Monday Poster Session
Category: Colorectal Cancer Prevention
P1783 - Colon Cancer Surveillance Recommendations After Abnormal Fecal Immunochemical Test and Normal Colonoscopy: Results From the Veterans Administration Population Data
Monday, October 23, 2023
10:30 AM - 4:15 PM PT
Location: Exhibit Hall
- IS
Ishani Shah, MD
University of Utah School of Medicine
Salt Lake City, Utah
Presenting Author(s)
Ishani Shah, MD1, Rachel Issaka, MD, MAS2, Jason A. Dominitz, MD, MHS3, Yiwen Yao, MS4, Andrew Gawron, MD, PhD1
1University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 2Hutchinson Institute for Cancer Outcomes Research, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center / University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA; 3University of Washington School of Medicine / VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; 4George E. Wahlen VA Medical Center, Salt Lake City, UT
Introduction: The Veterans Health Administration (VA) has achieved high rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) screening through combination of colonoscopy and fecal immunochemical testing (FIT). Patients with abnormal FIT results have a high risk of advanced adenomas or CRC and should complete a follow-up colonoscopy. This study aimed to describe surveillance colonoscopy recommendations in patients with an abnormal FIT result and without adenoma found on colonoscopy.
Methods: Using the National VA Healthcare system, we retrospectively identified US Veterans who underwent a colonoscopy with at least one abnormal FIT result within 1-year prior to the colonoscopy. We analyzed pathology data resulted within 30 days of the colonoscopy. Based on this, patients were divided into 3 groups: those without any pathology results, those with non-adenoma histology on pathology, and those with adenomas on pathology. Comparisons of surveillance recommendations between the 3 groups were performed.
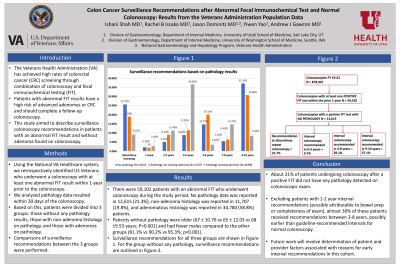
Results: There were 59,102 patients with an abnormal FIT who underwent colonoscopy during the study period between September 2019 through October 2022. No pathology data was reported in 12,615 (21.3%), non-adenoma histology was reported in 11,707 (19.8%), and adenomatous histology was reported in 34,780 (58.8%) patients. Patients without pathology were older (67 ± 10.76 vs 65 ± 12.03 vs 68 ±9.53 years; P< 0.001) and had fewer males compared to the other groups (81.1% vs 90.2% vs 95.3%; p< 0.001). Surveillance recommendations for all three groups are shown in Figure 1. In patients without pathology, surveillance recommendations for repeat colonoscopy were: 9-10 years in 37.1%, 3-8 years in 29.1%, 0-2 years in 9.7%, and discontinuation of screening in 25.7%. In patients with non-adenoma histology on colonoscopy, surveillance recommendations were: 9-10 years in 30.8%, 3-8 years in 38.1%, 0-2 years in 11.1%, and discontinuation of screening in 19%.
Discussion: About 21% of patients undergoing colonoscopy after a positive FIT did not have any pathology detected on colonoscopic exam. Excluding patients with 1-2 year interval recommendations (possibly attributable to bowel prep or completeness of exam), almost 30% of these patients received recommendations between 3-8 years, possibly earlier than guideline-recommended intervals for normal colonoscopy. Future work will involve determination of patient and provider factors associated with reasons for early interval recommendations in this cohort.

Disclosures:
Ishani Shah, MD1, Rachel Issaka, MD, MAS2, Jason A. Dominitz, MD, MHS3, Yiwen Yao, MS4, Andrew Gawron, MD, PhD1. P1783 - Colon Cancer Surveillance Recommendations After Abnormal Fecal Immunochemical Test and Normal Colonoscopy: Results From the Veterans Administration Population Data, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
1University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT; 2Hutchinson Institute for Cancer Outcomes Research, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center / University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA; 3University of Washington School of Medicine / VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; 4George E. Wahlen VA Medical Center, Salt Lake City, UT
Introduction: The Veterans Health Administration (VA) has achieved high rates of colorectal cancer (CRC) screening through combination of colonoscopy and fecal immunochemical testing (FIT). Patients with abnormal FIT results have a high risk of advanced adenomas or CRC and should complete a follow-up colonoscopy. This study aimed to describe surveillance colonoscopy recommendations in patients with an abnormal FIT result and without adenoma found on colonoscopy.
Methods: Using the National VA Healthcare system, we retrospectively identified US Veterans who underwent a colonoscopy with at least one abnormal FIT result within 1-year prior to the colonoscopy. We analyzed pathology data resulted within 30 days of the colonoscopy. Based on this, patients were divided into 3 groups: those without any pathology results, those with non-adenoma histology on pathology, and those with adenomas on pathology. Comparisons of surveillance recommendations between the 3 groups were performed.
Results: There were 59,102 patients with an abnormal FIT who underwent colonoscopy during the study period between September 2019 through October 2022. No pathology data was reported in 12,615 (21.3%), non-adenoma histology was reported in 11,707 (19.8%), and adenomatous histology was reported in 34,780 (58.8%) patients. Patients without pathology were older (67 ± 10.76 vs 65 ± 12.03 vs 68 ±9.53 years; P< 0.001) and had fewer males compared to the other groups (81.1% vs 90.2% vs 95.3%; p< 0.001). Surveillance recommendations for all three groups are shown in Figure 1. In patients without pathology, surveillance recommendations for repeat colonoscopy were: 9-10 years in 37.1%, 3-8 years in 29.1%, 0-2 years in 9.7%, and discontinuation of screening in 25.7%. In patients with non-adenoma histology on colonoscopy, surveillance recommendations were: 9-10 years in 30.8%, 3-8 years in 38.1%, 0-2 years in 11.1%, and discontinuation of screening in 19%.
Discussion: About 21% of patients undergoing colonoscopy after a positive FIT did not have any pathology detected on colonoscopic exam. Excluding patients with 1-2 year interval recommendations (possibly attributable to bowel prep or completeness of exam), almost 30% of these patients received recommendations between 3-8 years, possibly earlier than guideline-recommended intervals for normal colonoscopy. Future work will involve determination of patient and provider factors associated with reasons for early interval recommendations in this cohort.

Figure: Surveillance recommendations for follow-up colonoscopy in patients with abnormal FIT and colonoscopy with and without pathology
Disclosures:
Ishani Shah indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Rachel Issaka: Guardant Health, Inc. – Advisory Committee/Board Member.
Jason Dominitz indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Yiwen Yao indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Andrew Gawron indicated no relevant financial relationships.
Ishani Shah, MD1, Rachel Issaka, MD, MAS2, Jason A. Dominitz, MD, MHS3, Yiwen Yao, MS4, Andrew Gawron, MD, PhD1. P1783 - Colon Cancer Surveillance Recommendations After Abnormal Fecal Immunochemical Test and Normal Colonoscopy: Results From the Veterans Administration Population Data, ACG 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting Abstracts. Vancouver, BC, Canada: American College of Gastroenterology.
