifying a potential barrier in CRC screening.

Disclosures:
Ann Kopera, DO, Stephanie M. Woo, MD, Priyanka Kanth, MD, MS. P1753 - Analysis of mt-sDNA for Colorectal Cancer Screening, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, DC
Introduction: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the fourth most common cancer and second leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States. Based on data from 2022, an estimated 106,180 new cases of colon cancer and 44,850 new cases of rectal cancer will occur in the United States. The newest stool-based test available for CRC screening is mt-sDNA, which was FDA approved in 2014. This study sought to analyze demographics and determine completion rates and outcomes of ordered mt-sDNA screening tests.
Methods: A retrospective review was conducted which included patients who had a mt-sDNA test ordered at MedStar Georgetown University Hospital ambulatory clinics from 12/1/2019-2/28/2023. Patients were identified using the mt-sDNA order code in the electronic medical record. Patients ages 50-75 were included. The number of completed tests, results, referrals for colonoscopy, and biopsy results were analyzed. Demographic information was collected.
Results: There were 542 mt-sDNA tests ordered and 417 (77%) completed. There were 41 (10%) positive tests, and 27 (66%) went for diagnostic colonoscopy. Of colonoscopies performed, 18 had adenomatous polyps, 3 had tubulovillous polyps, 3 had hyperplastic polyps, and 3 were normal. No cancerous lesions were identified on pathology. The screening completion rate was 83.4% for white patients, 61.9% for African American patients, and 78.9% for Asian patients. There were 355 (65.5%) female patients and 187 (34.5%) male patients ordered a test in the cohort. Among females with an ordered test, 264 (74.4%) were completed. Among males with an ordered test, 153 (81.8%) were completed.
Discussion: In this observational cohort at clinics of a large academic center, more than 75% of mt-sDNA tests ordered for CRC screening at ambulatory clinics were completed. Two-thirds of patients with a positive screening test underwent diagnostic colonoscopy. Positive FIT-DNA tests were more likely to show at least one polyp on colonoscopy, none of which were CRC. Females were more likely than males to be ordered a test. The mt-sDNA completion rate was lower for African American patients compared to white patients, identifying a potential barrier in CRC screening.

Figure: Figure. Percentages of total mt-sDNA tests ordered, results of completed tests, and positive tests that went for colonoscopy. Panel A: Total mt-sDNA tests ordered. Green indicates incomplete tests and blue indicates complete Panel B: Results of completed mt-sDNA tests. Green is negative and blue is positive. Panel C: Percentage of positive mt-sDNA tests with completed follow-up colonoscopy. Green is complete and blue is incomplete.
Disclosures:
Ann Kopera indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Stephanie Woo indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Priyanka Kanth indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ann Kopera, DO, Stephanie M. Woo, MD, Priyanka Kanth, MD, MS. P1753 - Analysis of mt-sDNA for Colorectal Cancer Screening, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
